Clinical research has long faced significant systemic challenges, especially for small and medium-sized biotechs. Tricky matching, thorny data management, maze-like compliance, and other hurdles used to be the status quo in the industry. However, advanced solutions like clinical trial management software have transformed the clinical trial landscape.
A clinical trial management system (CTMS) is an essential set of tools that helps researchers manage all aspects of the trial and keep clinical research operations on track. In this blog post, we’ll look into key data points for custom CTMS and walk you through essential functionalities to improve your existing software.
What is a clinical trial management system (CTMS)?
A clinical trial management system is a type of software that enables life science teams to manage, plan, and track the entire clinical trial process. A CTMS typically consists of multiple modules, each designed to handle a specific function, such as site management, patient tracking, document management, and other functions.
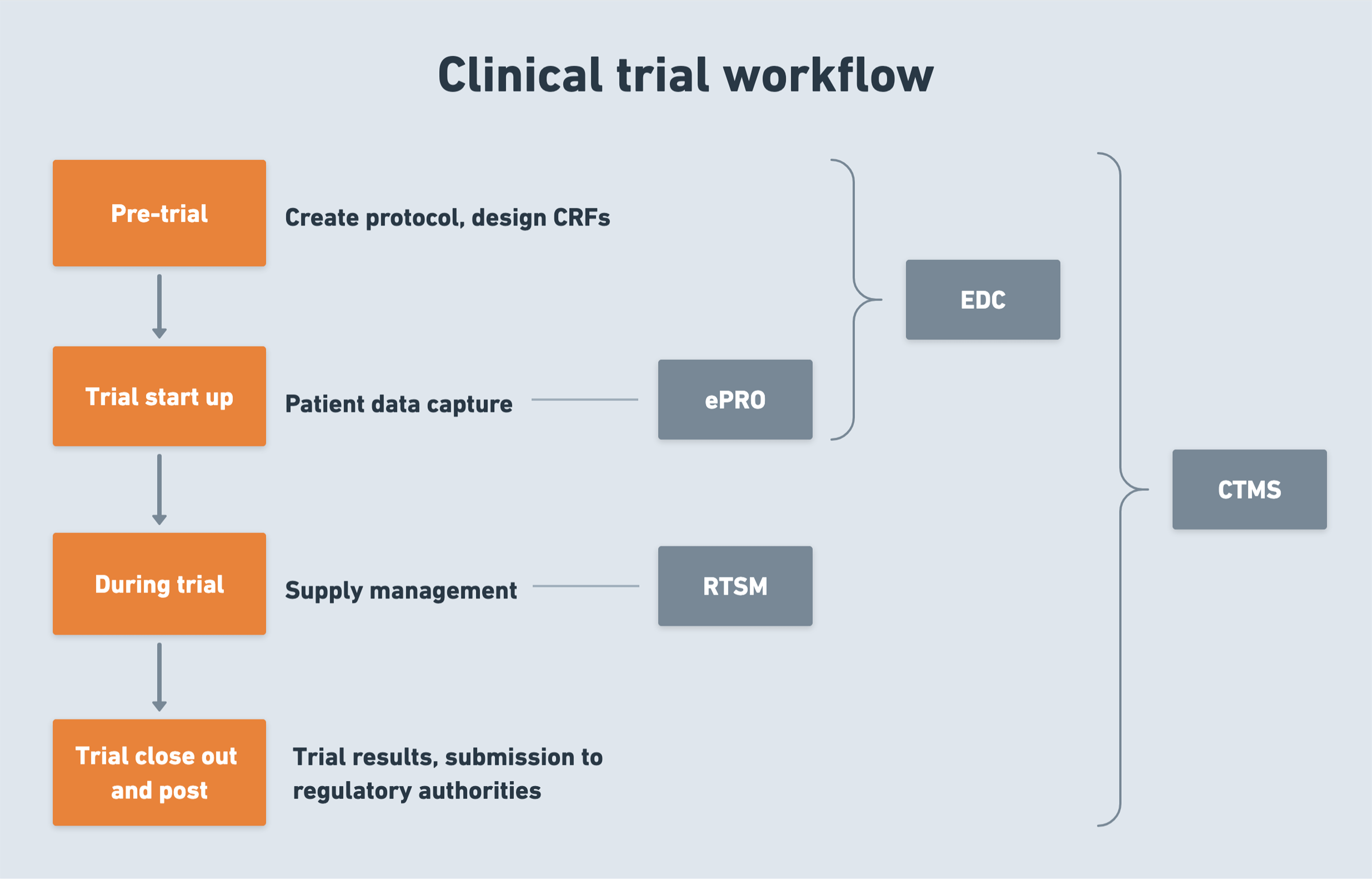
The struggles of clinical trials and how a CTMS can save the day
According to 70% of research sites, clinical trials are becoming increasingly complex. A CTMS reduces this burden by offering a streamlined approach to managing patients, data, and regulatory compliance.
Recruiting and retaining qualified patients
Two-thirds of trials today have a shortage of study participants, and 30% of trials are terminated before completion due to insufficient enrollment. Even with enough qualified patients at the onset, most industry reports indicate a significant dropout rate of 25-30%.
Clinical trial management solutions can help organizations reverse these negative trends by providing automated tools to screen, enroll, and manage participating patients. Such systems can integrate with patient registries, EHRs, and other databases to identify potential qualified subjects and expand the participant pool to previously underserved populations. Paired with remote monitoring, CTMS can reach even a broader population by enabling real-time data collection from diverse patient groups.
🔍 In one of our recent projects, the Orangesoft team helped a sponsor organization expand the participant pool by 15% through the integration of a custom CTMS with a real-world evidence platform (RWE). This integration enabled precise matching of patients to inclusion/exclusion criteria, enhancing recruitment.
If powered with AI, a CTMS can also predict patient eligibility, automate screening, and streamline communication with patients. AI can analyze inclusion criteria for patients to provide a more representative patient population, plus account for gender-specific differences in drug efficacy and safety thanks to a more granular analysis of patterns and correlations in trial data. However, this is only possible if the underlying health data accurately reflects historical disparities and when the model is trained on complete documentation for certain demographics.
Ensuring centralized clinical data management and its seamless sharing
Clinical trials often include multiple electronic systems with mandatory manual data entry. Error-prone data management processes can compromise the validity of the entire study, degrade data quality, and result in unexpected costs spent on re-entering and verifying data.
CTMSs can automatically consolidate external and internal clinical site data, claims data, and commercial data, validate it, and place it into a centralized repository for a unified view by all stakeholders, including sponsors, CROs, and investigators. For decentralized clinical trials, known for their natural data variability, a CTMS acts as an indispensable unified data hub that helps standardize data collection and consolidate all clinical trial data, regardless of its source (ePROs, wearables, or home visits).
Securing and maintaining regulatory compliance
From FDA and EU regulations to IRB approvals, bureaucracy in clinical research is a major bottleneck that extends clinical trial timelines. To ensure compliance, sponsors have to put a premium on data governance, doubling down on sample metadata capture, audit trails, and documentation.
Clinicall trial management systems facilitate an audit trail for regulatory inspections and data integrity checks. With automated report generation, alerts on potential compliance issues, source data verification, and robust built-in security features, CTMS solutions help sponsors put compliance at the center of the entire clinical trial. Supplemented with AI, CTMSs automate the review of error reports, identifying potential compliance deviations and flagging them for human review.
Modern CTMS solutions also entail advanced Serious Adverse Event (SAE) management capabilities paired with real-time notifications to make sure SAEs are taken care of according to EudraVigilance and 21 CFR Part 11 requirements.
Improving operational efficiency
CTMS enables research staff to move beyond traditional paper-based methods and automate clinical research management tasks, such as subject enrollment, reporting, and site visit scheduling. CTMS solutions automate routine tasks, take out redundancy, and allow research teams to get a better grip on resource allocations, making sure the trial process goes fast, smoothly, and within budget.
Moreover, a CRO with a quality, well-established management system towers above in the market, with the system itself potentially accounting for up to 30% of the CRO’s overall value.
Best CTMS software on the market
Here are the top five clinical trial management systems biotechs and CROs use to accelerate clinical research.
Medidata CTMS
Medidata CTMS is web-based, industry-standard software that offers a unified and secure space for patients, sites, sponsors, and CROs to handle onsite and decentralized trials. The platform bundles basic trial management features designed for patient management, data management, and trial management. Beyond generic capabilities, Medidata also offers a suite of AI solutions to enable smart data management, predictive modeling, and operational optimization. As for trial specialization, the platform has dedicated features to support oncology and vaccine trials.
Medidata is well integrated with EDC, eTMF, and other tools to deliver a real-time view of study-related information. The platform aligns with all regulatory data standards and key regulations, including ICH E6 (R2), 21 CFR Part 11, EU GMP Annex 11, and more. However, the platform has a large learning curve and may be overkill for smaller sponsors or studies, as noted by users.
Oracle Siebel CTMS
Designed specifically for CROs, pharmaceutical and biotech companies, and other clinical trial sponsors, Oracle Siebel comprises a wide array of features that support all aspects of clinical trial management. The platform also comes with a personalized Internet portal for site coordinators, clinical investigators, and CRAs to make clinical trials run smoother.

Siebel CTMS is designed to handle the complexities of modern clinical trials, supporting intricate hierarchies, global trials, and advanced trial designs. If necessary, users can purchase additional modules to accommodate their unique business processes. The platform supports the 21 CFR Part 11 industry standard.
Veeva CTMS
Veeva CTMS allows you to bring all clinical systems and processes into a unified, web-based interface with a single sign-on for study team members. The platform comes with a dedicated patient management app and separate modules for research operations management, data management, and research site management.
In Veeva Systems, integrations are made easy with Vault Connections, which seamlessly move data and documents between Vaults.
FlexDatabases CTMS
The web-based platform offers a spectrum of eClinical solutions that support all therapeutic areas and address varied levels of complexity. From CRA activity management to finance management, FlexDatabases enables CROs, biotechs, and pharmaceutical companies to monitor site progress. KPIs are easily tracked, and eSignatures streamline workflows for enhanced efficiency.
FlexDatabases covers all key international and local regulations, including FDA 21 CFR Part 11, GDPR, HIPAA, and more. The platform also allows for easy, API-driven integration with any EDC and TMF system.
RealTime CTMS
Tailor-made for clinical research sites, site networks, AMCs, sponsors, and CROs, RealTime CTMS boasts a comprehensive selection of tools that streamline all aspects of trial execution, including site management, CRC, recruitment, finance, and more. The platform provides real-time access to the site’s regulatory documents and allows users to reconcile the Site Study File with TMF remotely.
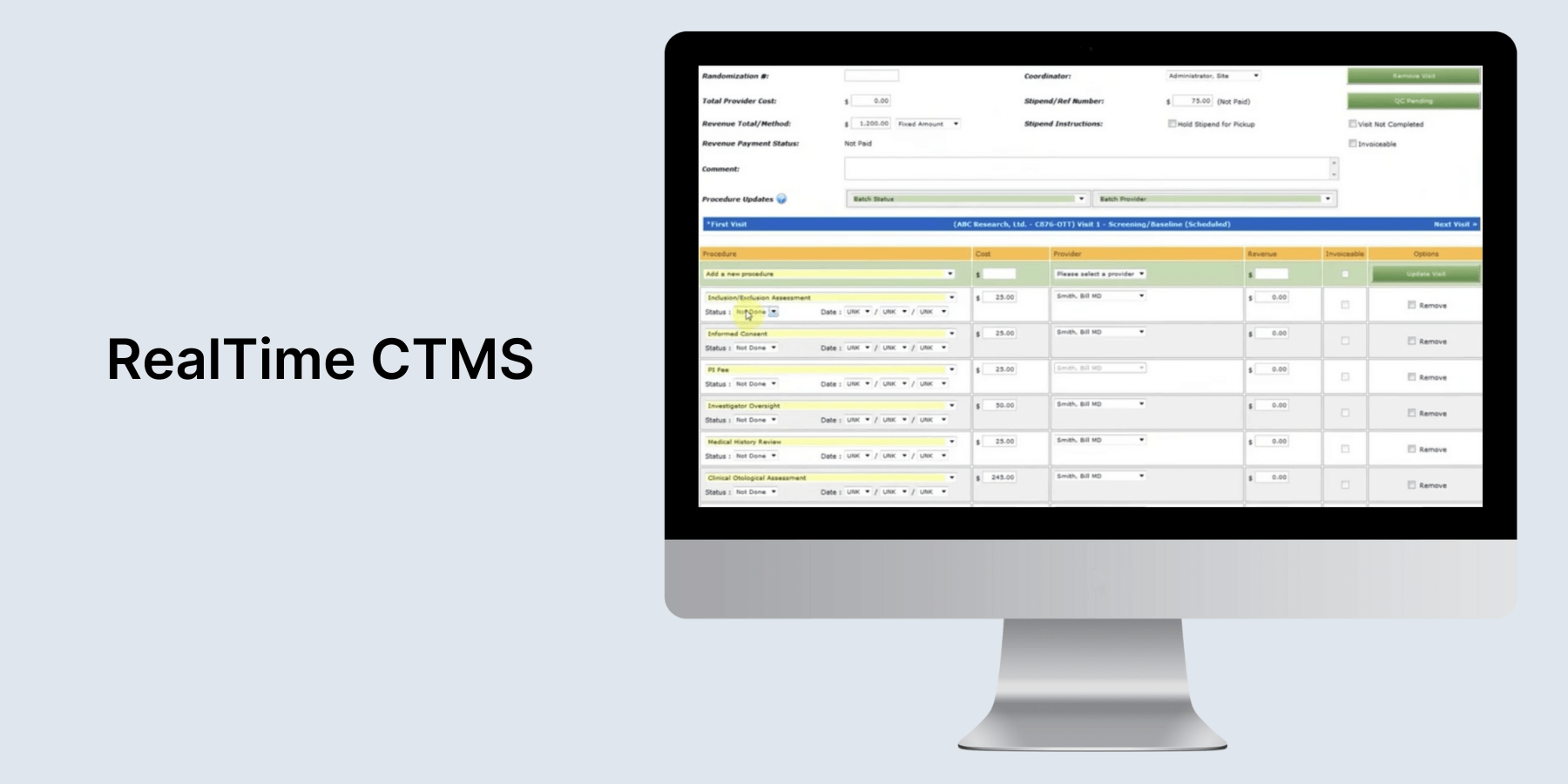
Users can also deal with research documents and tasks on the go via the RealTime mobile app. Its eRegulatory system operates in full adherence with FDA Part 11 validation standards. As for integrations, RealTime has out-of-the-box integrations and allows you to connect CRMs, ERPs, EMRs, analytics, and business intelligence (BI) platforms via API.
A custom clinical trial management system vs an off-the-shelf CTMS
For small biotech companies or CROs conducting more standardized trials, an off-the-shelf CTMS may be sufficient. However, in some cases, organizations might need to stack custom modules, functionalities, or integrations onto the ready-made solution to fine-tune it to their unique trial needs. These cases include but are not limited to:
- Specific data collection needs (e.g., when data collection includes unique scales or unique fields)
- The need for integrations with internal systems (e.g, customized APIs for EHR integration)
- Specialized reporting and analytics capabilities, and more.
Sometimes, customization won’t do the trick, requiring companies to go for a full custom build. This is the case when a company:
- Conducts trials with unique designs or trials for rare diseases with specific data collection and reporting requirements.
- Has 100+ studies in the portfolio and/or operates globally.
- Requires a high level of integration.
- Operates in a unique regulatory landscape that is not covered by a generic solution.
- Wants to use CTMS as a competitive advantage.
- Plans to go through an M&A process.
- Needs to integrate a large number of remote monitoring tools.
- Requires complete control over intellectual property.
To determine the right development approach for your needs, you can contact our team for a detailed analysis of your CTMS development options.
Must-have features to look for in a high-performing CTMS
No matter what type of solution you’re after — ready-made or custom — these are non-negotiable capabilities you need in your CTMS for a truly end-to-end experience.
Study planning and management
The ability to plan and keep tabs on study milestones is a must-have feature in clinical trial management software. Without it, research teams won’t be able to optimize resources and coordinate critical events, like making sure clinical supplies arrive on time for site initiation.
Here’s what falls under the category:
- Tools for trial design, scheduling, and tracking milestones (randomization, schemes, sample size calculations, etc.)
- Tools for budgeting and resource allocation tools (budget forecasting, cost tracking, etc.)
- Tools to define and monitor protocols (protocol templates, version control, deviation tracking, audit trails).
Project management
Among other things, a CTMS should double as a centralized hub for the entire project with features enabling:
- Trial timeline and milestone tracking (default milestones, definition of predecessors and lag between tasks, etc.)
- Resource allocation (automated alerts, tools for reallocating resources, predictive modeling for resource forecasting based on enrollment rates and other key metrics)
- Risk-based monitoring (risk assessment templates, change control management, etc.)
- Study team management.
Subject recruitment and enrollment
An insight into patient enrollment and engagement at the study, country, and site levels helps investigators spot potential challenges, set realistic enrollment goals, and ultimately improve the success of clinical trials.
Dedicated features for patient management include:
- Tools for tracking recruitment progress and enrollment metrics (enrolled subject trackers, enrollment forecasts, etc.)
- Data capture tools to match candidates with study criteria
- eConsent and unified ICF review
- Automated visit scheduling and subject visit tracking with protocol and screen fail integration and more.
Site and investigator management
Clinical trial management systems also have a designated module that allows users to lay out and engage with data on investigators, medical institutions, sites, regulatory authorities, and vendors.
This capability usually manifests as:
- Tools for site initiation and qualification
- Centralized repository for all site-related information (contact details, investigator profiles, site capabilities, contracts)
- Comprehensive profiles for all investigators, including qualifications, contacts, CVs, certificates, and licenses
- Tools for investigator and site performance tracking
- Capturing and tracking all site communication, and more.
Collaboration
To keep each site on the same page in terms of protocols and procedures, a CTMS should facilitate consistent communication and coordination among stakeholders, including sponsors, CROs, sites, and regulators, across all sites.
Collaboration features include:
- Task management and workflow automation
- Integrations with email, calendar, and collaboration tools
- Secure messaging and document sharing between sites and study teams
- Integration with EDC systems, ePRO systems, and more.
Regulatory document management
You can use a CTMS as the system of record for regulated data to eliminate redundancy in your document collection and management, stay inspection-ready, and provide CROs with real-time access to critical information.
Features essential for hassle-free regulatory compliance management include:
- Unified repository for key documents such as informed consent forms, contracts, and trial protocols, along with version control and metadata management (eTMF)
- Role-based access controls and audit trails
- Built-in features and tools to comply with regulatory standards such as FDA 21 CFR Part 11, HIPAA, GDPR, and ICH-GCP
- Tools to facilitate regulatory submission (templates, submission tracking, etc.)
Real-time reporting and analytics
A CTMS caters to multiple user groups who drill down into data in a variety of ways. That’s why having a system that offers a range of reporting options, from high-level portfolio summaries to granular site-level details, is crucial to ensure dynamic insights into the progress of a clinical trial and give PIs, CROs, and sponsors peace of mind.
Reporting capabilities of a CTMS can comprise:
- Customizable and ad-hoc reports for study progress and performance insights
- Reporting on key metrics, including enrollment rates, site activity, and budgets
- Historical and industry benchmarking to know the study’s trajectory
- AI/ML for image analysis and predictive modeling.
Integration with other systems
Research teams use a lot of tools and software depending on the specific activities and aims of their processes. To make sure no data slips through the cracks, a CTMS requires seamless, API-driven integrations with an EDC, EHR, LIS, patient portals, and other systems in use.
Safety reporting and adverse event management
Clinical trial management systems also automate adverse event management to make sure the participants are safe and to facilitate timely regulatory reporting. To address the complexity of AEs and interpret data rapidly and accurately, a CTMS is equipped with adverse event reporting, safety data management, and other pharmacovigilance functionalities.
Artificial intelligence capabilities
AI integration is another fixture in modern CTMSs that streamlines processes through and through, improves data accuracy, and slashes clinical trial cycle times. In CTMS, AI can supplement the following modules:
- Patient recruitment — AI algorithms sift through EHRs, patient registries, and other sources to identify participants who meet specific trial criteria.
- Data management — AI tools automate data collection from various sources, facilitate real-time monitoring of trial data, enable trial outcome predictive analytics, and provide real-time insights into key trial metrics and patient progress.
- Quality and compliance management — Powered with AI, a CTMS can provide real-time compliance checks, automatically generate audit trails, detect anomalies in trial data, predict the likelihood of quality or compliance issues, and more.
- Real-time monitoring and safety — Smart algorithms can identify potential SAEs, trigger alerts on patient symptom changes, augment risk-based monitoring strategies, and more.
🔍 Grappling with flawed patient-site referral communication and management, our client partnered with our company for a custom AI-enhanced platform for clinical trial matching. Our custom solution enabled faster and more accurate matching of patients with clinical trial eligibility criteria, leading to a 15% increase in treatment opportunities.
Steps to develop a clinical trial management system
Let’s say you decided to opt for a custom clinical trial management system to fit your way of working. In this case, you’ll likely turn to a third-party tech vendor to get your software developed from scratch. Here are the key steps involved:
Step 1: Conducting a discovery session
The development process starts way before the development itself. To lay a solid foundation and get the product right the first time, your development team needs to conduct a discovery phase with key stakeholders to map the specific workflows of your research studies, including clinical operations, data management, IT, regulatory affairs, and so on.
Depending on your requirements, the development team recommends an optimal development approach, whether it’s development from scratch or CTMS customization. For customization projects, your team also evaluates suitable CTMS options and analyzes which custom add-ons you need to cover your requirements.
Along with business analysis and user research, your team also runs market research and regulatory analysis. Both activities make sure your custom CTMS is up to the industry standards, tech-wise and compliance-wise.
At this stage, your development team maps your existing data estate and assesses the technical and regulatory feasibility of AI integration.
Based on the obtained insights, your team jots down functional and non-functional requirements for your product, including must-have features, integrations, compliance requirements, security measures, and more.
Step 2: Designing system architecture
With a clear solution scope and system objectives like scalability, performance, and others figured out, your development team proceeds with identifying major components of the system architecture, including interactions, data models, and other key elements. Building off your system objectives, the development team also selects an optimal tech stack that will ensure successful development and long-term sustainability of the CTMS.
Another important consideration your dev team takes care of is refining security measures and data controls to make sure security is built into the system's foundation rather than bolted on as an afterthought.
Step 3: Developing user-friendly interfaces
UX excellence is rare in clinical trial software, yet essential for both usability and data accuracy, considering the vast amounts of data floating in the system. Achieving UX excellence requires an iterative approach. That’s why your design team first maps user journeys for each role and then develops prototypes to run early user testing. Engaging real end users in UX prototype testing will help you design a user-first interface, thus ensuring a smoother system adoption in the future.
Once prototypes are validated, the design team finalizes the designs and develops layouts and visuals that fit the specific workflows of clinical trials.
Step 4: Development and testing
The coding process is closely followed by testing to stop potential issues in their tracks. The development team typically uses a combination of manual and automated testing to check the system.
Along with coding, developers also set up clear data exchange protocols with target systems like EHRs, EDCS, and eTMFs. To optimize development costs, your development team can use vetted third-party components and pre-built architectures.
Step 5: Deployment and support
Before the system is transitioned to the end user, the development team finalizes artifacts such as risk management documentation, system configurations, and others to ensure regulatory readiness. User manuals and training materials are also part of the process as they promote smooth user adoption and make sure the system is used as intended.
After deployment, developers maintain a vigilant watch over the system's performance and behavior to track down and nix any residual defects.
Step 6: Regular updates and maintenance
The longevity of your clinical trial management software depends very much on its upkeep. Security patches, feature enhancements, performance improvements, and data maintenance are backbone elements of this upkeep, which are also implemented by your development team.
Main hurdles to overcome when developing a custom CTMS
While implementing a CTMS can help research teams counteract challenges inherent in clinical trials, several hurdles must be overcome to reach the finish line:
Data migration and consolidation
Clinical trials have a notable data problem where all data is scattered across different data sources, including paper intake forms, cloud-based data storage, and a multitude of specialized systems. This fragmented data landscape poses a whole range of integration, standardization, migration, and compliance challenges during the development and, potentially, customization of CTMS.
AI implementation also becomes an issue in this case, as AI algorithms require complete, consistent, and accessible data to feed on. To address this challenge head-on, your development team should first analyze your data estate to determine the accessibility of the necessary data, develop a data standardization strategy, and design an optimal data migration strategy to minimize data loss.
Integration with existing systems
For a CTMS to be effective, it must work in conjunction with EDCs, EHRs, LISs, and other systems. However, setting in place a smooth, near-real-time data integration with various sources is a challenging endeavor, considering different data formats, terminologies, and coding systems in the clinical trial tech estate.
Before development, your tech team should account for the differences in data makeup and choose the right integration method to connect all systems with a CTMS. Compatibility with standard data exchange protocols like HL7 and FHIR will also allow your software to collect data seamlessly from different systems and enable end-to-end reporting.
Customizing for diverse trial requirements
Protocol complexity, various study designs, different therapeutic areas, and differing geographic regulations are something your development team has to factor in early on. One way to address this challenge is to put a modular architecture at the core of your CTMS. This will allow you to stack or remove specific modules or functionalities based on the needs of individual trials.
Another way to make a CTMS usable across a wide range of research projects is to make data collection forms, workflows, and reporting templates easily configurable.
Data management and quality
The average clinical trial generates 3.6 million data points that, unless managed effectively, can have negative repercussions on research integrity and compliance. In a CTMS, a comprehensive data management layer is specifically focused on data collection, cleaning, validation, and quality management to offset the risk of data errors and ensure the reliability of clinical data.
Automated queries within the CTMS’s data management system are an industry standard for identifying discrepancies. Instead of manually combing through data, researchers can run automated checks to flag a potential adverse event or an error in data entry.
Adopting clinical data standards from CDICS can also relieve you of multiple data management headaches down the road. Universal and easily customizable to all types of research, these standards provide a unified framework for data collection and data exchange across the whole healthcare ecosystem. Although not mandatory, CDICS standards are encouraged globally by regulatory agencies such as the FDA in the US and EMA in the EU.
Regulatory compliance
The increasing regulations in the industry and globalization of trials put more pressure on IT systems, requiring your CTMS to incorporate advanced, more comprehensive measures to ensure compliance across privacy regulations and health authority regulations. Common regulations that apply to CTMSs include ICH-GCP, 21 CFR Part 11 for the US, HIPAA for the US, FDA for the US, GDPR for the EU, and others.
In CTMSs, compliance demands a multi-faceted approach that involves capabilities for maintaining accurate documentation, systems for monitoring and reporting adverse events, real-time querying across different zones, and other features.
To implement the right set of compliance-friendly features, we recommend consulting regulatory experts before development. Even with all critical features implemented, make sure to conduct regular internal audits to address potential compliance issues head-on.
Data security
Multiple parties interact with clinical trial data, potentially exposing it to data breaches, compliance violations, and misuse. Due to an extensive attack surface, end-to-end data security is difficult to achieve in CTMS, yet essential to keep hackers at bay.
To minimize the risks, we recommend a tiered approach to data security, where the system uses multiple layers of security with specific security measures hinging on the gravity and size of the threat.
AI models also present a unique challenge to the safety of patient data, demanding a solid AI security strategy from organizations that includes:
- AI-specific data security techniques such as data anonymization and minimization, strong data encryption, and access controls.
- The XAI approach that focuses on developing and integrating explainable and transparent AI models.
- A security-first approach to model deployment backed by secure coding practices and vulnerability scanning.
- Ethical AI strategy supported by oversight mechanisms to ensure responsible AI usage.
Scalability and flexibility
A common limitation of off-the-shelf and outdated CTMS solutions lies in their inherent rigidity. They often have a hard time adapting to the varying demands of trials with diverse sizes and complexities. For example, they may not seamlessly allow users to switch between high-level study overviews and detailed subject-visit information.
By relying on a modular architecture and cloud-based solutions, you can bake in the system adaptability by default and make sure it can scale and follow suit.
Factors affecting clinical trial management software development costs
As much as we’d like to pin down a definite number, it’s hard to estimate a project without knowing its specs. Overall, it may cost you between $150,000 and $500,000+ depending on your starting point and unique needs. Below, we’ve listed the main cost drivers that impact clinical trial management software development costs.
The development approach
Not all organizations need to develop a clinical trial management system from scratch. In certain cases, it’s strategically more beneficial to fine-tune an off-the-shelf solution by adding custom modules, features, or integrations. In this case, a customized solution is less expensive to develop than building a CTMS from scratch.
Complexity and scope of features
The more complex and feature-rich your CTMS is shaping up to be, the higher the development costs will be. For example, basic features like protocol management and electronic data capture might be relatively easy to implement, while forecasting models and AI-based imaging analytics require more resources and dedicated expertise, thus increasing your expenses.
Customization requirements
The amount and complexity of customizations within your CTMS also impact the final costs. A few simple UI adjustments are far less resource-intensive than extensive workflow modifications since the latter involves software development and integrations.
Integration with existing systems
The number and complexity of integrations needed are among other cost drivers in the equation. Here, additional costs stem from API development, possible data transformation, third-party dependencies, and efforts focused on ensuring interoperability.
Regulatory compliance
Regulatory compliance is a salient but costly aspect of CTMS development. Compliance-related expenses include data security measures, auditing capabilities, ongoing maintenance, and more.
Development team composition
The development costs can vary greatly based on the team's size, its location, the expertise they bring to the table, and their collective experience. For example, you’ll need a different team to develop a purely web-based CTMS and to build a system with both web and mobile app components.
Develop a clinical trial management software with Orangesoft
A custom (or customized), secure, and easily adaptable CTMS can benefit any site that is looking for ways to improve budget forecasting, ensure enrollment diversity, enhance billing compliance, or keep the lines of communication open with patients or team members.
With 15 years of experience in health tech development and 300+ projects, Orangesoft can help you develop from scratch or customize high-performing clinical trial management software that highlights your site's efficiency and organization to sponsors and CROs. So contact us to get a free consultation on your CTMS development!
