The healthcare industry has always been one of the most conservative fields, agnostic to innovation. However, rising costs of care, staff shortages, and the shortage of qualified healthcare professionals in rural areas have led the healthcare industry to seek new care delivery models. Telemedicine apps emerged as a new, tech-driven way to address care gaps and reduce disparities in access.
Now a fixture used by over 78% of U.S. hospitals and favored by over 166 million global users, telemedicine app development attracts many startups as a profitable niche and a way to make a positive impact on communities worldwide.
As a health tech development company, Orangesoft has been delivering innovative digital care solutions to global startups since 2011. In this article, we’ve gathered the expertise gained from over 300 solutions and poured it into a hands-on telemedicine app development guide, with the benefits, challenges, and how-tos of the telehealth app development process.
Key takeaways
- The cost of developing a telemedicine app averages $90,000 for an MVP, but the number may range based on the app complexity, target platforms, planned data integrations, and other variables.
- Telemedicine apps incorporate features dedicated to remote healthcare delivery, with basic functionalities including video consultations, appointment scheduling, electronic prescriptions, and secure messaging between patients and providers.
- Current trends in telemedicine apps include the integration of AI for diagnostics, remote patient monitoring, personalized health analytics, mental health support, and seamless interoperability with electronic health records and wearable devices.
Telemedicine apps market overview: what is driving or drowning the demand?
In 2024, the global telehealth market was valued at $123.26 billion and is projected to surpass $455 billion by 2030. This might seem like a positive growth trajectory, and it is. However, changes to Medicare telehealth rules have thrown things into a spin multiple times, sending mixed signals to providers, patients, and regulators.
Nevertheless, the demand for virtual care is pronounced — so much that analysts see an opportunity in the next decade for $1 trillion in annual healthcare spending to shift away from traditional healthcare models toward a digital-first, personalized system of medical care.
Here's what's fueling the demand behind telemedicine platform development and the telemedicine market overall:
- Between 2015 and 2050, the proportion of the world's population aged 60+ will increase by 2x, from 12% to 22%. In the US, the number of Americans aged 65+ is expected to increase from 58 million in 2022 to 82 million by 2050 (a 42% increase).
- Next-generation models, such as AI-enabled intake and in-home care, are making otherwise impossible care modalities possible and scalable.
- Some of the largest hospitals advocate for telehealth. For example, the online care modality accounts for about 12% of Johns Hopkins' total outpatient care volume and roughly 8% of total Medicare visits.
Advantages of telemedicine apps for patients
What’s there about telemedicine software that makes patients switch from in-person to online care?
Reduced cost of healthcare services
Virtual consultations can save consumers as much as $141 per visit compared with an in-person urgent care visit and $120 per specialist visit. With televisits, patients can access remote medical services right where they are, avoiding the costs associated with transportation. By addressing minor health concerns via telemedicine apps, patients can also reduce the number of costly in-person visits that incur high out-of-pocket expenses.
This is especially true for chronic disease management programs, where patients can schedule remote consultations between visits, rather than waiting 3 or 6 months for a follow-up. By intervening early, both patients and providers save dozens of dollars on reactive care. According to a study, chronic disease patients experienced cost reductions of $31.54, $39.55, and $32.24 for chronic diseases, dementia, and rehabilitation, respectively, while caregivers saw reductions of $16.15, $29.25, and $26.16 for the same conditions.
Easier access to high-quality care
The accessibility of care depends on the availability of qualified health workers, among other factors. However, the global healthcare system is understaffed, with the global labor gap expected to reach 11 million by 2030. Telehealth solutions can break down geographic barriers, connecting patients with specialists who may not be available in their local area while also making it easier for individuals with limited mobility and the elderly to access care from the comfort of their homes.
Remote medical services delivered via telehealth also address healthcare disparities, providing equal access to care for patients in underserved communities.
Better care outcomes
According to a study conducted by MDLIVE, virtual visits resulted in a 19% reduction in ER and urgent care visits. Telemedicine apps allow patients to promptly address minor health concerns before they escalate into more serious conditions. Advanced analytics capabilities built into telemedicine apps also help detect early-stage diseases and improve patient outcomes.
As hospitals and doctors' offices are the ground zero for spreading illnesses, there is a high risk of getting an infection during in-person visits. It is especially dangerous during the pandemic and for those with weak immune systems. Virtual doctor-on-demand services help decrease the risk of catching an illness as patients have less exposure to others.
Advantages of telemedicine apps for healthcare providers
In 2024, 77% of physician telemedicine users reported using telemedicine at least weekly, and 35% reported using it daily. By combining telemedicine with in-person care, physicians and care teams can create flexible care models that better meet the diverse needs of their patients and allow them to do more with less.
Lower costs
Telemedicine reduces overhead costs for healthcare providers by eliminating such expenses as rent, utilities, and maintenance. According to khealth, the average cost of a telehealth visit for an acute respiratory infection was $79 compared to $146 for an in-person visit.
Additionally, telehealth platforms can take some administrative tasks, such as appointment scheduling and data collection, off staff’s shoulders, thereby reducing administrative costs. Thanks to increased convenience, accessibility, and the convenience of URL visits, telemedicine applications also reduce patient no-show rates.
By improving coordination between care teams, remote medical services also minimize the risk of duplicative care and unnecessary procedures that incur high costs in the healthcare system.
Improved work efficiency
Two-thirds of Doximity telemedicine users reported that telemedicine has helped them better serve their patients, and nearly a third reported that it has enabled them to see more patients per day. Productivity and efficiency gains delivered by virtual care stem from flexible scheduling, easier communication with patients, and seamless real-time access to patient medical records. Unlike traditional care, where paperwork and vitals have to be done manually, telemedicine digitizes these processes, allowing providers to spend more time delivering care to patients.
Now with AI scribes in the mix, doctors can offload even more tasks to telemedicine apps, automating follow-ups, clinical documentation, triage, and other time-intensive tasks.
Additional revenue
By combining in-person and virtual care, providers can reach more patients and increase visit volume, bringing in supplemental revenue. The flexibility of telemedicine also allows providers to serve patients in remote or underserved areas, thus expanding their patient base.
With telehealth, providers can also create new revenue streams that include episodic or ongoing care services. However, to unlock additional revenue, providers have to make sure their telemedicine platform can easily collect copays and bill insurance companies.
Higher patient satisfaction
In 2024, 96% of patients surveyed said that telemedicine visits turned out to be either equivalent or superior to traditional care. As an alternative and complementary addition to traditional care, telemedicine facilitates the patient journey, streamlining the communication between the two sides of care and keeping all caregivers connected. This uninterrupted flow of information ensures that nothing is lost in translation and that treatment plans are built based on accurate, up-to-date patient data, which leads to better outcomes.
Telemedicine also relieves patients of coordinating follow-up care, a burden previously placed on ER patients. Today, providers can use telehealth to set up follow-up appointments with specialists prior to discharge.
How to create a telehealth mobile app in 7 steps
Telehealth solutions can cure many healthcare illnesses, provided they are designed with the right functionality under the hood, in compliance with relevant healthcare regulations, and with the right business model at the core. Let’s see how to get these three ingredients right and develop a secure, compliant, and innovative virtual care solution that moves the needle.
Discovery
So, you are a telemedicine services company on a mission to develop a mobile telehealth app from scratch. You find an experienced telemedicine software development company and hire them to buckle into the end-to-end app development process. In this case, your collaboration starts with a deep dive into your custom telemedicine app idea to outline product requirements, size up the competition, and assess infrastructure limitations.
Already at this stage, your development team outlines high-level compliance and data security requirements to understand how the software will handle personal health information and what qualifies as PHI in the first place. The discovery phase isn’t only about identifying what to build, but also anticipating what could go wrong, which makes risk management a core part of the discovery process. FDA, MDR, and HIPAA compliance form the cornerstone of the risk management strategy.
At this stage, your team also plans the necessary integrations, including those with remote patient monitoring devices. When it comes to integrations, we recommend taking it slow and covering around 60% to 80% of devices in your first go.
Telemedicine app developers should also identify must-have telemedicine software features to include in v1. The deliverables of the initial development stage include a high-level system architecture, tech stack design, and clickable prototypes that inform design and development decisions later on.
Development planning
Based on the results of the delivery stage, your telemedicine application development team scopes the project and prepares a detailed product roadmap with milestones, KPIs, budgets, and timelines laid over it. On the tech side of things, your telehealth software development team also breaks down the high-level insights from discovery into a Software Requirements Specification (SRS) document.
At this stage, developers finalize the architecture diagrams of the telemedicine system, defining how core modules, such as video consultations, e-prescriptions, scheduling, payments, and EHR integrations, interact with one another. This is also when teams validate scalability, data isolation, and performance considerations against projected user loads.
Building on FDA, MDR, and HIPAA groundwork, your telemedicine mobile app development team incorporates privacy-by-design and security-by-design principles into the architecture. This includes encryption protocols, authentication flows, PHI access restrictions, and audit trails to ensure continuous compliance throughout development.
MVP design and development
Your UX/UI team tests the app prototypes with real users, including patients and healthcare specialists, to refine the interface and make sure it is built to the needs of the target audience. The final layouts are handed over to the development team, which codes them and brings them into reality. The healthcare software development team also sets up the backend of the application, configures predefined integrations, and implements the necessary ISO 27001 data security safeguards, such as data encryption, data minimization, access controls, and others.
A quality assurance team then runs multiple tests to check the performance, usability, accessibility, security, and compliance of the telemedicine application. User acceptance testing (UAT) comes next, where the telemedicine app is tested by actual end users, such as healthcare providers, patients, and administrative staff, to ensure it meets their needs and workflows.
During development, your telemedicine app development company also prepares comprehensive software documentation for demonstrating compliance with IEC 82304-1:2016, 21 CFR 11, HIPAA, FDA, and other applicable certifications.
Product launch and post-launch support
The big day comes, and your MVP (basic telemedicine app) is ready for take-off in the market. After launching it on the target platforms, your development team keeps a close eye on the application to fix defects, facilitate smooth operation, and make sure your app can accommodate device and OS version updates.
Moreover, your development team collects and prioritizes user feedback that lays the foundation for product updates and advanced features. Regular security audits also play a pivotal role in the post-development stage, as they keep your application HIPAA-compliant and ensure PHI is protected as required.
Scaling
Developing telemedicine apps is an ongoing process that doesn’t end with an MVP launch. As your telehealth app grows, it requires code and architecture adjustments to accommodate a growing user base and evolve alongside your company’s needs.
Core features to include in an MVP for a telemedicine app
When it comes to telemedicine software development, we recommend building a minimum viable product before investing in a full-fledged mobile health solution. An MVP, with its set of core features, can reduce your development costs by up to 30% and allows you to collect feedback from lighthouse users to inform your product roadmap.
An MVP for a telemedicine platform usually consists of the following modules:
- An application for patients and an application for providers
- Backend
- Admin panel.
The interface and feature set vary by user type, requiring the development of separate feature bundles for patients and doctors. Keep in mind that MVP features differ based on the unique project requirements and the type of telemedicine app.
Key telemedicine app features, patient side
A patient-facing telemedicine app module usually includes the following key features:
Sign up and patient enrollment
New patients set up an app account, filling in basic information such as contact details and personal information. The registration module should also allow users to add an insurance ID to see if the visits are covered and what the copay is. Keep in mind that telemedicine apps often require Know Your Customer (KYC) verification to comply with the regulations and demonstrate a commitment to data security.
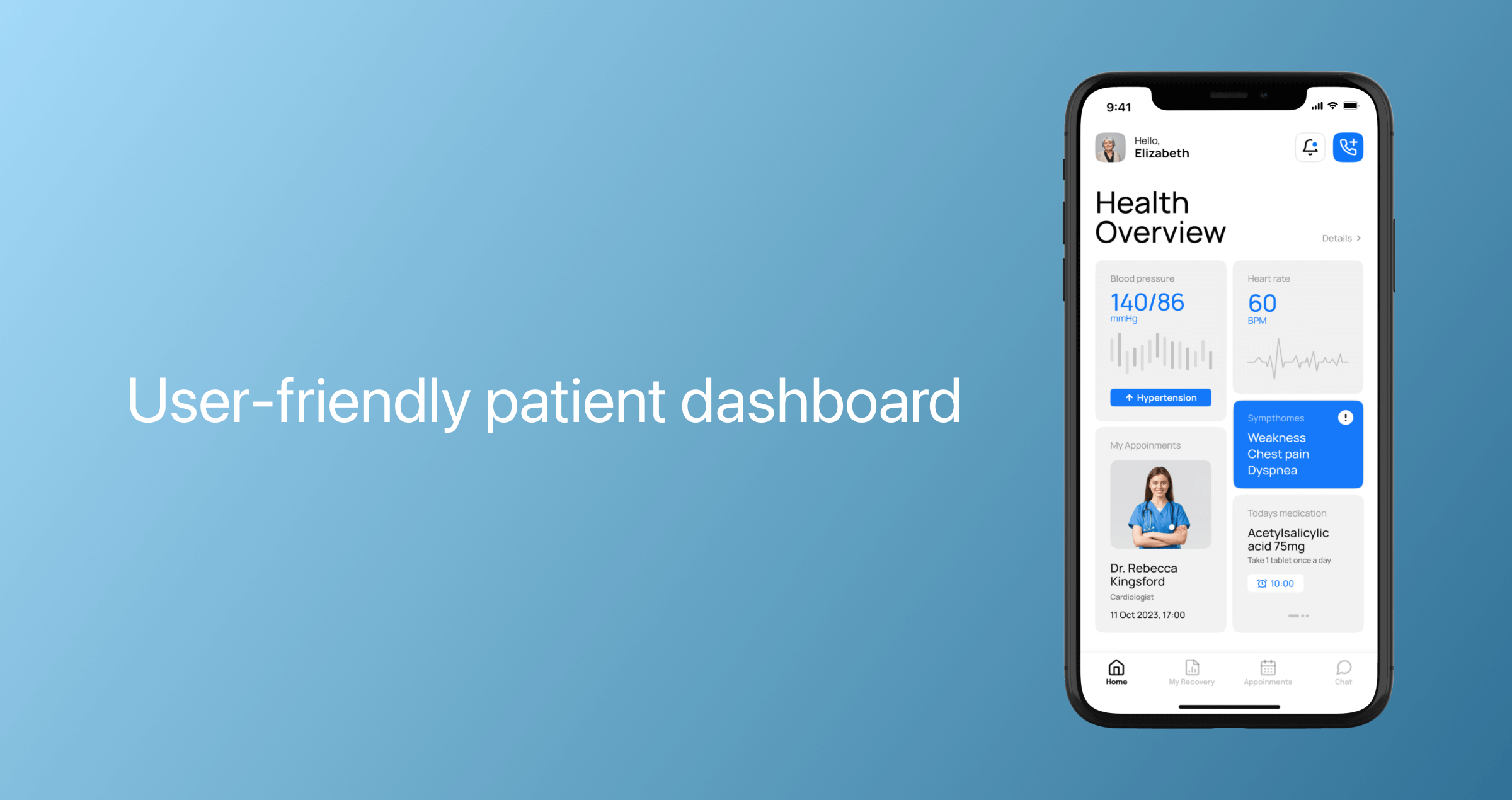
Profile management and patient dashboard
Depending on the application, a patient dashboard can deliver a real-time snapshot of health data, message history, appointment history, prescriptions, and medical recommendations. Patients should also be able to edit their profile information and delete their accounts after downloading all personal information stored in the mobile app.
Additionally, some apps allow patients to download a PDF of their consolidated medical record to share it with their care team or family members, or to send a limited-access link to providers and loved ones.
Search for a medical specialist
A telehealth app should also include a convenient search engine to match patients with the appropriate specialist based on their preferences. Search filters should include location, area of expertise, price, rating, language, and available time slots.
To improve search results, implement a category-based search so users can organize information by price, rating, and other criteria.
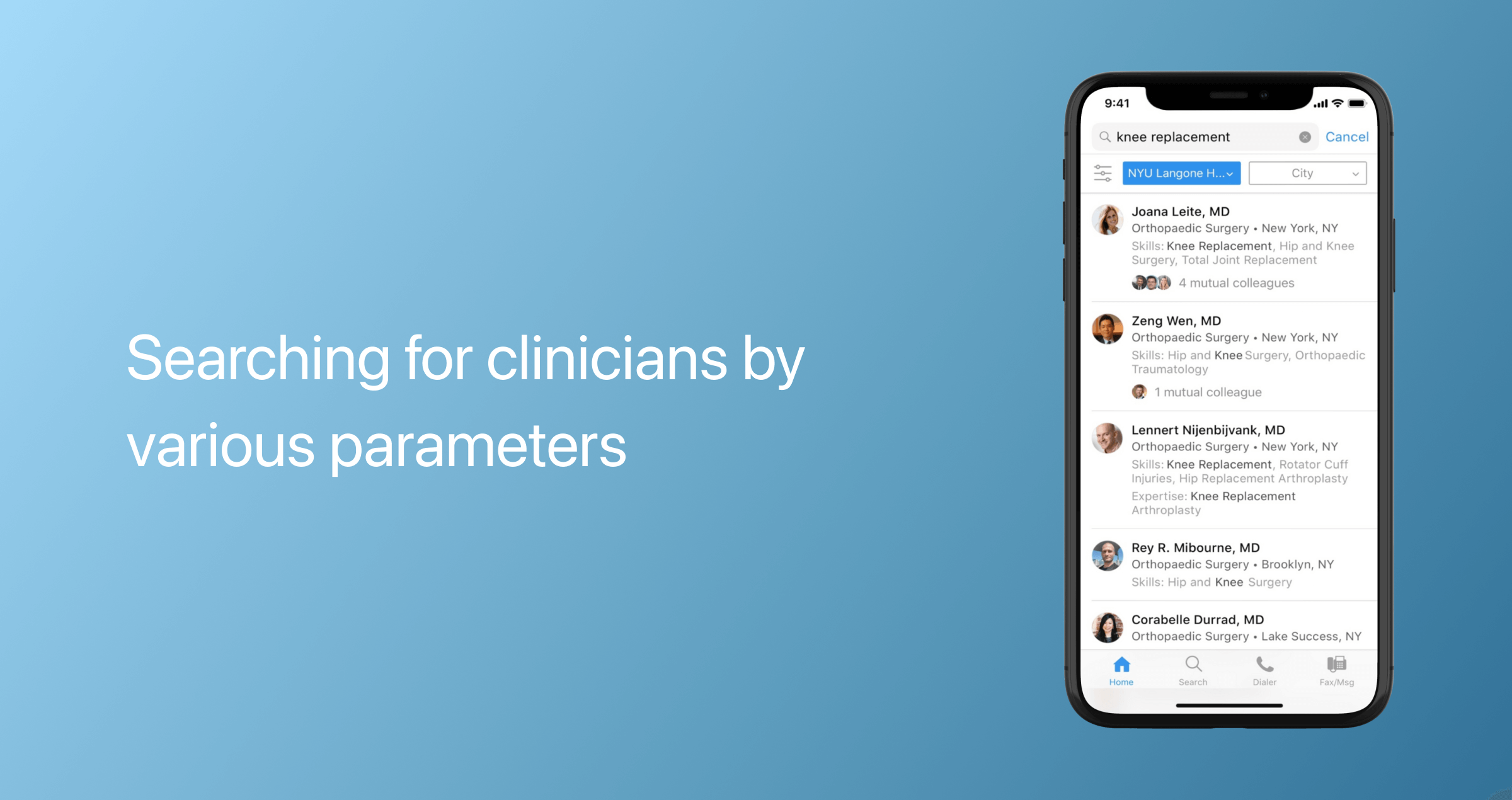
Another feature you may want to consider is making it possible to save previous search parameters and track relevant doctors.
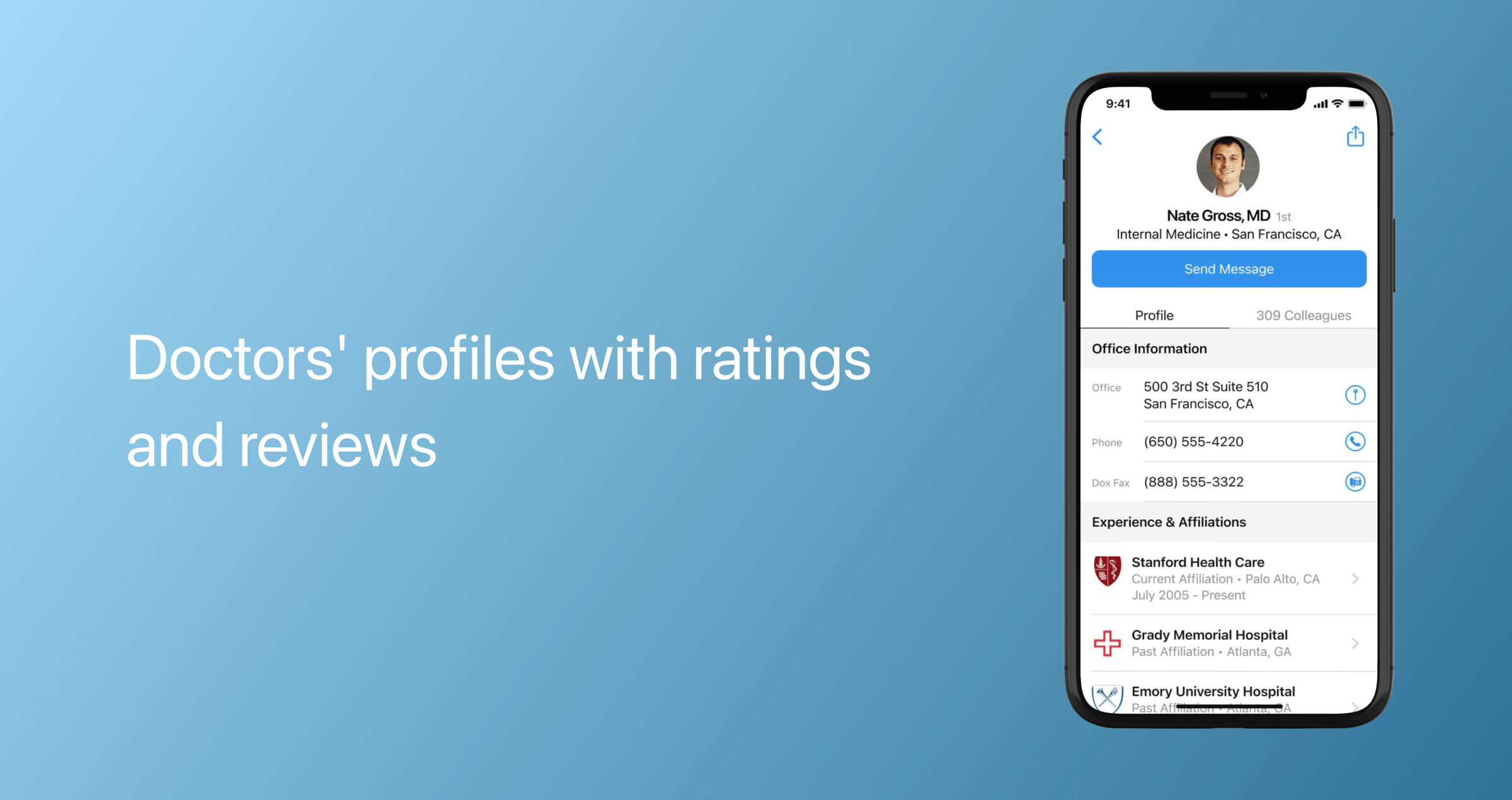
Doctors' profiles
The patients should be able to easily access detailed information about the doctors, including reviews and ratings.
Next to a doctor’s profile, patients should see the following options:
- Check appointment availability
- Book a video appointment
- Send a message
- Leave a review
- Block and report.
Messaging
A telehealth app should also include a messaging feature that can be used not only for consultations but also for asynchronous or store-and-forward care, in which users send medical records, photos, laboratory results, and other important information to a provider for review at a later time. Messaging should also enable both parties to share media in both DICOM and non-DICOM formats.
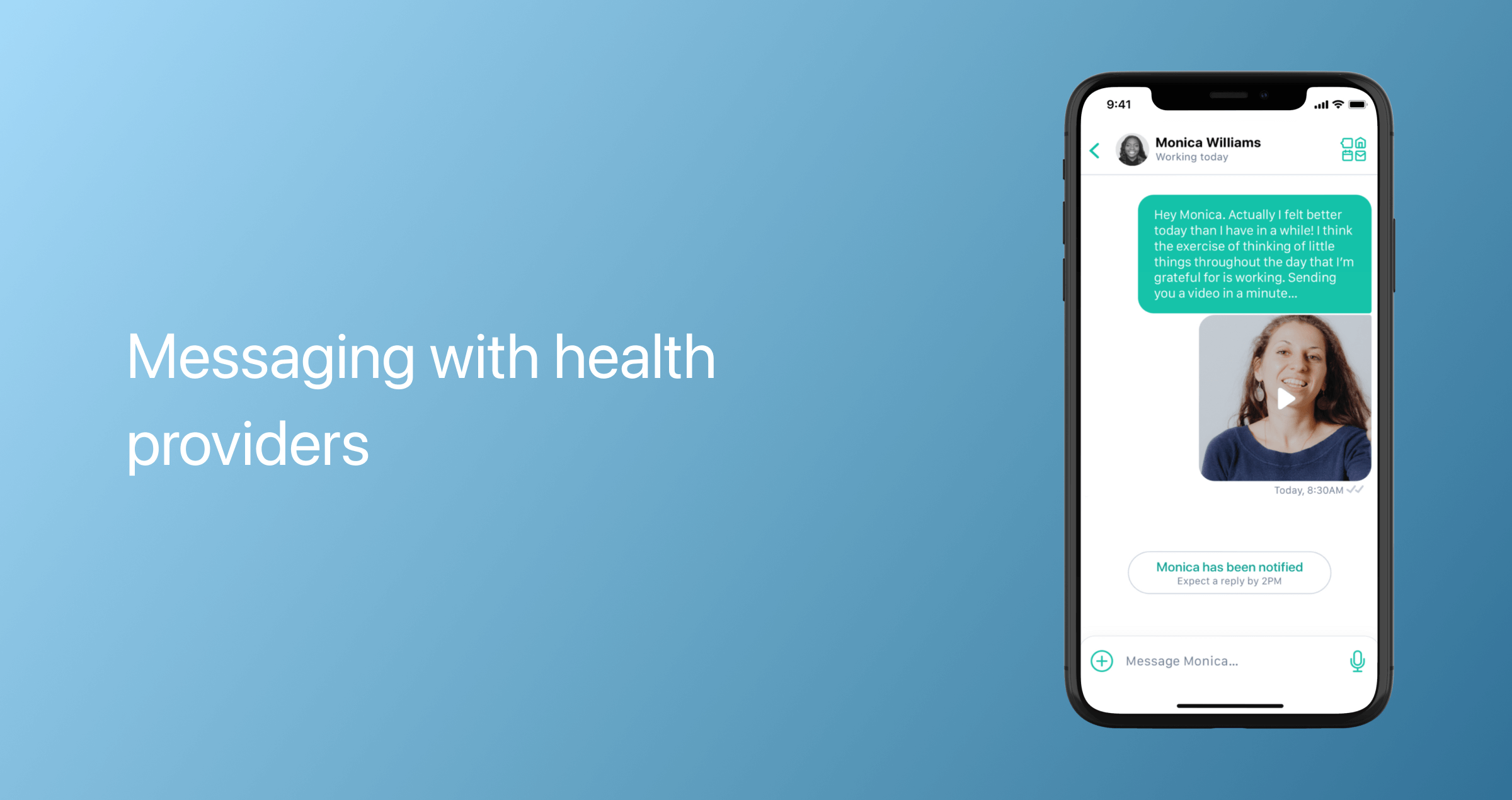
Video consultations
Compressed high-definition secure video calls with quality audio are a non-negotiable for telemedicine applications as they allow healthcare providers to see more details during consultations. Patients with challenging network conditions should be able to switch to alternative communication methods, such as audio calls or voice-to-text transcription.

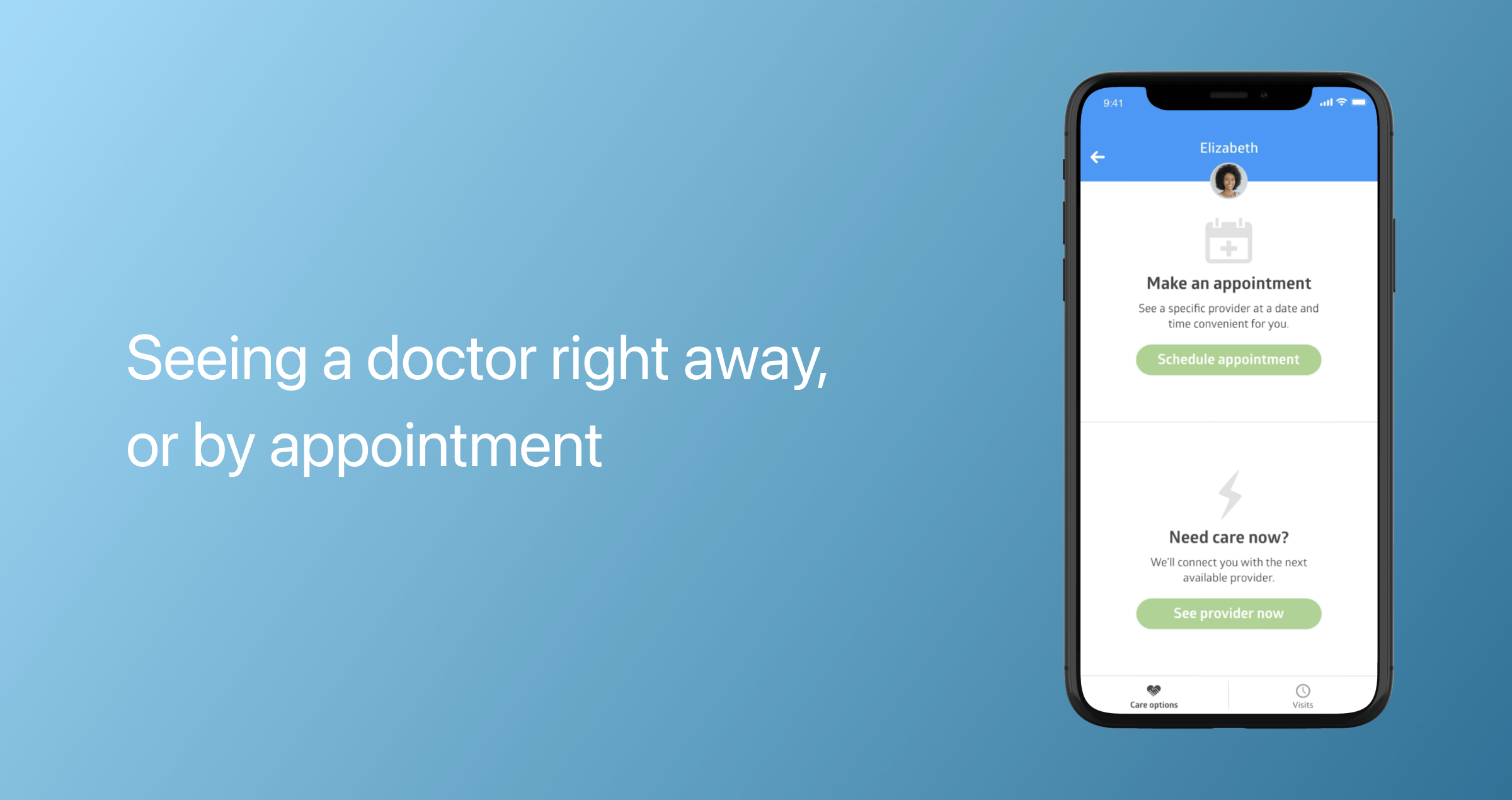
Appointment scheduling and management
Telemedicine app features usually include an appointment scheduler that helps patients manage their appointment calendars. Patients should be able to self-schedule, access the list of completed/upcoming/canceled consultations, and reschedule appointments.
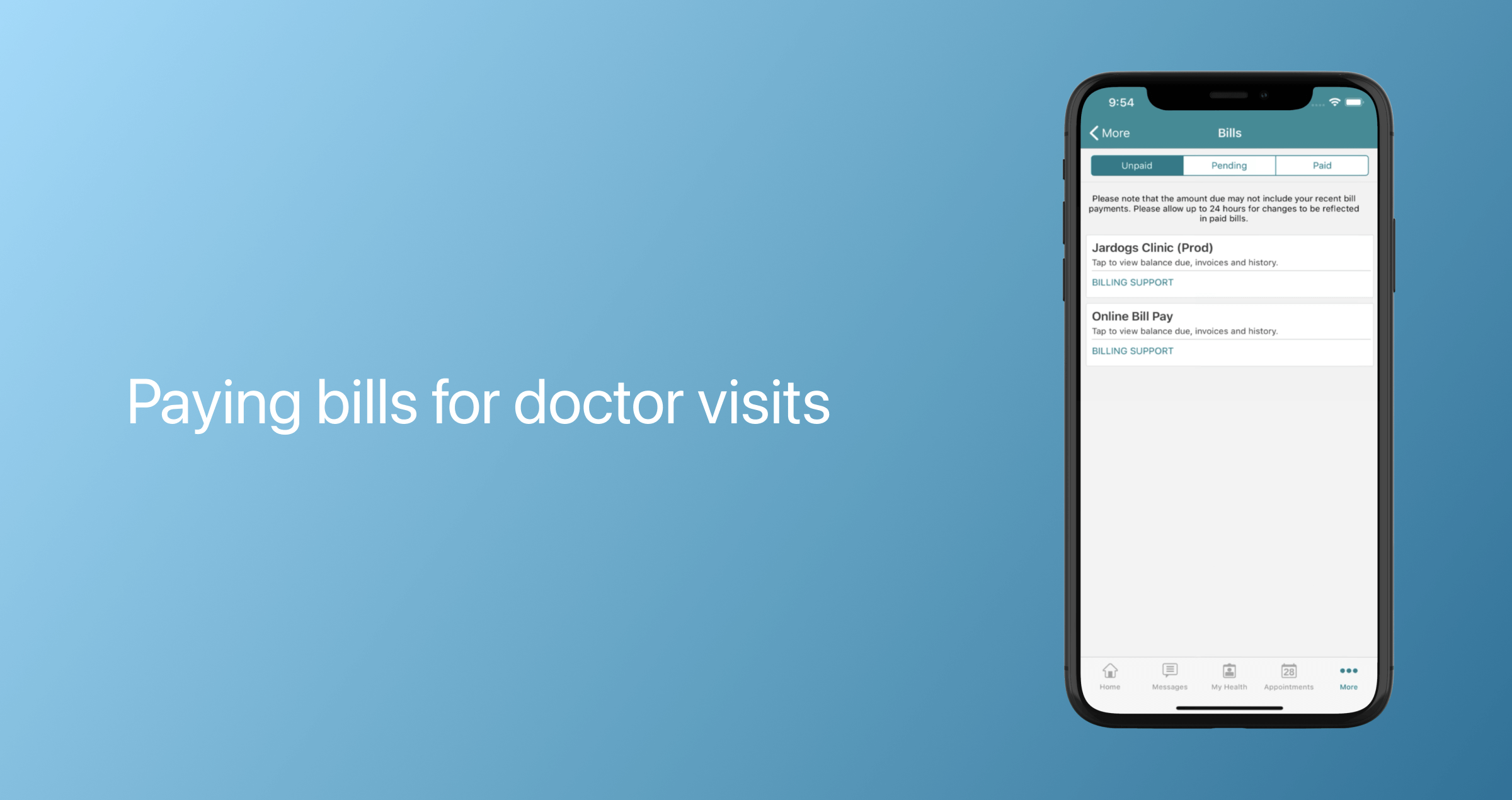
Billing
The opportunity to pay medical bills from a telemedicine application is a must-have feature for a seamless patient experience. Payment modules should allow for instant payment processing via integrated payment gateways and support multiple payment methods, including cards, mobile wallets, and other methods. Here, users should also be able to track their transaction history, payment cards, and available subscriptions.
Notifications
Push notifications remind users about upcoming consultations, new messages, test results, and relevant doctor recommendations.

Additional features for a telemedicine app, patient side
Once your app gains traction, you can add supplementary, nice-to-have features that extend its functionality and appeal to a broader audience.
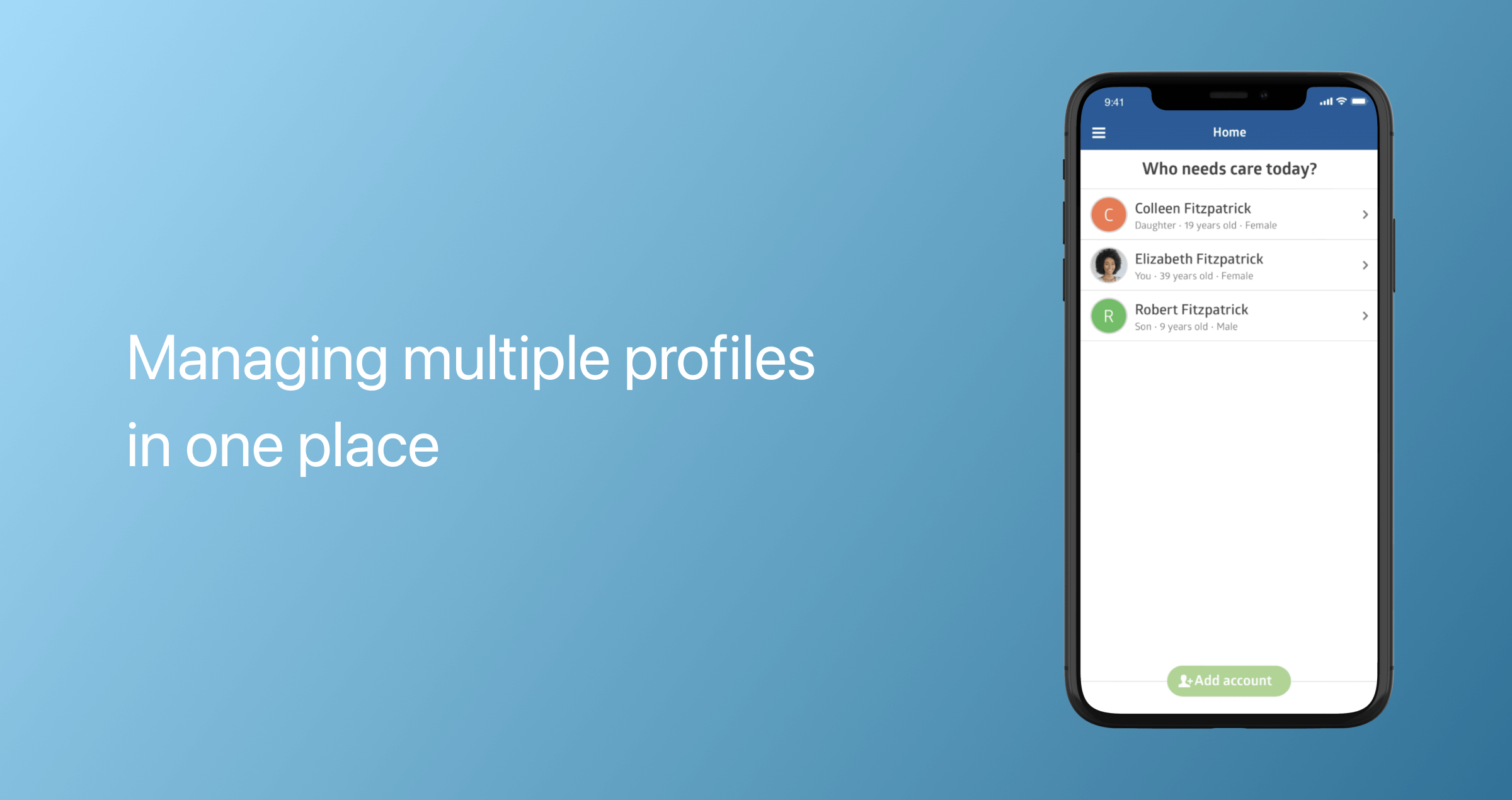
Multiple profiles
Multi-profile records enable patients to add their partners, children, and relatives to their profiles, allowing them to connect and stay updated on their family’s health data within a single interface.
Virtual waiting room
Akin to a traditional waiting room, a virtual reception area allows patients to check in remotely. A medical assistant can then do a preliminary evaluation and guide the patient to the consultation space. Medical assistants can keep the camera and microphone off until the provider is ready to see the patient, thereby avoiding potential connection issues during the consultation.
Electronic prescriptions
To provide a full spectrum of medical services, telemedicine apps can be integrated with an eRx module that enables providers to electronically prescribe medications. The module also syncs with an EHR system and pharmacies to streamline the prescription process and reduce hand-off errors. E-prescriptions are sent to patients via text message or email. The app can also send reminders to patients when their prescriptions are due for refills.
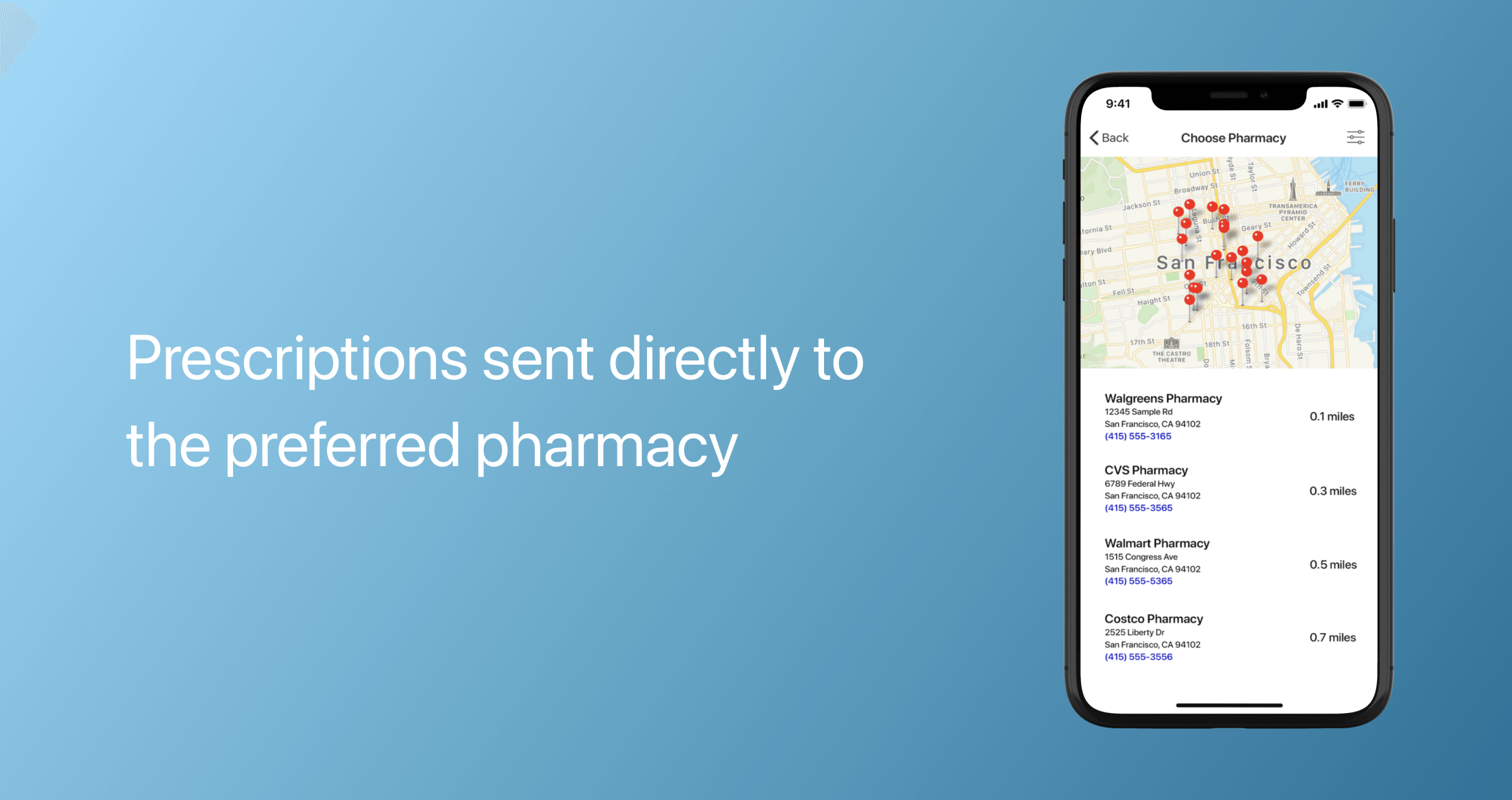
Medication tracker
Tracking medicine intake improves treatment adherence and promotes better care outcomes. This feature enables patients to set customizable medication reminders and track intake with a logbook that can be shared with their doctor.
Documents and photo storage
This feature provides patients and physicians with on-demand access to important medical records and enables easy sharing between them.
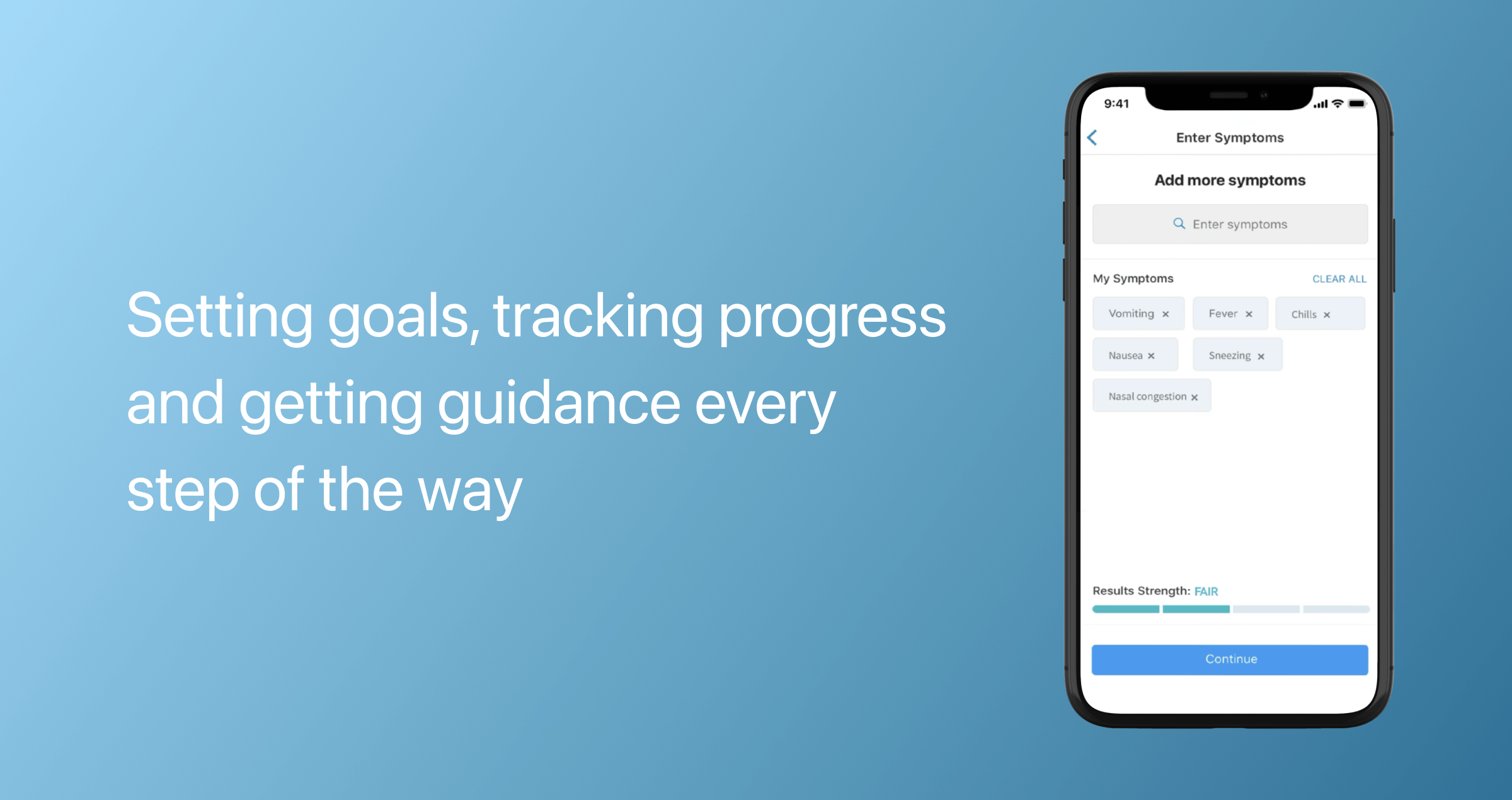
Symptoms tracker
By recording symptoms in real time, telemedicine apps enable healthcare providers to identify emerging patterns and prevent more serious conditions. Effective symptom logging also demonstrates the effectiveness of treatment lines and helps providers make more informed medical decisions. Virtual care solutions can automatically track symptoms via wearables or ask patients to report data.
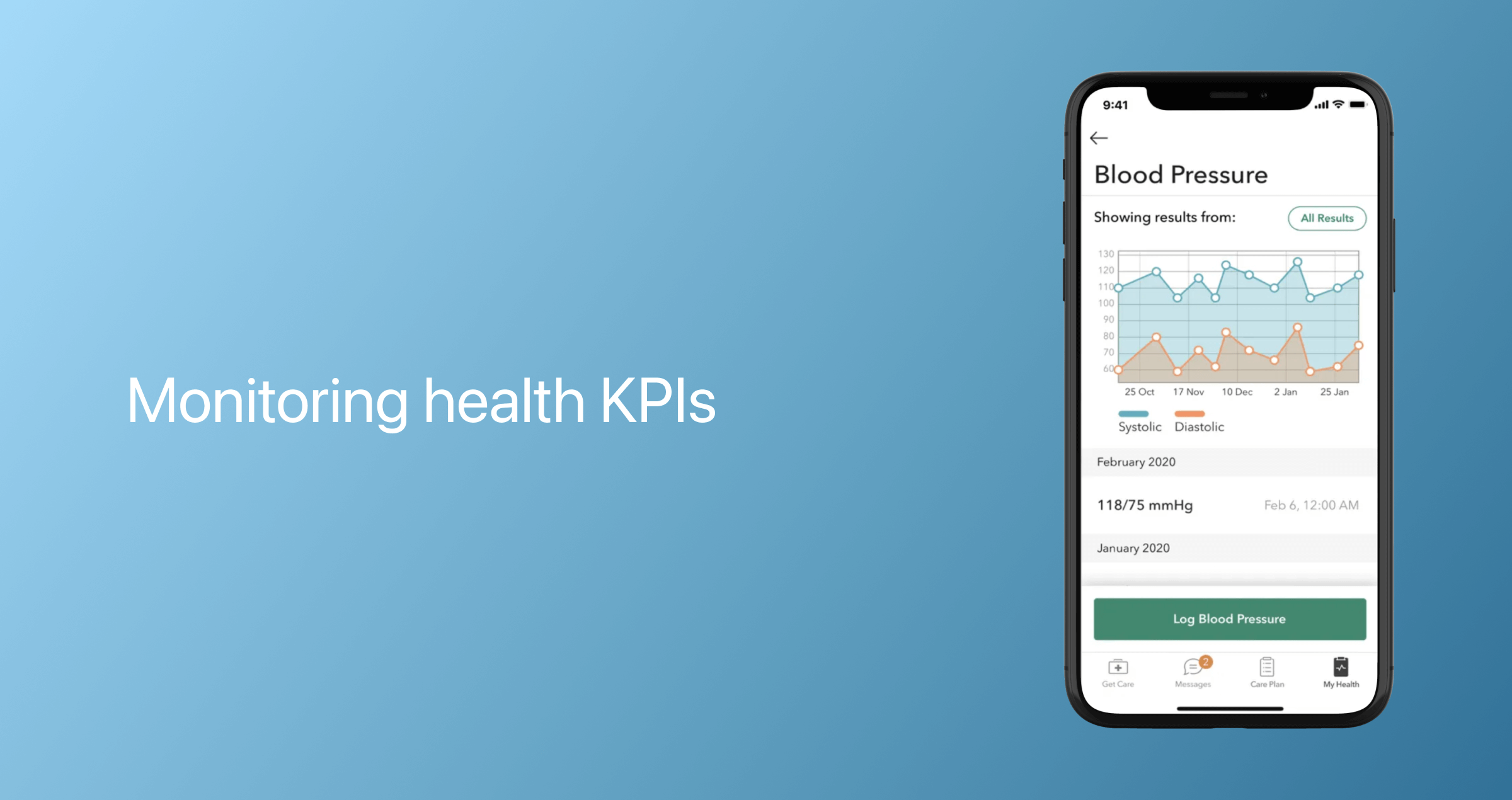
Dashboard with health analytics
Healthcare analytics solutions can be integrated throughout the telemedicine app to provide a consolidated, real-time view of a patient's health data, providers' earnings, appointment performance, and other metrics.
Key telemedicine app features, doctor side
On the doctor side, virtual care applications are kitted out with the following must-have features:
Healthcare provider dashboard
Physicians should be able to have a comprehensive, centralized overview of their patients, performance, and appointments.
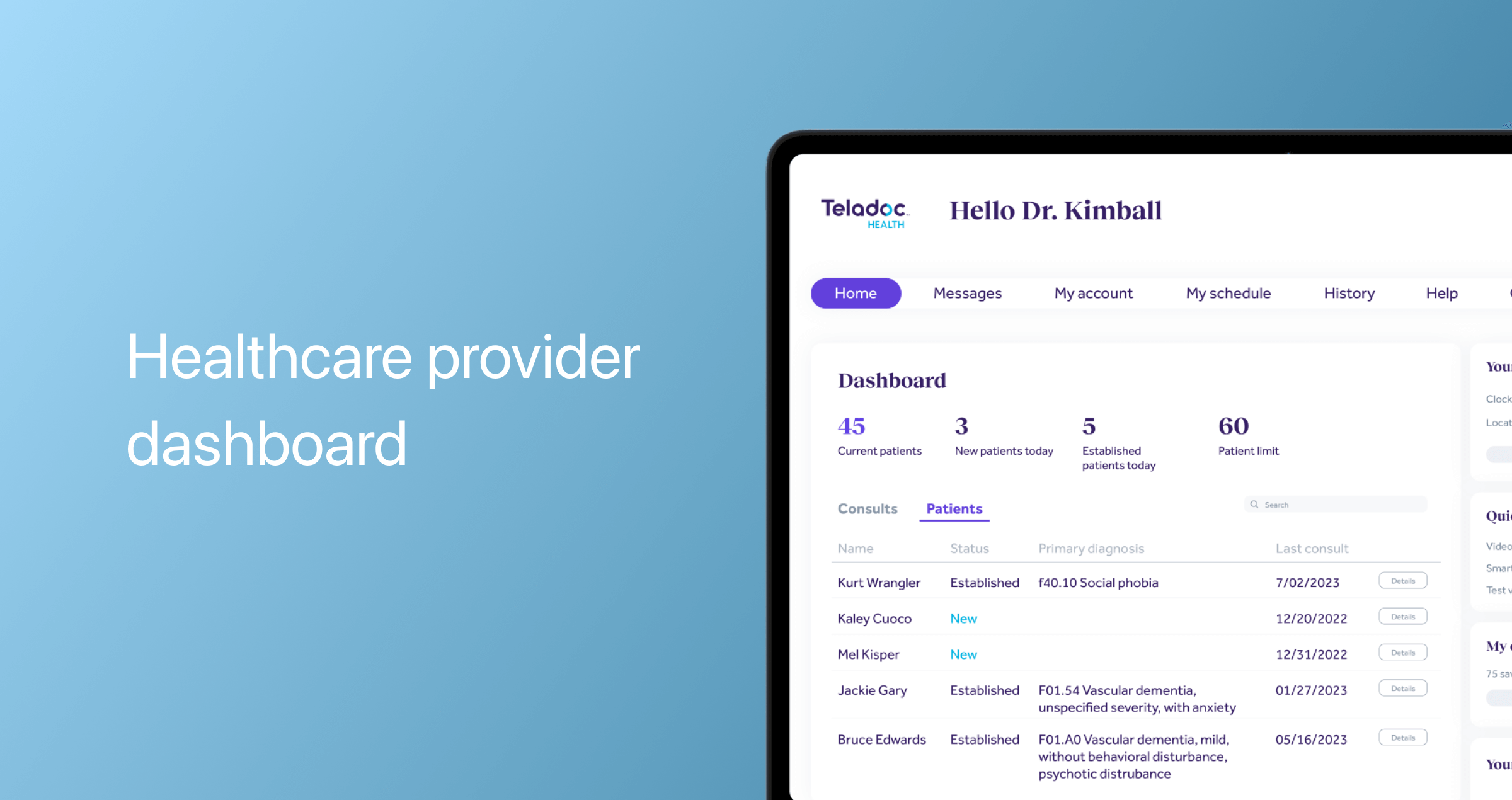
Appointment management
A telemedicine app should be equipped with a calendar functionality that allows specialists to set free time slots for appointments, access the list of completed, upcoming, canceled, paid/unpaid consultations, and manage or modify appointments. Some telemedicine apps also allow doctors to manage their upcoming appointments while they’re in a session.
Patient management
This dedicated functionality enables physicians to access the list of all patients on the go, along with their medical data, last session notes, completed questionnaires, and appointment history.
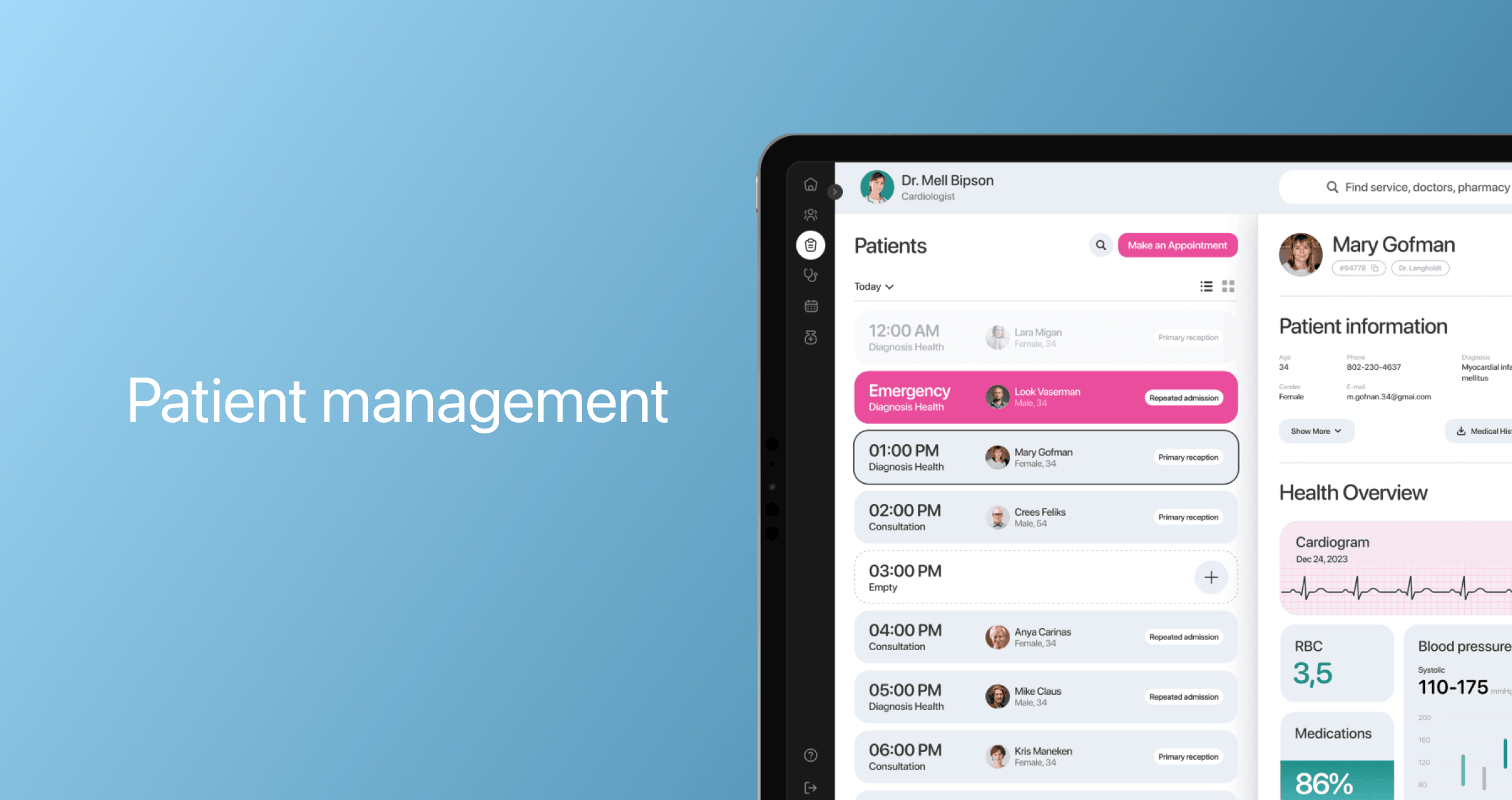
Messaging and video conferencing
Before video consultations, doctors can send pre-visit patient questionnaires to do intake assessments. During video calls, doctors should be able to share their screens with patients to present information. The option to record the call also makes it more convenient for specialists to review the consultation and ensure continuity of care.
Pre-designed and customizable forms and templates are another feature many telemedicine apps incorporate to streamline note-taking for doctors during consultations.
Access to EHR
Although not considered a must-have feature, EHR integration has become an industry standard for telemedicine applications. Working alongside an EHR, a telemedicine app provides a comprehensive view of a patient's health and enables physicians to create and update medical records directly within the app.
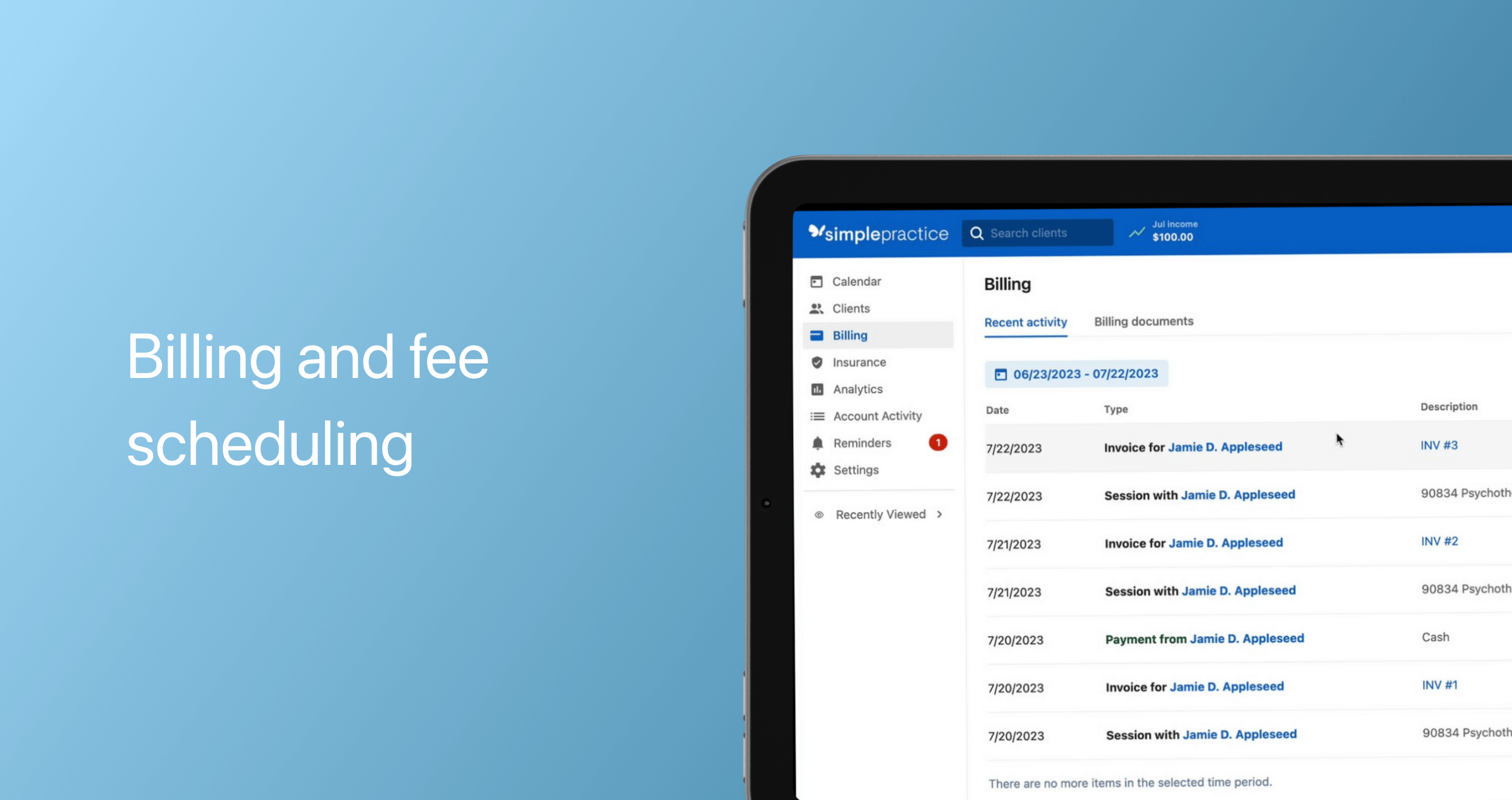
Billing and fee scheduling
In this module, providers can create and send invoices to patients for consultations, submit claims for reimbursement to insurance payers, and create custom fee schedules.
Trending technologies for telemedicine app development
It takes a lot to develop a digital health solution that can differentiate in today’s competitive landscape. To increase your chances of a home run, consider leveraging the latest tech advancements in the telemedicine space. Not only do tech boons give you a competitive edge, but they also make telehealth services play to their full potential.
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence — generative AI, machine learning, and NLP included — has become a foundational technology for cutting-edge virtual care solutions. 60% of IT decision makers in healthcare use AI to process and analyze medical data, 59% to update patient records, and 40% to diagnose medical conditions.
AI in telemedicine takes many forms, supercharging various application aspects:
- Generative AI and NLP empower conversational interfaces to understand and respond to patient queries in natural language, providing tailored guidance in real-time
- By analyzing medical records, logged symptoms, health data, and treatment outcomes, ML algorithms can uncover patterns, predict complications and risks, and personalize treatment recommendations.
- AI solutions can support clinical decision models, providing healthcare professionals with recommendations drawn upon patient data and evidence-based guidelines.
Also, artificial intelligence can automate administrative processes, such as patient intake, appointment scheduling, insurance verification, data entry, and more. For example, Healow, one of the leading telemedicine apps, relies on a medical AI scribe solution that integrates with EHRs and transforms conversations between patients and healthcare providers into clinical documentation.
Internet of Medical Things
The Internet of Medical Things comprises a growing ecosystem of devices, such as wearables, medical sensors, and remote patient monitoring systems, that integrate with telemedicine applications to enable a comprehensive overview of the patient's health. The integrated data is then sent to doctors and care groups for further analysis.
One of the remote care companies that bet on such integration is BodySite. The remote care platform integrates with Oura Ring to aggregate patient biometric data for easier progress monitoring and smarter care decisions.
Extended Reality (XR)
Encompassing Augmented Reality (AR), Mixed Reality (MR), and Virtual Reality (VR), XR is another trendy innovation that is rapidly gaining popularity in the field. Telerehabilitation is the main adopter of XR technologies in telehealth, using immersive experiences to support remote physical therapy, pain management, and relaxation.
Blockchain
Since virtual care entails continuous online exchange of electronic health records between patients and physicians, the risk of data breaches is high. Blockchain technology can mitigate this risk by enabling mutually agreed-upon, decentralized, and anonymous interactions between doctors and patients.
Blockchain can provide decentralized and encrypted storage for patient medical records, making it difficult for unauthorized parties to access them. Additionally, this technology can be used to manage patient consent, with each instance logged on the blockchain.
Although deemed effective, blockchain is still in its nascent state in telemedicine and overall healthcare. High implementation costs, the need for expert talent, lack of standardization, and regulatory complexities hinder the adoption of blockchain and put it on the back burner.
Challenges in telemedicine app development
The road to an effective telemedicine app development solution is laid out with challenges that you need to account for early in the development process to avoid setbacks later.
Challenge 1. Data interoperability
In healthcare, 97% of IT decision makers report that their organizations have legacy technology. Due to a lack of data standardization, outdated software can become incompatible with telemedicine technologies, preventing healthcare organizations from integrating telemedicine solutions into their ecosystems.
Also, the lack of data interoperability between virtual care applications and EHRs makes it challenging to enable a seamless flow of data between the systems. As a result, providers must manually enter diagnoses, prescriptions, and clinical notes from virtual appointments into patient records.
To address this obstacle, telemedicine providers should use standardized data formats, such as HL7 FHIR or USCDI, and standardized APIs.
Challenge 2. Compliance with regulations and data security standards
In the U.S., telemedicine applications face a complex regulatory landscape that includes an interplay between federal laws and state-level data laws. In particular, telemedicine providers must either align with insurance plans and comply with HIPAA or operate on a cash-only model and abide by state data privacy laws, provided those laws don’t exempt businesses or data regulated by HIPAA or other federal laws.
When it comes to HIPAA, telemedicine software must implement a specific set of data security and privacy measures to comply with the regulation, including:
- The login controls, monitoring process, and storage of data should all be synchronized
- A HIPAA-compliant product must have no scope of data leakage or unauthorized access by any third parties
- The usage of AWSCloudTrail and AWS CloudWatch tools to help your telehealth app development meet the regulations
- There should be SSL-enabled endpoints to provide the best solution to secure the data during the transfer process
- A HIPAA-compliant app must encrypt data at rest and in transit
- An application must implement strong access controls to restrict access to PHI
- A compliant telehealth platform should use only secure API frameworks and libraries, and more.
These are just a few examples of security measures you need to implement in your telemedicine app to make it HIPAA-compliant. To achieve full compliance, we recommend engaging a vendor with expertise and experience in developing HIPAA-compliant mobile applications. Keep in mind that HIPAA requires companies that outsource telemedicine development to enter into a Business Associate Agreement with the vendor to ensure data security.
Challenge 3. Accessibility
Telehealth applications have the potential to address long-standing health inequities as they can help remove barriers to care. However, if your telemedicine application is not developed with accessibility in mind, it’s likely to add to already existing digital barriers. Today, around 13 million older adults have difficulties accessing telehealth services due to hearing difficulties, cognitive impairments, a tech curve, and visual impairments. Additionally, 25% of users have difficulty accessing telehealth due to spotty internet/cellular connectivity.
To address the digital divide, your telemedicine platform should be designed according to WCAG guidelines, the WHO-ITU Global standard for accessibility of telehealth services, and regional accessibility standards and regulations.
Additionally, your telehealth solution should allow for multiple communication modes, such as video-based consultations, phone-based consultations, and text-based messaging. For one of our projects, we also implemented voice-to-text transcription for real-time app consultations to maintain clarity even under challenging network conditions. If you’re planning to implement an AI-powered functionality, ensure the model prioritizes equity and unbiased data.
How much does it cost to develop a telemedicine app?
Telemedicine app development costs vary based on the development platform (web or mobile), the number and complexity of features, integration requirements, advanced technologies, and other variables. Below, our development experts have broken down the cost of an MVP based on estimates from our previous projects.
| Features | Development time, hours | Backend development time, hours | Approx. cost, $ |
|---|---|---|---|
Patient | |||
| Sign in / Sign up | 42 | 32 | 3,700 |
| Personal information | 32 | 16 | 2,400 |
| Filters | 32 | 32 | 3,200 |
| Doctors' profiles with ratings and reviews | 32 | 24 | 2,800 |
| Messaging | 120 | 96 | 10,800 |
| Video calling | 148 | 40 | 9,400 |
| Scheduling and appointment management | 50 | 32 | 4,100 |
| Personal profile | 48 | 24 | 3,600 |
| Payment integration | 64 | 64 | 6,400 |
| Notifications | 24 | 24 | 2,400 |
Doctor | |||
| Sign in / Sign up | 42 | 32 | 3,700 |
| Personal information | 56 | 32 | 4,400 |
| Personal profile | 64 | 32 | 4,800 |
| Appointments screen | 96 | 40 | 6,800 |
| Messaging | 16 | 16 | 1,600 |
| Video calling | 16 | 16 | 1,600 |
| Notifications | 24 | 24 | 2,400 |
General | |||
| Architecture | 32 | 32 | 3,200 |
| Server interaction & API | 32 | – | 1,600 |
| Database | 24 | 16 | 2,000 |
| Admin panel | 156 | 110 | 13,300 |
| Total | 1,150 | 734 | 94,200 |
Keep in mind that this estimate covers only the costs associated with MVP development. By building an MVP first, you can validate your product concept early and gather valuable user feedback needed for full-fledged development.
You can contact us to get a consultation and a ballpark estimate for your project.
Money talks: how to monetize a telemedicine app
So, you've invested an impressive amount of money into developing a remote care solution and hope to make a return someday. Here are the most efficient ways to break even and make a profit in the telemedicine industry.
Subscription
This is a common business model for a mobile app based on renewed membership plans, both for patients and doctors. Subscription plans could be monthly, semi-annual, or annual. You can also include a free trial to demonstrate the value of your product.
Pay per appointment
In this case, the doctors set the prices for their services, while the platform charges a fee for every payment. Pricing per appointment may vary depending on the qualifications, specialization, and the type and time of consultation.
Develop a telemedicine app with Orangesoft
No matter the challenges telemedicine is facing today, it has already become a centerpiece in the future of healthcare delivery, making high-quality care inclusive and accessible for all. With 15 years of hands-on experience and an exclusive focus on healthcare, Orangesoft helps telemedicine startups deliver on the promise of effective virtual care.
Collaborating with us, you get a competitive tech edge that is made of:
- An experienced, full-cycle development team with extensive experience in mobile and web app development, quality assurance, discovery, UI/UX services, and more.
- Experience implementing AI, IoMT, and XR solutions for telemedicine.
- A proven track record of developing compliant telemedicine solutions according to HIPAA, HITECH, FDA, HL7, etc.
- Data security excellence in line with ISO 27001.
Share your vision with us, and our specialist will help you transform it into a successful app solution.
