No one likes staying in a hospital. Not because it’s a classic setting for scary movies, but because it’s confining, inconvenient, and expensive. Getting better is easier at home, and probably that’s why 95% of U.S. adults aged 55+ prefer home-based care to institutional pathways.
The market attests to the demand: consumer interest in home care services is projected to increase 22% by 2034 from $286 billion in 2024. However, the demand for home care far outstrips the supply: there are simply not enough home care aides to support the novel model of care delivery.
The scarcity of caregivers, perennial pressure to reduce the overall cost of healthcare, and shifting consumer preferences created a breeding ground for innovative technology solutions like AI to save the day.
Top 4 technologies transforming home healthcare
The home health technology market is dynamic, with diverse approaches to empower patients and their care teams. Today, home health software and hardware can be broadly grouped into passive, the ones that don’t require an individual to operate them, and active solutions, each serving a distinct function.
Remote patient monitoring (RPM)
By 2027, remote patient monitoring platforms are expected to monitor over 115 million patients, many of whom are older adults. Primarily focused on physiological data, RPM platforms help medical professionals keep tabs on chronic disease, the elderly, post-operative, and other archetypes of remote patients.
Depending on the type of sensors they integrate with, RPM solutions can actively or passively capture vital signs, mobility and activity data, symptoms, and other information and send it for review to a remote provider or a home health agency via apps or tablets.
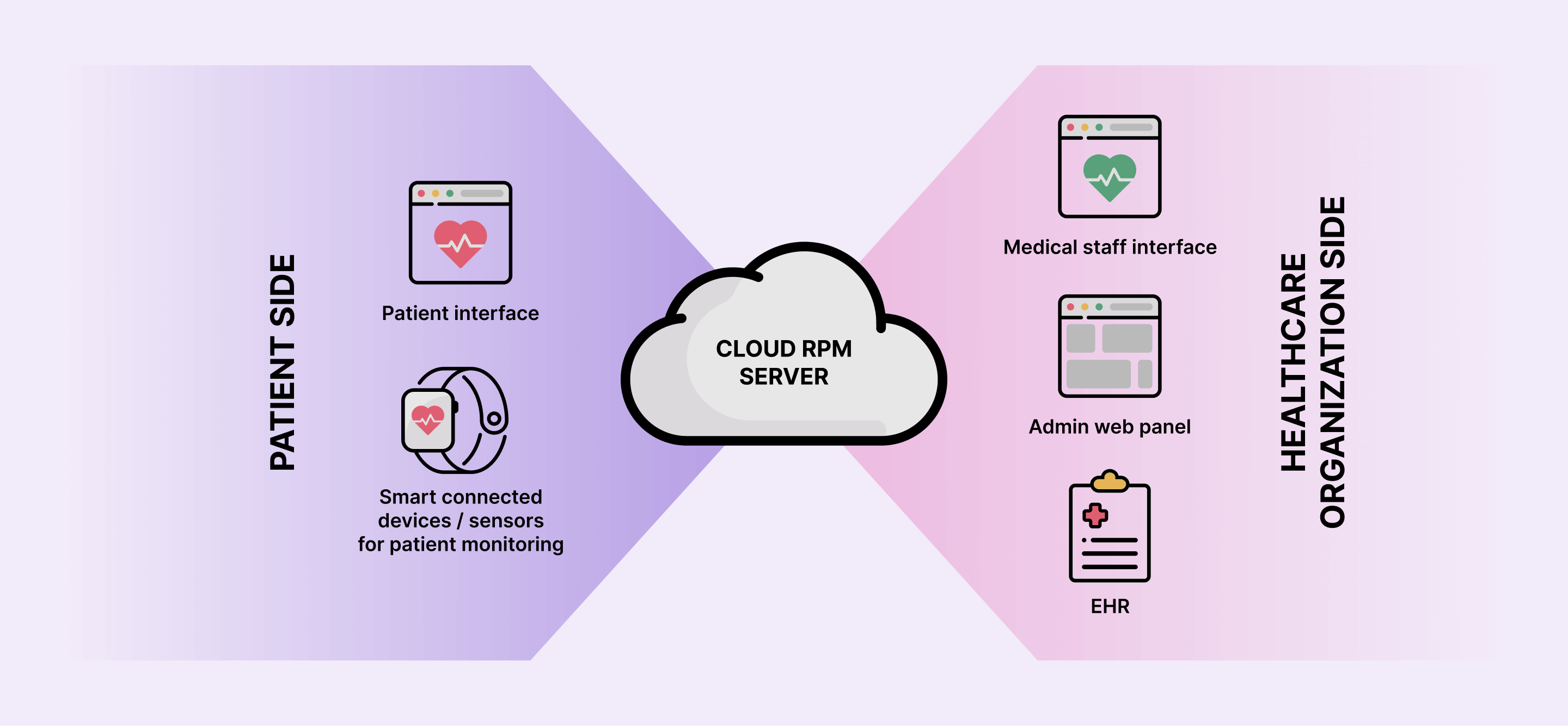
Beyond physiological data collection, RPM solutions also enable healthcare providers to:
- Build a more complete picture of a patient’s health outside traditional visits.
- Identify subtle changes and initiate early interventions to prevent hospitalizations and complications.
- Calibrate and personalize treatments based on longitudinal data.
- Track movement and medication adherence in real time.
- Provide assistance and resources to patients during care transitions.
Ambient AI sensors, the latest RPM trend, have extended the capabilities of remote monitoring systems to passive and contextual data. Creating a wearable-free environment, ambient sensors can unobtrusively monitor activity patterns, sleep quality, bathroom visits, and other behavioral and functional insights, to alert caregivers or family members to any unusual patterns detected.
Telehealth and virtual care platforms
Originating as a means of reaching patients in remote areas, telehealth has become a backbone element of the home health care toolkit. Telehealth enables real-time, two-way video and audio communication for remote check-ins by nurses or other healthcare professionals.
Bundling telehealth elements, virtual care platforms extend the scope of home health services, allowing for:
- Care planning and coordination — virtual care platforms make it easier for caregivers to share updates and track changes in the care plan.
- Appointment scheduling and management — this module helps patients schedule a telehealth visit around caregivers’ preferred shift dates and times.
- Billing and payment processing — virtual care platforms often streamline revenue cycle management for home health care services, including visit fees, remote monitoring charges, insurance claims, balance due, and more.
- E-prescribing — home care providers can electronically send prescriptions directly to the patient’s pharmacy of choice via NCPDP-defined transactions.
Specialized virtual care platforms also incorporate a suite of dedicated monitoring, education, and engagement features to support a variety of clinical uses, including chronic disease management, palliative care, mental health management, and more.
mHealth apps for patients and caregivers
Home-based care is a complex ecosystem with multiple stakeholders, including patients themselves, family caregivers, and clinicians. Whenever one part of this system breaks down, care gaps crop up, potentially leading to adverse events like hospitalizations.
Mobile healthcare apps can bridge whatever communication, care coordination, and monitoring gaps the home healthcare ecosystem is stuck with, through real-time, on-the-go updates. Based on the application’s focus, mHealth can make up for gaps in:
- Care coordination — mHealth apps store and organize information about care conditions and activities of the home care recipient for everyone’s unified access.
- Medication management — by tracking prescriptions, dosages, and refill schedules, mobile applications help all sides of care keep track of the home-based patient's medication regimen.
- Health tracking — shared digital logs allow both patients and caregivers to gain a common understanding of care progress and related activities.
- Documentation — mHealth apps provide a two-way channel for secure documentation exchange to promote a more collaborative record of care.
Voice assistants and smart home integration
With breakthroughs in natural language understanding, the aging-in-place community, people with disabilities, and other individuals receiving care at home are empowered with more autonomy and control over their well-being, in their preferred environments.
Augmented with conversational AI, natural language understanding, sentiment analysis, and other cutting-edge technologies, voice assistants act like empathetic companions in home-based care management. From medication reminders to proactive check-ins based on identified emotional insights, voice-operated assistants like ElliQ are always there, checking in on users and helping monitor changes in their health over time.
Integrated with a smart home ecosystem, smart voice assistants enable hands-free control over lighting, temperature, security systems, entertainment devices, and other home essentials. By translating voice commands into digital signals, voice assistants create a more convenient and accessible living environment that will benefit older adults, people with limited mobility, and anyone looking for more independence in their homes.
Artificial intelligence in home care: high-tech meets high-touch
In home healthcare, AI’s unmatched data analytics capabilities empower caregivers and providers to react faster to high-risk events, inform diagnostic processes, and handle the administrative tasks related to home-based healthcare services. For individuals on the other side of care, artificial intelligence and its offshoots provide proactive clinical support whenever healthcare providers aren’t available.
Predictive analytics for health monitoring
Home healthcare analytics solutions aggregate patient-specific clinical data, home healthcare service data, patient behavior insights, and contextual data to generate predictions on disease progression, treatment response, and recovery rates. These solutions can uncover insights into how a patient reacts to medical treatment, how to adjust a care plan to an individual patient profile, and what patients are at risk of adverse events or readmission.
For home health care agencies, predictive analytics is by far the only feasible way to monitor home-based patients at scale without compromising patient satisfaction and quality of care.
Conversational AI platforms
Home health agencies and hospital-at-home organizations deny around 60% to 76% of eligible patients because of insufficient capacity. The lion’s share of providers’ time is spent dealing with forms like the OASIS one. Conversational AI solutions can engage patients during the intake process and marry this data with EHR insights to pre-fill the documentation.
Home health agencies can also expand their capacity by using conversational AI to provide high-touch personalized recommendations. By analyzing different physical, physiological, and psychological data points, conversational AI platforms provide emotional support, clinical guidance, and assistance with well-being in times of need.
Personalized and adaptive сare plans
In healthcare, one size does not fit all — hence, the need for contextual care plans that dynamically accommodate the evolving care needs of home-based patients. Advanced AI algorithms can run in response to real-time events like changes in blood pressure, irregular heart rhythms, and others to suggest optimal care plan adjustments for a given patient.
Based on the underlying mechanisms, AI systems can either notify clinicians of the necessary adjustments or trigger those adjustments themselves with pre-set parameters and clinician oversight. The latter is often the case with medical devices like insulin pumps or automated medication dispensers, where real-time data demands immediate action.
Intelligent care coordination tools
Over 40% of older patients experienced issues with care coordination, with almost 15% receiving conflicting medical guidance. In home settings, where services are often interprofessional, smart care coordination allows all participants to avoid gaps in communication, duplication of efforts, and conflicting instructions.
Usually a part of care coordination or health management apps, smart care orchestration tools analyze the data logged by patients, nurses, and clinicians in real-time to highlight the blind spots and overlaps.
Real-time AI-powered alerts within care coordination apps keep each side of care on the right page, ensuring they get notified of the necessary changes, medication adherence, upcoming appointments, and other crucial milestones.
Behavior and activity monitoring
Without AI, raw data fetched from wearable devices, smart home sensors, ambient sensors, and medical devices would stay exactly that. Artificial intelligence algorithms can take that wealth of data, analyze it, and provide nuanced insights into sleep patterns, meal times, and medication intake.
This capability allows AI to detect falls and trigger alerts in real time by comparing the current movement patterns and sensor readings to the benchmark patterns. By monitoring everyday life activity, smart algorithms can also spot deviations like later morning wake-ups, lack of movement in certain home areas, and other changes that could be associated with missed medications.
Benefits of AI and technologies in home care
Digital care interventions at home have the potential to radically transform care, providing a unique opportunity for individuals to live longer, healthier lives in their own homes and request primary care whenever they need.
Improved patient outcomes and safety
According to a study, home group care patients in a telerehabilitation program experienced 18% fewer falls than those on conventional pathways. Artificial intelligence and various technologies like telehealth, IoMT, and others bring care to comfortable and familiar settings while also keeping an eye on the patient’s safety, treatment adherence, and overall well-being.
This continuous monitoring and data analysis paint a holistic patient profile for home care aides, allowing them to tailor treatments, jump on early interventions, nail down fall detection, and improve the overall quality of home-based care.
Increased efficiency and caregiver support
By 2031, the U.S. demand for home health and personal care aides is estimated to increase by about 25%. With caregivers stretched thin, home-based care agencies can resort to automation to tackle the shortage of home health aides in face-to-face efforts.
From the automation of repetitive clerical tasks to basic health assessments, technology can augment the capabilities of healthcare professionals and show up for home-based care recipients when support is critical.
Cost savings for healthcare providers and insurers
In the US, a randomized controlled trial demonstrated that bringing the care home and supplementing it with remote monitoring, virtual care, and at-home testing could reduce the adjusted mean cost of the acute episode by 38%. Across acute care and beyond, digital interventions reduce the length of a hospital stay, eliminate hefty facility fees, and reduce the need for frequent in-person check-ups.
Indirect cost savings tied to home-based care technologies also stem from their ability to improve care outcomes and forestall implications.
Data-driven insights for better care planning
In traditional healthcare settings, clinicians often draw up care plans based on historical data and routine guidelines. Such care plans may not always correlate with individual nuances of a patient’s health condition and their everyday life. Home-based care technologies accurately reflect the as-is state of an individual’s health, allowing care teams to draw upon real-time, richer data to create highly personalized routines.
Challenges and considerations for adopting home health care technologies
Tech-driven care interventions can transform the paradigm of home-based care, but only if the companies adopting them find a way around the inherent limitations and challenges that come with them.
Technical infrastructure requirements
To deliver their intended benefits, virtual care platforms require reliable, high-speed Internet connectivity, which is not always available in rural areas. Developers can partially compensate for this limitation by optimizing the infrastructure for low-bandwidth requirements and augmenting it with offline capabilities and features for asynchronous communication.
Another consideration is that remote care ecosystems usually rely on the interplay of different medical devices and sensors. That’s why during the system architecture planning, companies need to think through the device compatibility and integration protocols.
Data privacy and security concerns
Data security is probably the largest concern when it comes to home-based care because of the less-controlled home environments and larger vulnerability surface. End-to-end encryption of all transmitted data, access controls with role-based permissions, and software solutions developed with the data security practices outlined in healthcare regulations and global data standards will help healthcare providers keep sensitive patient data secure and compliant.
Also, virtual care platforms should have explicit patient consent mechanisms in place to collect and share data to keep the patient in control of their sensitive information.
Training and adoption barriers for elderly users
Home health care agencies shouldn’t make assumptions about their patients' ability to use the technology, because the recipients of home care are not a heterogeneous group. To account for the differences in the patients’ tech literacy levels, physical capabilities, and accessibility needs, companies developing the software should involve different user groups in the design research to validate their hypotheses.
Almost 70% of the 65+ adults say that technology is not designed with their age in mind. If you don’t want your remote care solution to become part of those statistics, you should design it with an eye for intuitive, simple, and straightforward interfaces. Healthcare app design for elder users is also about including the necessary visual cues, affordances, and support for assistive devices.
Integration with existing healthcare systems
The value of remote care data doesn’t end at its immediate context and face value. To participate in care, data needs to be plugged into various healthcare systems such as EHRs, pharmacy systems, billing platforms, and others. That’s why a home-based care technology should be developed with standardization and interoperability in mind, and with respect for standard data exchange formats like FHIR or HL7.
Regulatory and reimbursement complexities
Telehealth providers, RPM providers, and medical device manufacturers must navigate a challenging and sometimes conflicting federal-level, state-level, and regional-level regulatory landscape. Combined with the lack of clarity around the reimbursement models for home-based care services delivered via technology, healthcare providers might show a hesitant adoption of virtual care technologies.
For companies developing such solutions, compliance with relevant regulations, whether it’s HIPAA, GDPR, the FDA, or any other regulatory body, and solid clinical evidence supported by pilot programs and real-world data, is essential to prove their worth in real-world home healthcare settings.
Ethical considerations
As AI and technology permeate virtually every aspect of home-based care, adopters must double down on ensuring their fairness and equity to make them equally valuable for all patient populations. The XAI approach to AI algorithms, high-quality data representative of all patient groups, and the human-in-the-loop approach are some of the essentials healthcare companies need to put front and center in the development of home-based technology solutions.
Partner with Orangesoft to accelerate your upcoming health tech project
The value and overall ROI obtained from the home-based care model will likely lead to a greater number of health organizations adopting this care modality. For patients, telehealth, self-administered treatments, skilled nursing facility services at home, and other forms of in-home healthcare offer unmatched convenience, autonomy, and greater control over their well-being. So it’s safe to say that the shift will gain more traction in the coming years.
Whether you’re building a focused health tool or a full home-care platform, Orangesoft has the technical capabilities to get your projects off the ground. Along with 15 years of experience, we have a deep understanding of the regulatory and interoperability challenges that come with healthcare innovation, and we apply best practices in UI/UX, data security, AI, and compliance to ensure your solution meets the highest standards. Contact us to get a tailored estimate for your project.
