Technology is reshaping healthcare, making it more accessible and patient-focused. However, successful healthcare innovation is a careful balance between technology, compliance, and user needs – a balance that is notoriously difficult to achieve.
That’s why custom healthcare software development is more than just a technical solution. It's a multifaceted process that requires a deep understanding of the healthcare ecosystem, thorough compliance know-how, and a laser focus on end users.
This article is your step-by-step roadmap to developing high-quality, secure, and compliant healthcare solutions that make a difference.
A pulse check on the healthcare software landscape
Rising healthcare costs, clinical workforce shortages, aging populations, and increasing competition among healthcare providers are straining healthcare ecosystems. The industry is responding by increasing healthcare IT investment, with the health tech market size projected to grow from $354 billion in 2025 to over $981 billion by 2032.
Types of healthcare software
Today’s healthcare software mirrors the industry’s complex challenges. On a macro level, the overarching goal of healthcare software applications centers on one of three areas: streamlining administration, informing clinical decision-making, or supporting patients and consumers. Each solution is designed to target a specific aspect of one or more of these pillars.
| Purpose | Healthcare application types |
|---|---|
| Patient engagement | · Patient portals · Medication management applications · Lifestyle tracking apps |
| Remote care | · Telemedicine applications · Remote monitoring systems · Virtual triage apps |
| Clinical support | · Electronic Health Records (EHRs) · Clinical decision support systems (CDSS) · Imaging & diagnostic tools · AI-powered diagnostic assistants |
| Administrative workflow automation | · Scheduling & appointment apps · Medical billing systems · Insurance claims management · Ambient AI tools |
| Preventive health | · Fitness and wellness applications · Health tracking apps · Education and guidance applications · Personalized prevention and coaching apps |
| Rehabilitation and recovery | · Post-surgery recovery apps · Physical therapy tracking · Speech therapy tools · AR/VR platforms |
Key healthcare stakeholders
The healthcare system is a complex, heterogeneous environment with many interconnected players. Understanding how these players interact is key for healthcare innovators to think through the necessary integrations for their custom healthcare software, secure buy-in from relevant stakeholders, and make sure the solution has all the features its end users need.
| Stakeholder group | Role | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Patients | Beneficiaries of healthcare services and products | Individuals, caregivers, and patient advocacy groups |
| Providers | Deliver medical care and services directly to patients | Doctors, nurses, therapists |
| Payers | Reimburse care administered by a healthcare provider, impacting what healthcare services are offered and covered | Insurance companies, Medicare, and Medicaid |
| Regulators | Set, enforce, and oversee standards related to patient safety, quality of care, and ethical practices | The Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and European Medicines Agency (EMA) |
| Sponsors | Fund, support, or champion healthcare initiatives. | Research and development, and medical device manufacturers |
Benefits of software development for healthcare
In 2024, 75% of providers and payers said they increased IT spending over the past year and plan to ramp up their investments moving forward. Why? Because healthcare software solutions have long progressed from a simple tech upgrade to a strategic move that delivers measurable improvements in patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
Improved patient care and outcomes
Custom healthcare software benefits patients in many ways: reducing medication errors, improving diagnostic quality, increasing the accessibility of healthcare services, and more. Technological innovation also ushered in a new era of care — remote and virtual modalities, allowing chronic care patients, older individuals, and underserved populations to receive necessary medical attention, wherever they are.
According to AMA, 60% of physicians reported that telehealth enabled them to provide high-quality care. Orangesoft has firsthand witnessed the positive impact of such solutions on patient outcomes. Our virtual hospital platform helped a US-based healthcare company increase patient satisfaction scores by 40% and achieve a 25% improvement in medication adherence.
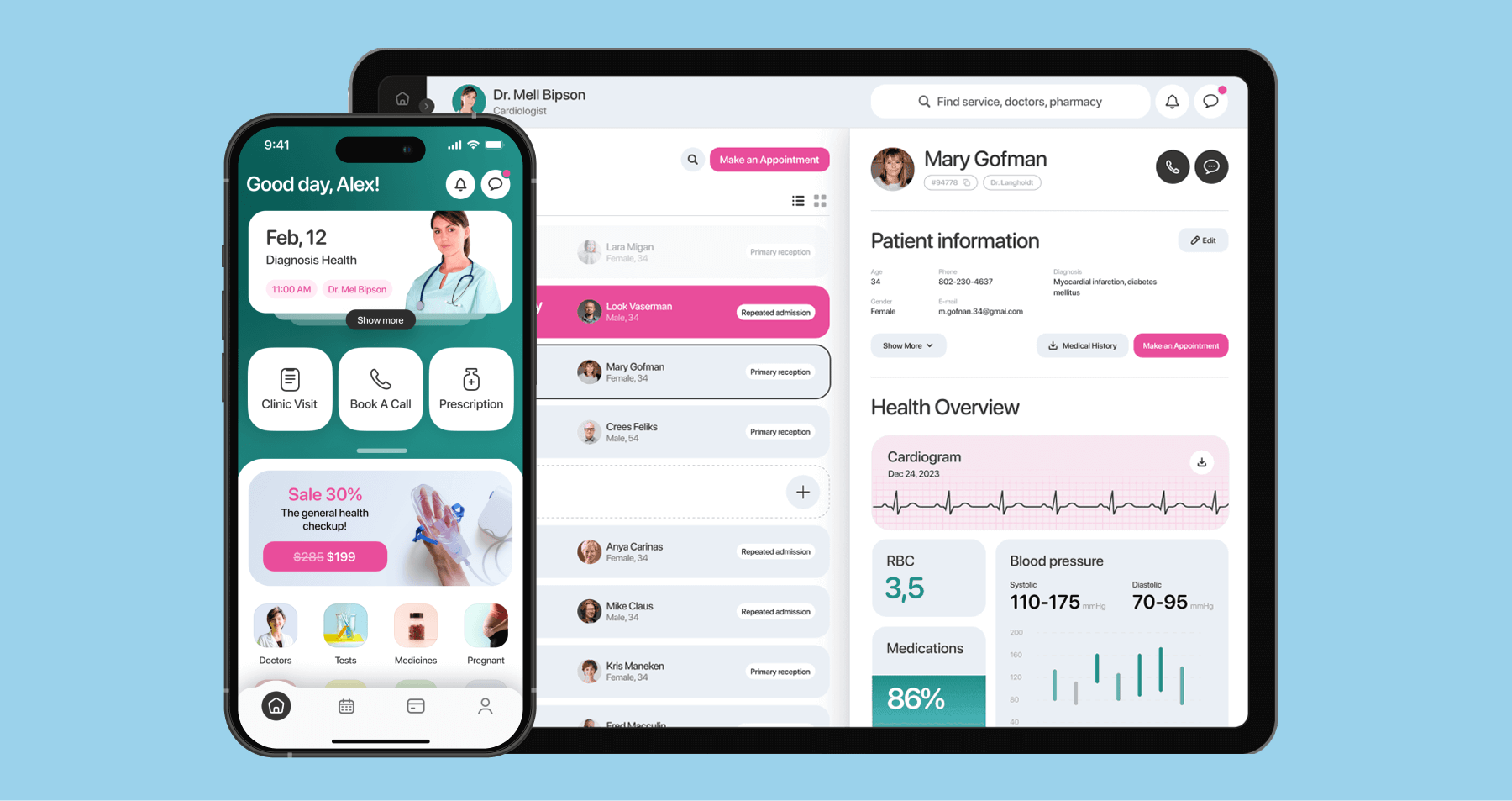
Elevation in clinical efficiency and productivity
An average caseload of 20 to 30 patients, complex documentation taking up around 35% of the clinician’s time, the challenging regulatory landscape, and other barriers make productivity gains difficult to realize for the healthcare sector.
However, tech solutions can help healthcare professionals gradually reduce these inefficiencies. For example:
- Ambient AI tools free clinicians from the burden of extensive notetaking, delivering time savings of around 41%.
- Intelligent scheduling systems yield an average increase of 5-10% in physician utilization.
- Remote chronic patient monitoring platforms empower a single nurse to monitor 125 to 250 patients.
Cost reduction and operational savings
The healthcare sector is actively investing in AI: around 66% of physicians use AI in their practice, up from 38% in 2023. The majority of this innovation money went to automating administrative tasks and reclaiming the time spent on them by healthcare staff.
By taking over tasks like insurance verification, medical billing, and even initial analysis of medical images, AI-enabled software can potentially save the U.S. healthcare system up to $360 billion per year.
Beyond AI, other types of healthcare software also contribute to cost reduction. Telemedicine apps reduce the overhead costs associated with in-person visits. Remote patient monitoring solutions prevent hospital readmissions. Equipped with self-service options, patient portals cut down on administrative tasks for staff.
Better data management and analytics
Healthcare data is rich in insights that can literally save someone’s life. But due to data quality issues, silos, and its inherent complexity, healthcare data sits gathering dust, locked away tight behind legacy health systems. Dedicated healthcare data management software can release some of that trapped data potential by providing the tools and capabilities to unify, clean, and process health-related information and patient data.
Analytics tools, such as AI-powered imaging analysis apps and disease prediction tools, can clean and transform that AI-ready healthcare data into actionable insights, including subtle patterns invisible to the human eye.
Data security and regulatory compliance support
Due to strict regulatory and data security standards, the latest custom healthcare software solutions are designed with built-in safeguards, including end-to-end data encryption, access controls, and other measures. Security of this caliber is simply impossible to achieve with manual data management and legacy systems.
Most healthcare software applications also come with compliance management features, such as audit trails, automated reporting, version control, and others that help healthcare organizations demonstrate their compliance with regulations like the FDA and HIPAA.
Competitive edge
These days, the healthcare service industry is a crowded arena with non-traditional healthcare players vying for market share against traditional incumbents. For any of these contenders, innovative healthcare software products present a tech moat and a strategic differentiator — one that can unlock new value streams and attract more consumers.
Off-the-shelf vs custom healthcare software development
As a healthcare company steps into innovation, a fundamental question arises: Should it opt for off-the-shelf software or develop a custom healthcare software solution? Our developers have pitted the two options against each other so you can choose an optimal solution based on your needs.
| Criterion | Off-the-shelf healthcare software | Custom healthcare solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Speed to implementation | Faster to implement; requires minimal setup | Slower to implement; can take up to 4+ months |
| Initial investment | Lower upfront; pay-as-you-go or subscription-based | Higher upfront; requires investment in planning, development, and testing |
| Fit to unique workflows | Designed to match standard clinical or admin flows | Built around your organization's specific needs and processes |
| Scalability | Limited — built on a pre-defined architecture; typically requires upgrading to more expensive plans or purchasing additional licenses | Scalability is a core design principle; the architecture and database design are optimized for your current and future needs |
| Security and compliance | Dependent on the vendor | Full control over compliance and data security features |
| Integration with existing systems | Comes with a limited set of integrations | Built to integrate with your internal systems and third-party tools |
| User experience | Built for broad user bases | Designed with clinician/patient journeys in mind |
| Space for innovation | Limited by vendor roadmap and update cycle | Full flexibility to innovate, iterate, and test new features or care models |
| Support and maintenance | On the vendor; may have delayed response times and limited customization | Dedicated support; updates, maintenance, and improvements on your terms |
| Long-term ROI | May decline; costs pile up due to licensing and limited differentiation | High thanks to the competitive edge, better fit, and full IP ownership |
| Vendor lock-in | High; switching platforms can be complex and expensive | Low; you own the intellectual property and can scale, pivot, or migrate freely |
| Training | Standardized learning resources | Custom training requirements |
From our experience, custom healthcare software development services are a better and more strategic option for healthcare organizations with unique workflows that ready-made solutions cannot replicate.
Companies whose healthcare products are their core intellectual property will also benefit from custom healthcare solutions, even at an early product stage, as these platforms offer full ownership and can maintain a competitive edge through proprietary features that off-the-shelf tools simply cannot provide.
But when you need more of a functional system rather than a core differentiator, and a ready-made application covers roughly 80-90% of the requirements, customizing an off-the-shelf application seems to be a more pragmatic approach.
Key milestones of the healthcare software development process
The sensitive nature of patient data, the critical implications of software malfunctions on patient safety, and a keen regulatory eye require healthcare solutions to be developed within a uniquely rigorous environment and with certain twists. Here are the key data points to consider when building for the healthcare industry.
Starting with a clear problem definition
The path to a successful, high-demand healthcare solution starts with understanding the exact problem that needs that solution. This might be a clinical inefficiency, a lack of patient engagement, difficulties in data management, or the launch of the new healthcare service.
Once that problem is identified, you need to drill down into its context, including key stakeholders, the regulatory landscape, the workflows involved, existing tools and processes, and other pertinent factors that shape both the problem and the solution. Identifying these variables will help you create a preliminary draft of software requirements that you can share further with your health tech vendor.
Selecting the right healthcare development partner
If you’re after custom medical software development or looking to calibrate an off-the-shelf solution and don’t have an in-house team of developers, you need to partner with a trusted healthcare software development company that knows firsthand the complexities of the industry.
The choice of the development partner depends heavily on your unique needs, requirements, and limitations. However, regardless of your specific healthcare needs, make sure the selected healthcare software development companies have:
- Proven experience in compliant development, including HIPAA, the FDA, the MDR, PIPEDA, or any other regulatory requirements relevant for your project.
- Deep understanding of HL7 and FHIR standards for data exchange.
- A strong portfolio of healthcare projects to corroborate their claims.
- A technology stack that aligns with your software project.
- A firm grasp of the latest technologies like machine learning, generative AI, IoMT, and their responsible and ethical implementation within the healthcare context.
Prioritizing security and compliance from day one
High-impact healthcare applications that handle confidential patient data and personally identifiable information (PII) are usually classified as higher-risk by global regulatory bodies and, therefore, fall under intense regulatory oversight.
This scrutiny often equates with the specific rigor healthcare development companies require in their development process. Depending on the solution’s risk level, this rigor may require a Quality Management System (QMS), specific frameworks and certifications, such as ISO 27001 or SOC 2, as well as secure coding practices to prevent vulnerabilities.
Designing for usability in healthcare settings
Making your healthcare software effectively usable for its target users is half the battle when it comes to its long-term adoption. A healthcare system with good usability mimics the natural flow of clinical practice or patient interaction, plus anticipates the diverse needs and abilities of all potential users.
To achieve that level of usability, you need to engage target users early in the design process, ideally during the user research stage and when testing the clickable prototypes for your healthcare application. This way, your design team can test the hypotheses against real user feedback and spot usability issues when they’re cheapest to fix.
⚠️ Because of the HIPAA requirements, you can’t test an application with real-life patient records. However, you can use synthetic data (dummy records) and a demo environment to create a realistic testing space. Real patient records can only be used after they have been properly de-identified in accordance with HIPAA standards.
Planning for interoperability and integration
System integration relies on other technologies such as data integration tools, APIs, and others to bridge the gap between different systems, while interoperability ensures the platforms speak the same language inherently. Since interoperability standards like FHIR are becoming mandatory in many jurisdictions, we recommend planning for both interoperability and integration.
The exact method of integration depends on the interplay of the specific systems, their existing capabilities, the volume and velocity of data exchange required, security requirements, and the target level of real-time interaction. As for interoperability, your developers adjust your application to support standardized data formats and common terminologies like SNOMED CT, LOINC, ICD-10, RxNorm, and others.
Risk-based testing and validation
In healthcare development, a system, element, or process is tested according to the potential risks associated with it. If that specific component can harm a patient if it malfunctions, its testing must be more rigorous, exhaustive, and moved to the front of the line in the development lifecycle. Your QA team must also document their testing activities and results to ensure full auditability of the process and facilitate compliance.
During testing, the QA team ensures that the final software product meets the needs and intended use of the target end users and prepares it for validation in a real-world medical context, if necessary.
Preparing for deployment and maintenance
Once the software is given the final sign-off, your development team sets up the environment, configures the infrastructure, and applies the necessary security settings. If the new system replaces an old one, your developers also migrate data and integrate it with existing systems.
For release management, healthcare software is typically launched in phases, with rollback plans in place in case anything fails. Post-release, the software must be under the control of your development team to ensure that no performance or security vulnerabilities escape attention. As any regulatory requirement can evolve over time, your post-release maintenance schedule must also include periodic compliance audits and updates to keep your software up to date with the best industry practices.
Measuring success and improving
Unlike other digital products whose success is calculated based on straightforward criteria like user acquisition or revenue, the success of a healthcare software solution is a much more complex notion. The triumph of such solutions is associated with their ability to drive meaningful clinical outcomes, maintain regulatory compliance, and ease the load on providers.
To measure that success and have a fuller picture of ROI, healthcare companies should take a multi-step approach towards evaluating both qualitative and quantitative outcomes across clinical, operational, and user experience dimensions.
- Define the ‘what’ — Establish the context and scope of measurement that are tied back to the app’s intended purpose and goals. Identify the best sources to collect such data (e.g., direct user data like in-app analytics, patient-reported outcomes, compliance reports, etc.)
- Identify — Select specific KPIs that are aligned with business and customer priorities.
- Implement — Collect real-time, page-level performance data through integrated analytics tools and automated data collection.
- Monitor — Compare each metric against the benchmark and target values, identify areas where your metrics fall short, and build on the insights gained to continuously improve your solution.
Cost of custom software development in the healthcare industry
Medical software development companies don’t provide upfront prices for healthcare software simply because there are far too many variables. The cost of healthcare software development solutions is calculated based on a specific project scope and its unique challenges, including:
- The target development platform (mobile, web, etc.)
- The technology stack (software architecture, advanced technologies, etc.)
- The complexity of required features and functionalities
- Integrations needed with existing healthcare systems
- The extent of must-have security measures and data privacy protocols, and more.
Drawing upon our experience with similar projects, we've developed preliminary development cost ranges for different healthcare software categories:
| Healthcare software type | Estimated cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| Electronic health records (EHR/EMR) | $150,000 – $500,000+ |
| Telemedicine platform | $100,000 – $300,000 |
| Remote patient monitoring (RPM) | $120,000 – $350,000 |
| Healthcare CRM | $80,000 – $200,000 |
| Medical billing and coding software | $100,000 – $250,000 |
| Hospital management system (HMS) | $200,000 – $600,000+ |
| E-prescription (eRx) solution | $70,000 – $180,000 |
| Medical imaging and diagnostic software | $250,000 – $700,000+ |
| Patient portal | $60,000 – $180,000 |
| Medication management software | $50,000 – $150,000+ |
| mHealth app (wellness/fitness/chronic) | $50,000 – $150,000 |
Key trends to watch in healthcare software development
The unique and unprecedented challenges buffeting healthcare demand a significant restructuring of the industry. New technological solutions accelerate and enable that transformation, driving healthcare towards a more outcome-oriented future and evolving care models.
Artificial intelligence improves clinical and administrative workflows
In 2024, more than half of health system and health plan executives assigned AI an immediate priority, with 73% ramping up their investments in the technology. Among all areas of AI adoption, admin automation is the low-hanging fruit, as it offers fast and measurable wins with minimal data complexity. Ambient AI, agent-based tools, and LLMs have all become a part of this automation wave, relieving care teams of paperwork glut.
On the clinical side, point-of-care AI-powered decision support tools and diagnostic assistance solutions reduce the time to diagnosis, allowing physicians to focus more on direct patient interaction.
Generative AI enables self-service patient support
Today’s consumers are digital-first, even when it comes to healthcare. According to the 2024 Care Access Benchmark Report by Kyruus Health, more than one-third of all consumers are ready to abandon a provider that does not offer self-service tools, such as online scheduling and pre-visit questionnaires.
Generative AI solutions have stepped in to address this demand, bringing forth an innovative way to transform traditional, pre-programmed self-service options. Unlike scripted chatbots, generative AI chatbots, virtual health assistants, and gen AI companions can dynamically respond to more complex patient inquiries about symptoms, appointment scheduling, prescription refills, billing inquiries, and health information.
Predictive analytics shifts the focus of healthcare from treatment to prevention
Each year, the traditionally reactive U.S. healthcare system spends $4.5 trillion on chronic and mental health conditions. Proactive care management, spearheaded by predictive analytics solutions like clinical risk prediction tools and AI diagnostic assistants, helps identify health risks early and potentially bend the cost curve associated with these prevalent conditions.
By comparing data anomalies against known outcomes, predictive analytics solutions can calculate the risk score of a given patient with high accuracy. Healthcare providers can then engage with at-risk patients and offer proactive interventions to prevent health complications.
Remote care solutions reach older patients in their homes
Over 90% of U.S. adults aged 55 and older want to safely age at home, but a shortage of eldercare professionals makes this preference increasingly difficult to fulfill for both seniors and their families. Remote monitoring systems, combined with AI-enabled sensors, can keep an eye on senior patients and give caregivers peace of mind with fall detection, alert systems, and medication management.
For medical professionals, remote care systems serve as a source of real-time data on vital signs, activity levels, and potential emergencies like falls. Combined, this data gives care teams a fuller picture of a patient’s health outside of scheduled appointments.
mHealth applications maximize patient engagement and health outcomes
Once patients step out of the healthcare consultation, medical professionals have no control over their adherence to treatment plans, condition management, and lifestyle choices. mHealth applications support patients beyond the clinical setting, providing access to health information, monitoring tools, and behavior change support.
Medication reminder applications, chronic disease management apps, activity tracking platforms, and other mHealth applications help patients take control of their own care, improving engagement and equipping them with tools for effective and informed health management.
Transform patient care with our healthcare software solutions
Too often, healthcare innovators prioritize cutting-edge features over real-world usability and regulatory compliance. Designed with transformation in mind, these solutions often fall short in practice, failing to gain traction among end-users and playing a perennial catch-up game with regulatory bodies.
At Orangesoft, we develop healthcare software that draws a fine line between positive transformation and practical implementation. As a healthcare software development partner with over 14 years of experience, we help health tech businesses across the entire value chain to:
- Develop secure healthcare web and mobile applications in adherence to ISO 27001 practices and global or regional healthcare regulations, including HIPAA, the MDR, the FDA, and others.
- Create accessible designs that account for sensory, cognitive, physical, neurological, and age-related differences and build on the best accessibility practices outlined by WCAG, ADA, and the European Accessibility Act.
- Augment the capabilities of healthcare solutions with AI, gen AI, IoT, and AR/VR technologies.
- Customize off-the-shelf software for the last mile and set up integrations with existing healthcare ecosystems.
With over 300 projects in our portfolio, we have a calibrated delivery workflow that enables our team of 100+ developers to deliver on their promise and ship marketable healthcare products on time and on budget. Contact our team to get a custom estimate for your healthcare software solution.
