Medication non-adherence is a hidden epidemic that yet noticeably undermines patient health and puts an economic strain on healthcare. Polypharmacy patients, in particular, experience significant challenges in following the treatment regimen because of the complexity of managing multiple medications, each with its own dosing schedule and potential side effects.
Although unable to eradicate non-adherence completely, medication management software can become a convenient and low-cost intervention to support treatment compliance and mitigate the challenges associated with it. The potential of such software is corroborated by its demand: by 2029, the market volume of medication checker apps is expected to surpass $3 billion, up from $1.74 billion in 2024.
If you’re planning to venture into medication management app development, there’s a lot to take heed of. Orangesoft’s health tech development team has prepared a go-to resource for your company on how to approach such projects and develop a medication management app that keeps users accountable.
Four challenges solved by one medication management app
Medication non-compliance can occur due to multiple factors. Patients’ lack of involvement in treatment decisions, poor communication between the sides of care, fragmented care, and other events can easily overwhelm patients. Medication management tools can flip the script by simplifying complex medication regimens and offering direct communication channels with healthcare providers and pharmacists.
Medication errors
According to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), over 100,000 medication errors are reported each year, affecting around 7 million U.S. patients per year. While these can take place due to multiple reasons, medication management tools can address the following root causes:
- Prescribing errors — drug management systems notify users about potential drug interactions, therapeutic duplications, unnecessary polypharmacy, allergies, and contraindications.
- Prescription errors — a medication management app keeps both healthcare providers and patients on schedule regarding medication refills, dosage schedules, and appointments.
- Timing errors — personalized reminders reduce the risk of missed, late, or early doses, while medication tracking features prevent accidental overdoses.
- Prescription drug abuse — pill reminder apps offer clear information about medication usage, side effects, and potential interactions.
Poor adherence to prescriptions
More than anything, medication reminder apps help patients stay on track with their medication and monitor medication adherence across all types of medication and delivery methods. Calendar-based alarm reminders with specific dosages fit users’ unique regimens, helping them stay consistent and fostering accountability. Users can also integrate a voice assistant to send them spoken reminders.
If supplemented with AI and GPS, such apps can also remind users to take their medications only when they’re at home, optimizing reminder timing.
Additionally, such applications keep a personal log of a user’s medication history, analyzing taken and missed doses to calculate adherence rates and display them on interactive dashboards.
Polypharmacy
Chronic and older patients often see multiple physicians, each prescribing a new medication or changing dosages, which increases the risk of polypharmacy complications, including falls, kidney impairment, frailty, and hospitalization.
Medication management systems can reduce the chance of overmedication, oversedation, and other issues caused by polypharmacy:
- Centralized medication lists — apps keep an inventory of all medications filled anywhere, including over-the-counter medications, along with intake schedules and dosages; suggest potential medication adjustments or deprescribing options.
- Drug interaction checkers — a drug management system identifies potential interactions between medications.
- Duplicate therapy identification — the app checks for therapeutic duplication by comparing medication classifications within the ATC system.
- Dosage schedule optimization — a medication management app can optimize dose-schedule regimens to minimize toxicity.
- Medication photo logging — the app allows users to take photos of their medications and see the difference between them.
Limited patient engagement
Far too often, patients feel like just another number, disconnected from their healthcare providers and left out of the loop regarding their own treatment plans. Around 25% of patients are unaware of the next steps around their prescription medications, and 29% don’t understand how to manage their medical condition right after a healthcare visit.
Medication management apps can pick up where healthcare providers left off, giving patients the tools to self-manage their prescriptions and breaking down communication barriers. These applications can integrate with electronic health records to allow providers to track fill behavior over time and across multiple outlets — and suggest potential medication adjustments. Many applications also include secure messaging channels, allowing patients to send messages directly to their healthcare provider or pharmacy.
Patient education features such as educational content, videos, and interactive quizzes encourage patients to take an active role in their treatment regimens and address informational gaps regarding the potential side effects and proper storage of prescribed medications.
Types of medication management apps
All medication tracking solutions can be divided into two main categories: those geared toward patients and general users and those designed specifically for healthcare professionals.
Personal medication management solutions
Personal medication management solutions are simple and easy-to-use software that helps individuals stay on track with their treatments. These systems include the following app subcategories:
| Pill reminder apps | Allow users to set time-based or dose-specific reminders to ensure timely medication intake and refills. |
| Medication tracking apps | Enable users to log medication intake, track overall health, and get information about prescriptions; can alert caretakers when refills are necessary or in the case of missed medications. |
| Pill identifier apps | Help users identify the purpose, dosage, and potential side effects of prescription drugs and over-the-counter medicines. |
| Condition-specific medication management apps | Cater to individuals with specific health conditions, including chronic diseases, mental health issues, and others. |
Professional medication management tools
Designed with physicians, nurses, and pharmacists in mind, these tools help healthcare providers manage medication administration and make sure no medication error slips through the cracks.
| Medication administration software (eMAR) | Specific component of an EHR system that delivers up-to-date data on patients’ medications and helps nurses manage medication administration. |
| Medication reconciliation tools | Allow healthcare providers to compare a patient's current medication regimen against a medical record to identify discrepancies. |
| Medication management platforms (MMPs) | Keep tabs on the flow of medicines and medical devices and automate their logistics; streamline medication dispensing and administering. |
| Pharmacy management software | Designed specifically for pharmacies, automates prescription management, inventory control, billing, patient data tracking, and drug interaction checks. |
Five popular examples of medication management apps
Before you head right into medication management app development, it’s essential to size up your competition and spot unaddressed opportunities. We’ve done part of this groundwork for you.
MediSafe
Billed as the leading medication engagement platform, MediSafe helps users and their family members keep track of their medicines and refills, supporting complex regimens. MediSafe is also a clinically validated platform that provides a direct digital channel between support teams and their patients, automating the document submission process.
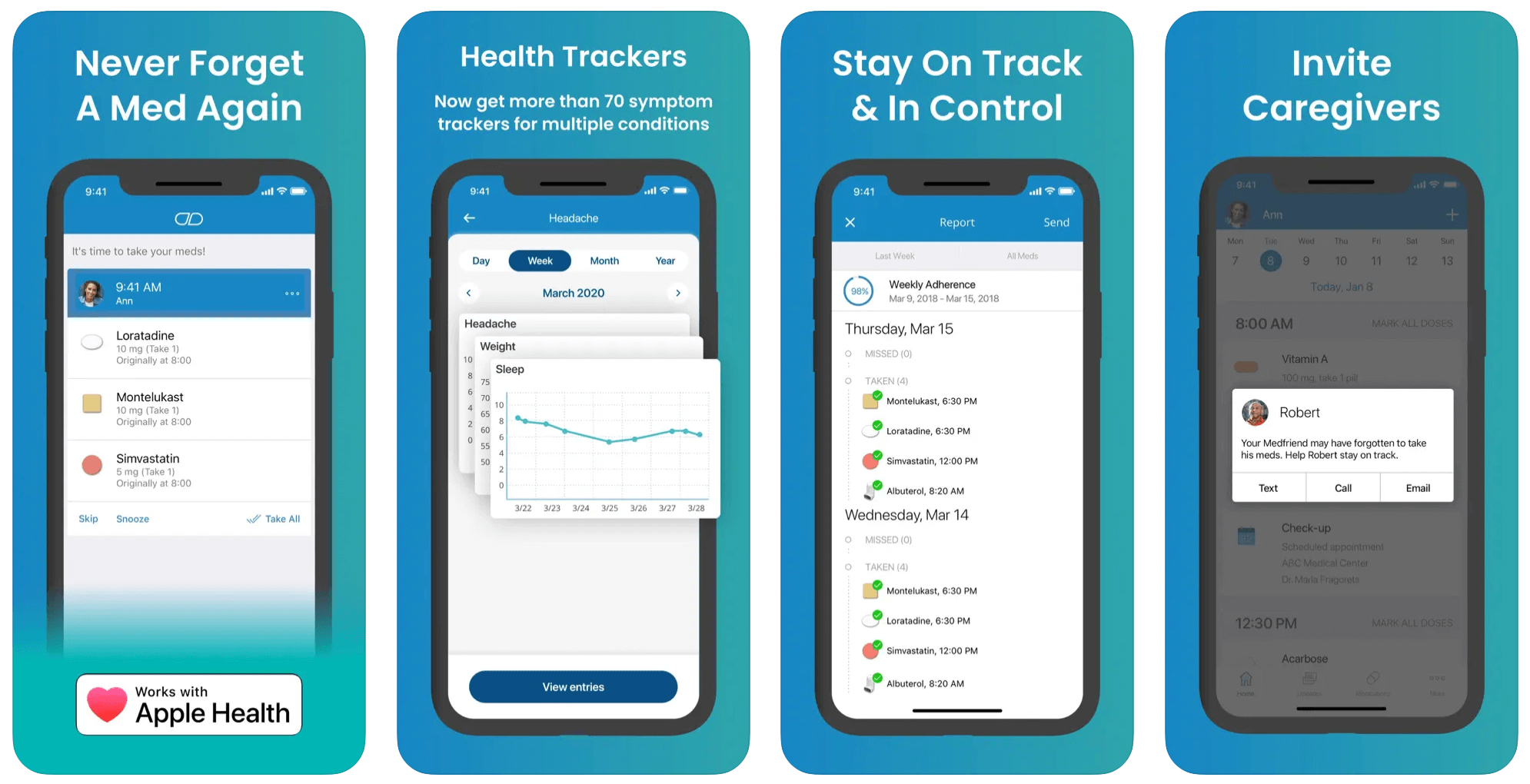
The application can also review each patient’s medications, including OTC and supplements, and indicate drug interactions. The app exercises an omnichannel approach and allows users to interact with it wherever they are, including web, mobile, and wearables, thus syncing data across multiple devices. Today, Medisafe caters to over 10 million users.
MyTherapy
This application allows users to create a medication list and set reminders to keep medication intake on schedule. Along with medication tracking, MyTherapy integrates a patient diary, allowing users to record their vitals, doctor visits, and symptoms. Users can get notifications directly on their wearable devices, and the app can automatically record medication intake based on device usage patterns.
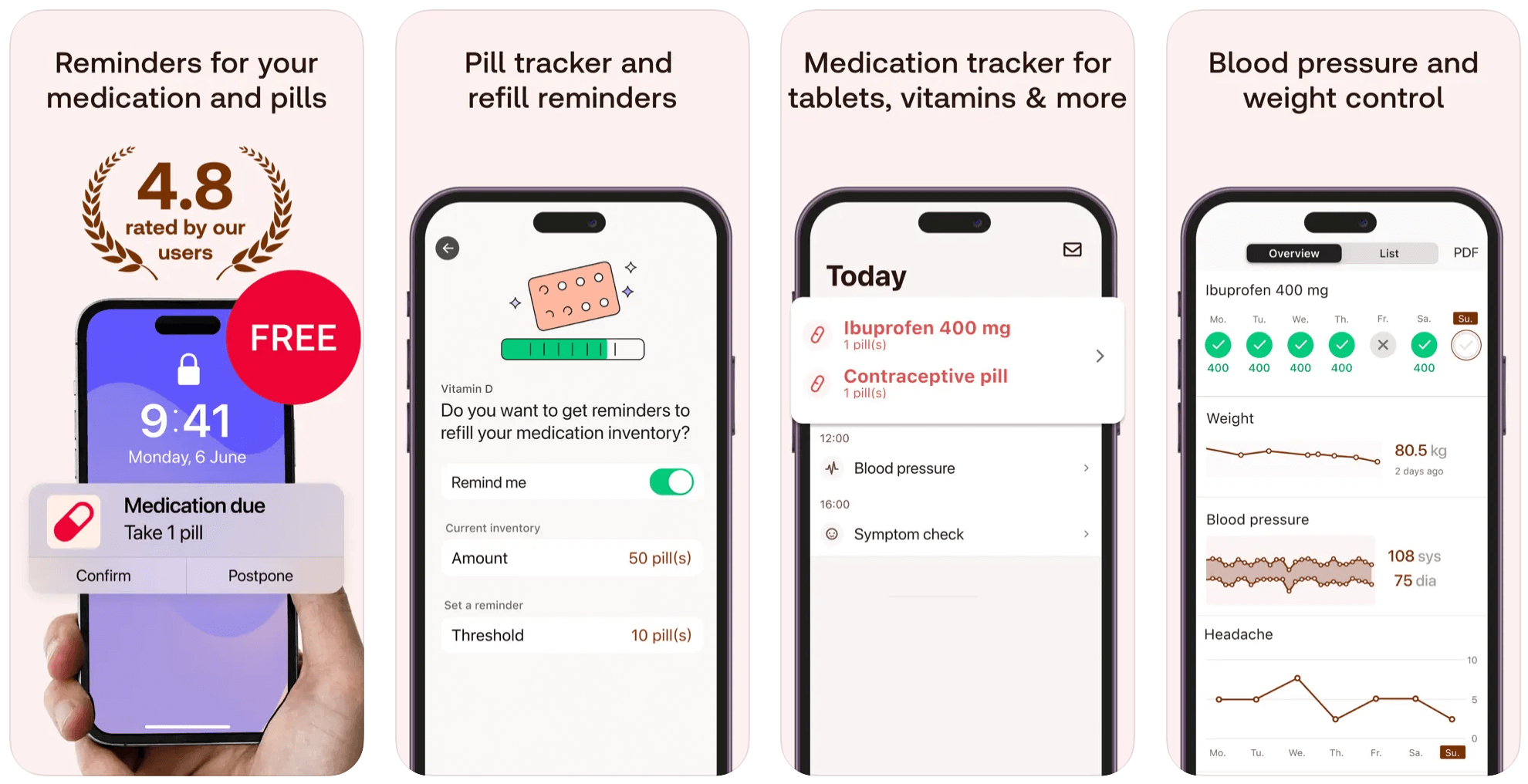
This application is also convenient for caregivers and doctors, as users can share their health reports in PDF format, allowing for more informed care.
EveryDose
Designed specifically for family caregivers and seniors, EveryDose simplifies the complexity of drug intake tracking by offering custom reminder scheduling. This medication reminder app also integrates educational resources, flags drug-to-drug interactions, and delivers a comprehensive view of users’ intake behavior that can be shared with caregivers.
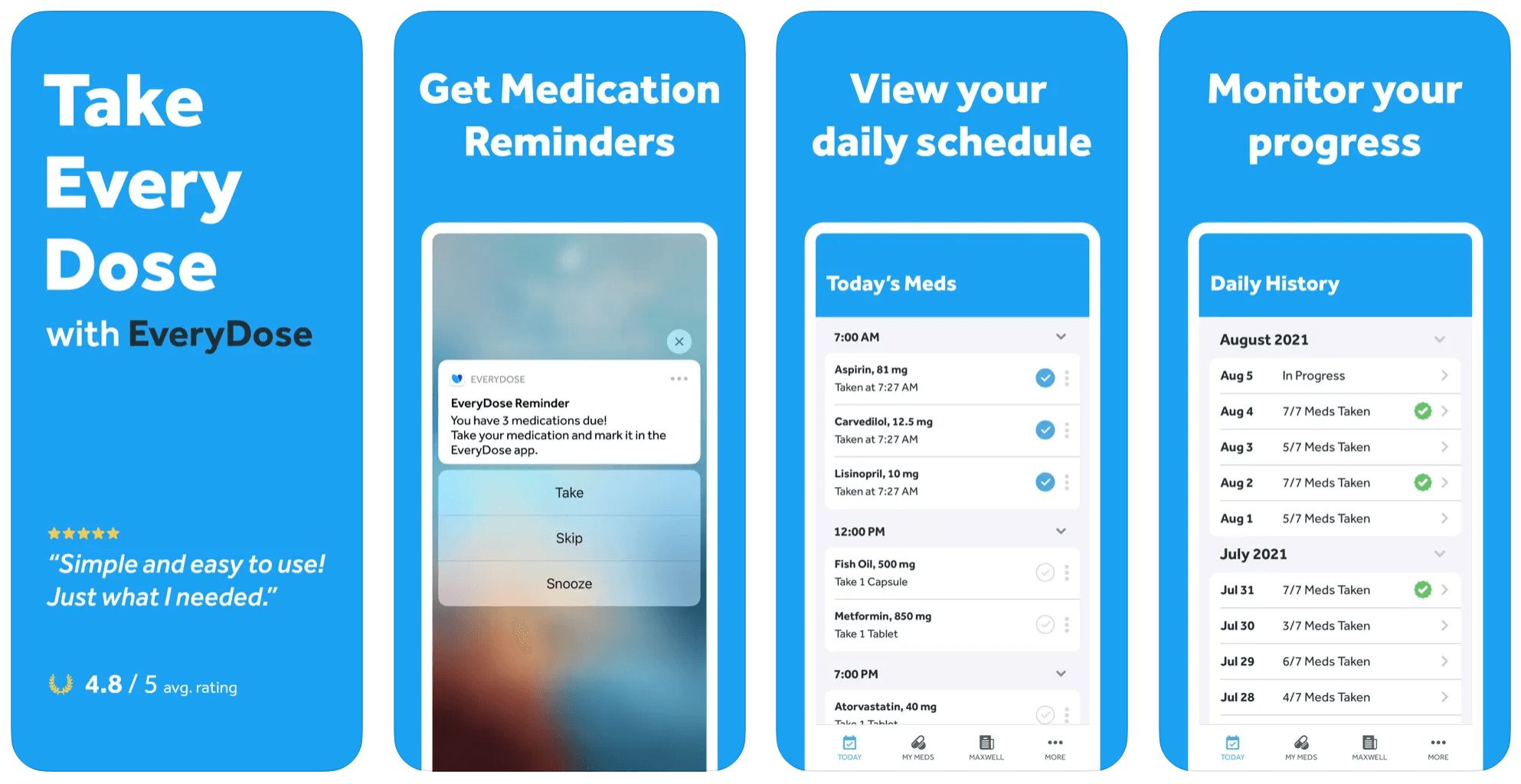
Premium users can log vitals, manage medications for the whole family, and get access to detailed charts and analytics. The application also integrates an online store where users can purchase lower-cost generics online. According to the app, its users engage with it over 100 million times a month.
Dosecast
With over 1 million downloads, Dosecast is a trusted, clinically validated medication management app used by U.S. military pharmacies. Dosecast serves all sides of care, including patients, pharmacies, payors, and healthcare providers. Designed to bridge medication management gaps, Dosecast includes a wide variety of features such as outpatient pharmacy automation, intake process automation, AI- and video-observed therapy, secure messaging, and more.
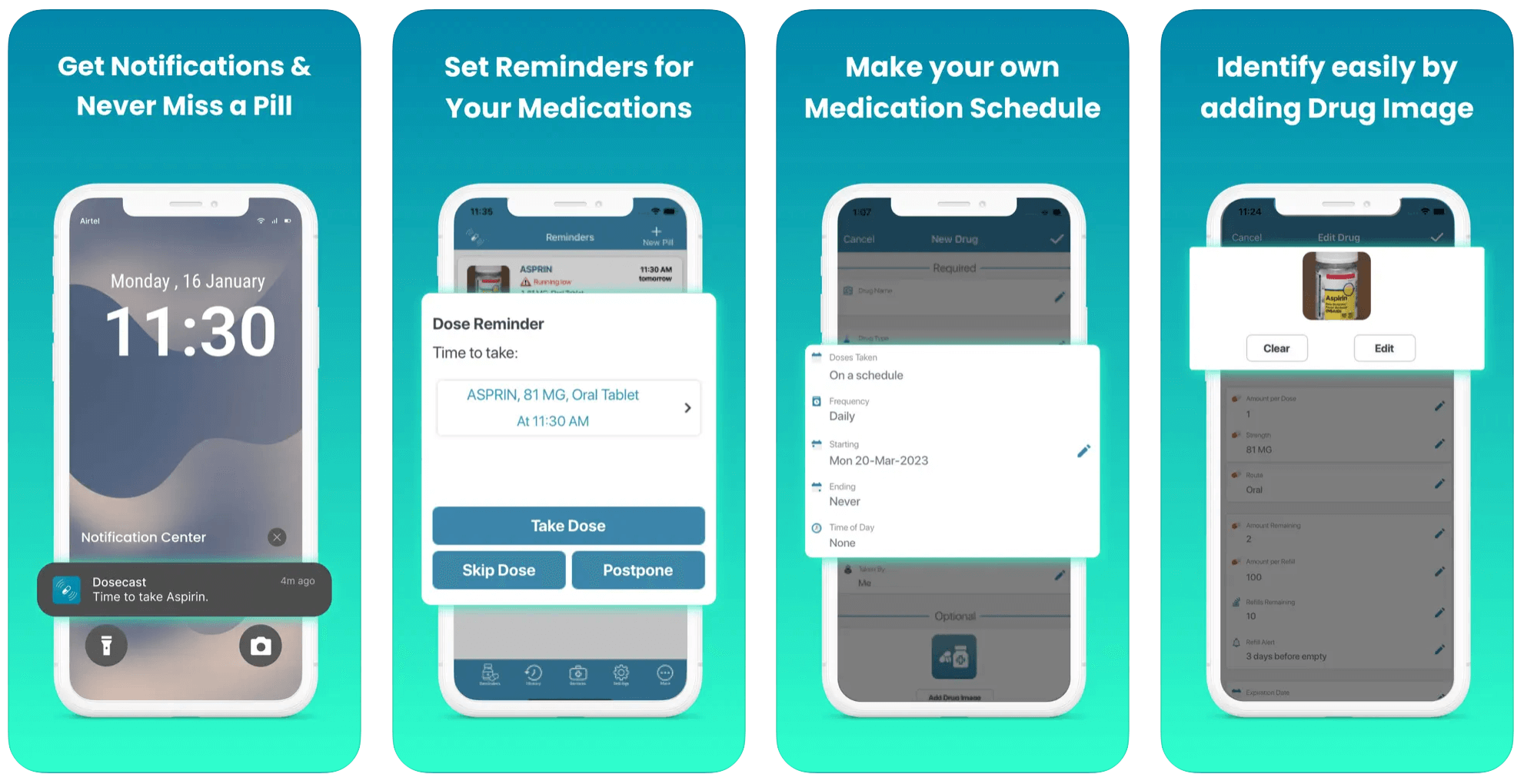
The application also adjusts to users’ schedules, tracks remaining quantities, sends refill reminders, and shares medication adherence data with healthcare professionals.
Pill Reminder
Pill Reminder is a user-friendly medication reminder app that allows users to create any type of recurring reminders. The application also tracks medication levels and notifies users when they’re running low on supplies. Pill Reminder has offline capabilities, allowing users to monitor their medication schedule wherever they are.
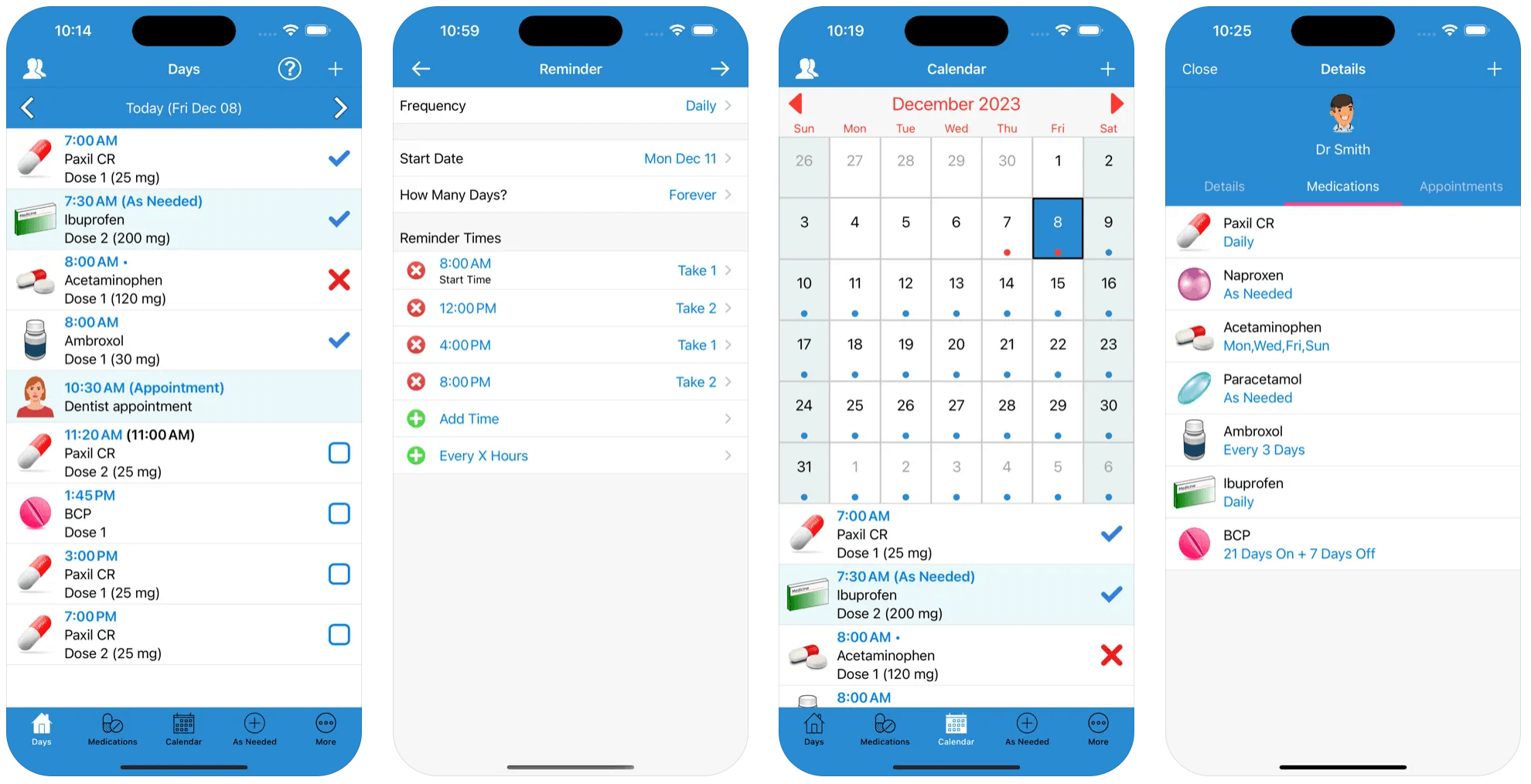
Besides, the application allows users to keep track of symptoms to identify side effects and the necessary regimen adjustments.
Medication management app development process: 7 steps towards high-value user experience
Healthcare software development, including medication management apps, requires a holistic, 360-degree approach to take into account all technical, legal, and ethical considerations. In particular, app developers must comply with strict regulations, implement specialized data privacy and security measures, and prioritize user experience to create safe and effective solutions. Here’s how it goes at Orangesoft.
Product discovery
Savvy companies use product discovery to create a blueprint for the entire development process and ensure that the final product meets user needs, market standards, and business goals.
Your development team kicks off the process by performing thorough market and competitor research to corroborate your application idea and identify untapped market opportunities that your application can address. By analyzing competitor products, developers can also determine core features for your medication management system and prioritize their development to create a competitive advantage.
In-depth user research allows the team to develop detailed profiles of your target users, user flows, and information architecture to inform development efforts and solidify core features your audience needs to reach their goals.
Based on the insights obtained from market and user research, the design team develops wireframes that outline the basic layout of your application. Wireframes help project stakeholders experiment with various visual styles and iterate on the spot.
Research compliance and security requirements
If your medication management app handles Protected Health Information, such as patient names, medical conditions, medication lists, and treatment plans, it is subject to healthcare regulations such as HIPAA, FDA, NCPDP, FTC, CFR 42 Part 2, and EU MDR (for medical devices). That’s why you need to first identify the types of personal data your application handles and then determine relevant regulatory requirements.
As compliance typically mandates that your app integrate strong security measures, you should also determine the specific data security measures, such as access controls, encryption, and data archival and clearing mechanisms. In addition to data security mechanisms, you should also plan explicit user consent forms that outline how users’ data will be used, stored, and shared, along with the policies for data retention and deletion.
Development planning
When all the groundwork is finished, your development team determines functional and non-functional requirements and transforms them into software requirements specifications (SRS). At the same time, developers decide on an optimal system architecture, considering your technical limitations (if any), performance requirements, and scalability.
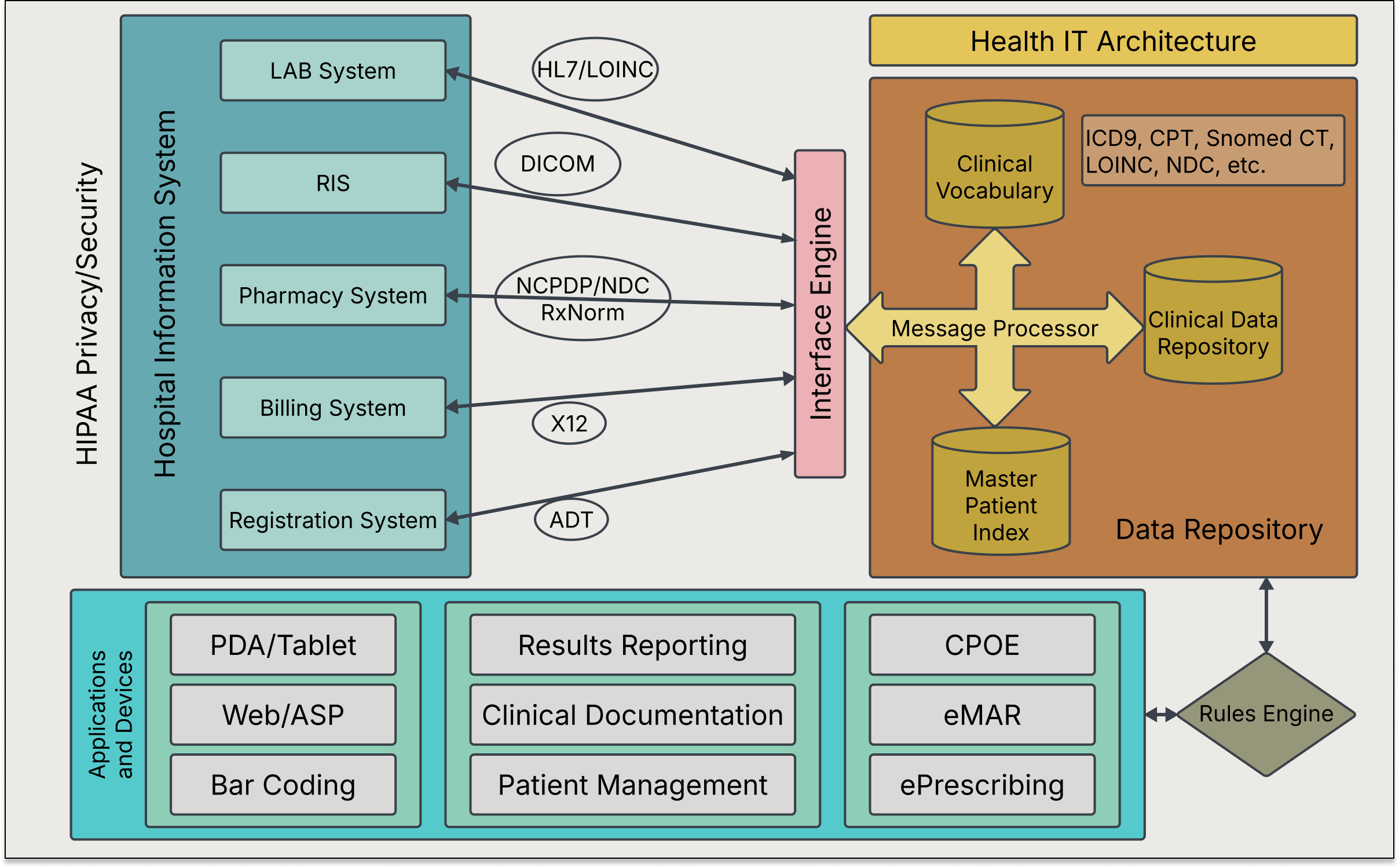
If you plan to integrate your medication tracking solution with healthcare systems (e.g., EHRs, pharmacy management systems), telehealth platforms, wearable devices, or any other solutions, your development team designs the necessary integration components.
At this stage, your team also creates a detailed project plan that outlines timelines, milestones, resource allocation, and a budget.
Application design
Many drug management applications are designed for the general population, paying no heed to the unique needs of older adults and users with disabilities. So, when transforming wireframes into prototypes, make sure your UX/UI team designs your application to be both good-looking and accessible. Font adjustment capability, compatibility with assistive technologies, high-contrast color schemes, and other accessibility features should supplement your application design.
Our UX/UI design team follows WCAG and ADA guidelines to ensure your medication management application breaks down barriers to medication adherence. We also conduct usability testing with older adults and users with accessibility barriers to validate and optimize the accessibility features we’ve added.
After app prototypes are tested by real users and approved by your team, the design team prepares final design layouts and hands them off to the development team.
MVP development
Minimum viable product development allows you to optimize your development budget by focusing only on the necessary features your development team prioritized earlier. Developers build up the core functionality of your product iteratively, implementing necessary security features. Keep in mind that the development process should adhere to industry standards such as ISO 27001 so you can demonstrate your commitment to information security and compliance.
One of the main regulatory compliance requirements is to have a contingency plan in place. That’s why your development team also implements backup mechanisms and disaster recovery.
At this stage, tech specialists also develop integration logic based on the selected integration method.
Test for usability and compliance
The quality assurance and testing process happens in tandem with the development to test each deliverable as soon as it’s built. The QA team uses a combination of automated and manual testing to check the functionality, performance, security, and accessibility of your application.
When the final solution is ready, the team double-tests it for usability and revises the project documentation to ensure compliance.
Launch and further updates
Once you obtain the necessary certifications, the development team rolls the app out to the target audience. If necessary, we can opt for a soft launch to get early feedback and iterate before a full-scale release.
After the application rollout, our development team closely monitors the product, resolving bugs, keeping it up-to-date with OS updates, and delivering timely security patches. User and stakeholder feedback gathering is another salient post-launch activity that requires dedicated efforts from your team. By collecting and prioritizing it, you can plan further improvements for your product.
Key features to include in your medication management app
Medication adherence requires that “five rights” be met, including the right dose, medication, patient, time, and route. While the last element might require physical actions and clinical expertise, the rest of the four can be covered with the following features.
Secure user authorization
Whenever a user tries to access the system, your medication management app must offer multiple measures that guide against identity theft and unauthorized access. The following authentication measures make the backbone of medication management software:
- Two-factor authentication — a security measure that requires users to provide two forms of identification (passwords, codes, email, biometric authentication).
- Strong password requirements — users must set unique passwords with a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters, plus regular password changes.
- Session timeouts — users are automatically logged out after a period of inactivity.
- Role-based access controls — users (patients, caregivers, healthcare providers) are granted specific permissions based on their role.
User profile
User profiles contain personal user information that helps the app personalize its features and content to meet the unique needs of each user. Along with basic demographic information, profiles usually include the following data:
- Medical history — the app allows users to input information about their medical conditions, allergies, etc.
- Medication list — users can create and manage a list of their current medications, including dosage, intake frequency, instructions, and refill information.
- Emergency contacts — users can store emergency contact numbers to be notified in case of an emergency.
- User preferences — the app’s looks, notifications, and other functionalities can be customized to the users’ preferences.
Medication reminders
Elderly people, individuals with complicated pill regimens, or those grappling with general forgetfulness will find this feature beneficial, as medication reminders help users adhere to their med timetable, no matter how complicated it is. Medication reminders tell users what to take, when to take it, and when to reorder. They can be set for each medication, specifying the exact time, date, and frequency.
Here’s what to consider when implementing this feature:
- Make sure your medication management app can send various types of reminders, such as push notifications, emails, or text messages.
- The application should be able to get through to the user even if the device is in sleep mode or low battery.
- The app should leverage the user’s location information to automatically adjust to different time zones.
- Integrate accessibility features, such as voice commands, large fonts, and color-coding, to ensure the reminder is clear to all users.
Pill identification and dosage instructions
Whenever a user finds a stray pill in their cabinet or mixes up medicines by mistake, the medication management app can help them out by telling exactly what pill the user has on hand — by its shape, color, and imprint code. The application cross-references whatever identifier the user inputs with a database of medications to identify possible matches.
Many medication management apps also offer medication detection, meaning the app integrates techniques like image recognition and machine learning to identify pills from photos.
Once the app picks out the medication, it can provide detailed drug monographs customized based on the user's specific health condition and medical history. To do that, your app needs to integrate with third-party databases or APIs such as FirstDatabank, MedlinePlus, Lexicomp, Micromedex, and others.
Dosage tracker
This feature helps users stay on top of their regimen by recording the exact time and day of the user’s last dose. Typically, apps offer easy-to-use options for medication intake logging, such as simple checkboxes or a more detailed log.
To ensure users’ safety, the application should trigger overdose prevention features, such as visual cues, audible warnings, and/or haptic feedback when a user’s medication intake nears a dangerous level.
Some medication tracking applications also enable users to share their adherence data with healthcare providers and caregivers on an ongoing basis and in case of emergency.
Prescription refill reminders
Automated refill reminders ping users when their medication supply is running out — but well in advance of the actual refill date. To calculate refill dates, medication tracking apps usually analyze prescription information, including dosage and refill quantity.
Some applications also sync with pharmacy systems to source real-time data about prescription status and refill availability, as well as to send automated refill requests to the pharmacy.
Drug interaction checker
By folding this feature into the app, you allow it to flag potentially unsafe combinations of prescription medications, over-the-counter drugs, and herbal supplements and send drug interaction warnings whenever such a combination is detected. The application should also factor in the user’s data, such as age, weight, and underlying health conditions, to run more nuanced interaction assessments.
Symptom and health tracker
Tracking the effectiveness of treatment is essential for physicians to truly understand whether the prescribed medication is working or if the patient’s regimen needs adjustments. Symptom trackers can take over this task by monitoring users’ health status, including symptoms, side effects, and other relevant vitals such as blood pressure, blood sugar, and others.
Users can track symptoms and their health data manually — through symptom checklists, rating scales, and free-text entry — or leverage the integration with wearables to have this data put down automatically. Based on the health data, the app can also provide personalized recommendations, such as medication dosage adjustments or consultations with a healthcare provider.
Caregiver notifications
Medication management apps can notify caregivers or family members via push notifications, email, or text messages when:
- The patient misses a dose;
- The patient has been inconsistent in their medication adherence;
- The patient has recorded adverse symptoms or side effects;
- There’s been an overdose risk or emergency situation detected.
Along with algorithm-based monitoring, the app can set such alerts based on predefined thresholds tailored to specific clinical guidelines, expert recommendations, and user-associated factors.
Integration with EHR
By setting up a direct link between a medication management app and electronic health records, you enable the app to:
- Pull patient medical data, such as current medications, medical history, allergies, and more directly from an EHR system;
- Reflect changes in medications, dosages, and prescriptions in real time;
- Provide dosage recommendations based on the patient's medical history and current medications.
- Offer a secure messaging platform for communication with healthcare providers and in-app appointment scheduling.
Keep in mind that this integration is possible only if your application complies with FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) data exchange standards.
Engagement features
Paradoxically, in order for these medical apps to improve medication adherence, users have to keep them close at hand. The following engagement features can help your application stay top of mind and keep users hooked:
- Gamified features — rewards, badges, points, and progress tracking make the process more fun, encouraging users to stick to their medication regimen.
- Educational resources — medication information and health tips help users understand the reasons behind their medication regimen and highlight the potential benefits of medication adherence.
- Social features — community forums and peer-led support groups provide a safe space for individuals to share their experiences.
Comprehensive progress and adherence reports
Medication management applications hinge on self-monitoring, putting users in charge of tracking their medication intake. Visual summaries and reports are instrumental in passing the data on medication adherence, health metrics, and treatment progress to end users.
The clearer, simpler, and more accessible the in-app visualizations are, the faster and easier it is for users to gain valuable insights into their medication regimens.
Summaries can also be shared with caregivers and healthcare providers for more informed decision-making.
Six medication management app market trends to watch in 2026
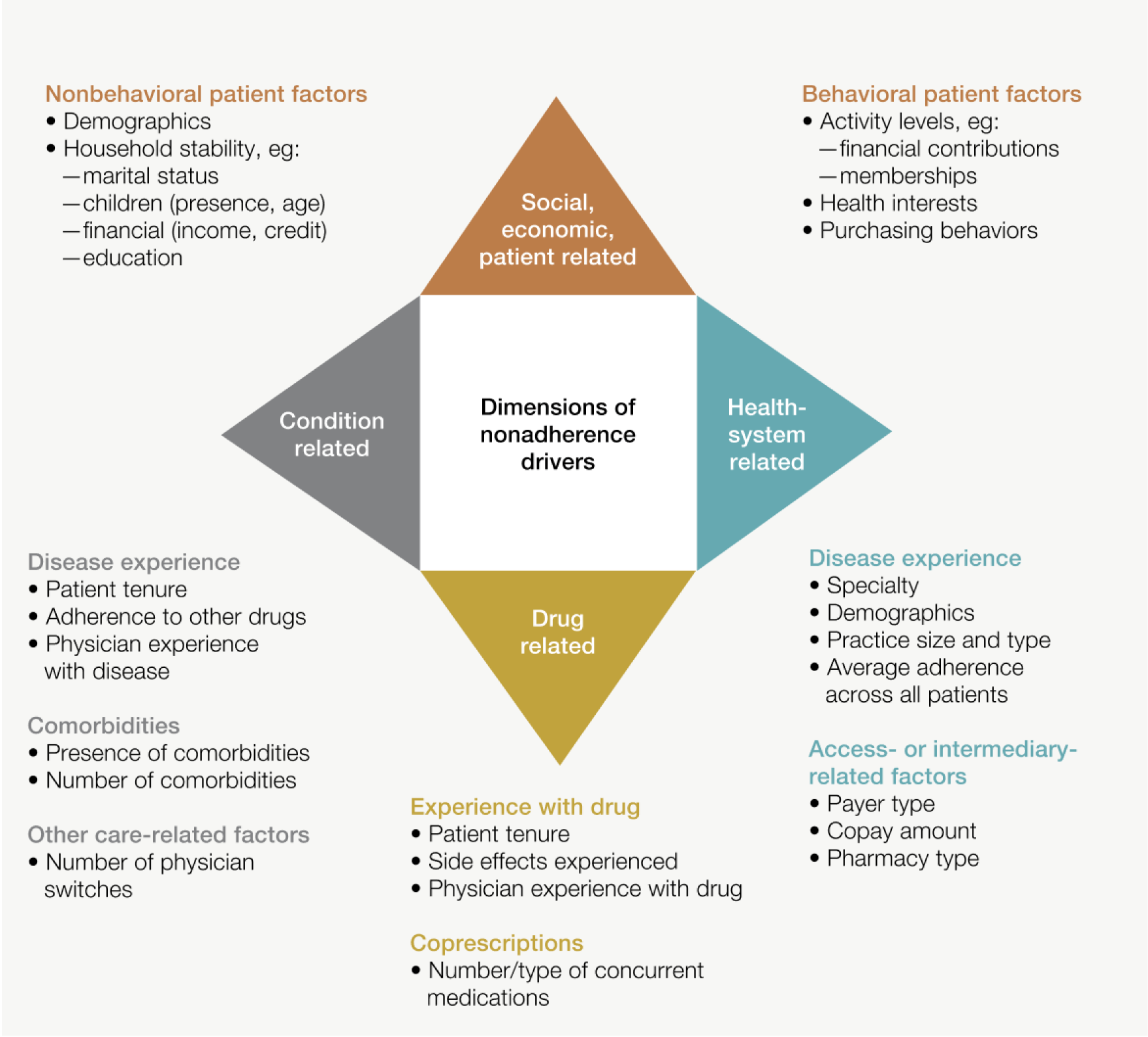
Healthcare providers traditionally stuck to a lack of interventions, such as follow-up consultations and general warnings, to encourage medication compliance. Now, they have shifted to a more holistic approach, considering not only adherence rates but also contributing factors such as behavioral patterns, demographics, and unique lifestyles.
Telehealth and remote patient monitoring
Telehealth and remote patient monitoring (RPM) have brought patients closer to healthcare providers than ever. Along with keeping care providers connected to the most vulnerable patient cohorts, the powerful combo of telehealth/RPM platforms and medication management systems can:
- Enable physicians and pharmacists to connect directly with patients, optimize medication use, and improve the “last mile” of population health at the individual level.
- Facilitate medication tracking by using RPM devices to gather real-time data on dosage intake and timing.
- Help doctors spot adverse drug reactions early through continuous monitoring of vitals.
- Provide data-driven insights to better inform and fine-tune treatment plans.
- Reverse the non-adherence trend through regular check-ins between patients and providers, proactive interventions, and flexible scheduling.
How to leverage this trend: Design your medication management apps to be integration-ready with telehealth and RPM devices. To enable integration, they must be compatible with standard data exchange formats, such as HL7 FHIR, align with standardized communication protocols, and implement secure data exchange protocols.
Integration of artificial intelligence and data analytics
Artificial intelligence is the missing link to effective medication management and successful drug-tracking solutions. Without it, raw data remains just that — raw. Contrastingly, unrivaled analytics and predictive capabilities of AI enable patients and providers to make sense of the complex interplay of factors impacting medication adherence, drug interactions, and treatment outcomes.
Providers can make use of AI to:
- Identify patients who are at high risk of near-term hospitalization due to polypharmacy issues — through adverse drug reaction prediction, patient profiling, and medication adherence monitoring.
- Enhance prescription fill history to improve medication reconciliation and track adherence.
- Offer personalized medication recommendations, including regimens, dosages, and administration schedules, based on individual patient data.
- Predict potential adherence issues by analyzing medication history, demographics, and social determinants of health.
- Identify unnecessary drugs for polypharmacy patients using large language models as a clinical support tool.
Artificial intelligence adds a few layers of personalization for patients, adjusting medication reminders to their unique lifestyles, facilitating drug interaction checks, and helping them understand medication adherence trends.
How to leverage this trend: Use reliable data sources, such as electronic health records, claims data, and patient-generated health, as the foundation for your AI models. Data anonymization and other data security best practices are crucial for protecting patient privacy and complying with data regulations.
Focus on mental health and chronic disease management
Today, around 133 million Americans live with at least one chronic illness, while about 1 in 4 U.S. adults experience a diagnosable mental disorder. Considering the frequent coexistence of chronic and mental health conditions with complex medication regimens, effective medication management solutions should account for the unique needs of users grappling with such conditions.
Taking a multifaceted approach to medication management requires your solution to:
- Integrate condition-specific features such as mood trackers, symptom diaries, goal-setting tools, and others.
- Provide condition-specific educational resources.
- Consolidate data from wearable devices to deliver a more comprehensive look at the user’s health and well-being.
- Give the option to receive silent notifications, which is important if users are afraid of social stigma.
- Offer immediate access to crisis hotlines and emergency services.
How to leverage this trend: Besides integrating the features we mentioned above, make sure to include the aforementioned patient groups in your user research.
Voice and chatbot assistance for user support
Part of the reason why individuals slack off on medication is because they don’t have clear and accessible information on their prescriptions. Voice-activated chatbots can partially solve this problem by addressing the questions users might have about their medication regimens or drug interactions and offering personalized support. Along with 24/7 support, chatbots send personalized reminders and check in about users’ medication adherence.
Compared with text-based chatbots, voice-based conversational interfaces are more accessible to older people and users with visual impairments, motor disabilities, or cognitive limitations. That’s why we recommend speech-enabling your chatbots if you plan on integrating one.
How to leverage this trend: The accuracy of chatbot responses is directly linked to the quality of training data. Make sure to feed the chatbot with clinical data and enable easy access to real-time data, patient insights, and user interaction data.
Integration with wearable devices
Over 34% of Americans now own and use a wearable device. Although traditionally associated with fitness and wellness, wearables can also provide patients, doctors, and pharmacists with a higher level of medication oversight. By tracking heart rate, sleep patterns, activity levels, skin temperature, and other metrics, wearable devices can help assess the long-term impact of a certain medication, providing insights for necessary treatment adjustments.
Unlike manually input data, wearable insights are not spaced, meaning that both patients and providers get an unbiased, real-time view of the treatment progress.
How to leverage this trend: Leverage application programming interfaces (APIs) provided by the wearable device to enable the application to access relevant health data.
Concerns to hurdle to ensure an Rx for your app success
The complex and sensitive nature of healthcare data, strict regulatory requirements, and the imperative for precision make medication management app development a challenging endeavor. Here are the core considerations you need to take care of before entering the market.
Data privacy and security compliance
For medication management apps, the true challenge of regulatory compliance is not the compliance itself but a lack of specific, comprehensive security guidelines and regulations that govern the development of such applications. These gaps in regulations translate into unclear data security standards and increased risks both for companies and users.
Regulatory compliance requirements differ by country and the specific functionality of the app. For example, in the US, medication management applications typically need to comply with HIPAA, GDPR, FDA, NCPDP, FTC, and CFR 42 Part 2. In the UK, medication management apps are subject to the MHRA regulation, with medical device apps requiring UKCA or CE marking. The European medication management app market is regulated by GDPR (plus the ePrivacy Directive) and MDR.
Whatever the regulation is, your application requires a combination of robust data security mechanisms, such as data encryption, access controls, data minimization, strong authentication, and other measures, to keep sensitive data secure. Regular ISO 27001 and ISO 13485 audits can help keep your app up to the mark in terms of security and quality standards.
Accuracy and reliability of information
Medication management apps are considered to reduce medication errors, but when they rely on incomplete and outdated data, the effect is reversed. Incorrect data inputs — such as a patient keying in the wrong dosage, errors in cross-referencing drugs, or dated drug information — can lead to dire consequences, potentially harming one’s health.
To make sure your medication management app operates on accurate data, you need to take into account the following considerations:
- Integrate your application with trusted medical databases such as Micromedex, Clinical Pharmacology, or Lexi-Comp and introduce regular updates to keep up with the latest drug information.
- Blend validation checks into the app to avoid errors in the user’s data entry.
- Make use of cross-referencing to compare drug information across different sources.
- Sync the application with EHR to automatically collect popular health data.
- Double down on training and retraining your AI models to accommodate changes in data.
Compatibility and integration with healthcare systems
To unlock two-way data sharing between patients and providers, your medication management app must speak the same language as healthcare systems. However, medical IT infrastructure is notoriously known for its maze of different data standards, formats, and APIs, which makes integration a tall order for medication tracking app providers.
To avoid integration challenges down the road, gear up your app’s data model for interoperability from the very beginning by aligning it with the HL7 FHIR standard. Determining specific API integration points will also help you prepare for the integration and make the necessary adjustments in your system’s architecture.
Ethical considerations
When healthcare data is used as capital outside a strictly medical context, specific ethical concerns crop up. The lack of transparency around in-app data handling, insufficient informational self-determination, and potential misuse of sensitive health data dampen users’ enthusiasm regarding any mHealth apps.
To develop trust with users and guarantee the ethical soundness of your solution, remove any ambiguity around the in-app data handling practices by integrating a comprehensive data policy. Also, you must obtain express consent from users before processing their health data.
As for AI and data analytics models, make sure your development team sticks to the principles of ethical AI, prioritizing data responsibility and privacy, explainability, inclusion, and other core ethical tenets.
How much does it cost to develop a medication management app from scratch?
The cost of developing a medication tracking solution depends on many factors, from the application’s type to its complexity and the number of integrations. It’s impossible to price a project without analyzing it first. Based on our previous experience, Orangesoft’s team has put together a table with ballpark estimates for a custom medication management solution. This estimate includes the time required for development, testing, and project management.
| Features | Average time, hours | Average cost, $ |
|---|---|---|
Patient application | ||
| Authentication | 73 | 3,643 |
| Medication list management | 109 | 5,465 |
| Medication reminders | 106 | 5,299 |
| Dosage tracker | 50 | 2,484 |
| Prescription refill reminders | 26 | 1,325 |
| Symptom and health tracker | 79 | 3,974 |
| Progress and adherence reports | 176 | 8,777 |
| Caregiver | 70 | 3,478 |
Caregiver application | ||
| Authentication | 23 | 1,159 |
| Monitoring | 93 | 4,637 |
| Notifications | 43 | 2,153 |
| Patients | 30 | 1,490 |
General | ||
| Architecture | 60 | 2,981 |
| Server interaction and API | 53 | 2,650 |
| Database | 66 | 3,312 |
| DevOps | 109 | 5,465 |
| Total | 1,166 | 58,291 |
Solving the problem of medication adherence with a dose of tech
While a spoonful of sugar helps the medicine go down, a medication management app helps the medicine go down right and at the right time. From the right set of features to accessible design and responsible data use, there’s a lot that goes into developing such solutions. Having a trusted tech partner on board will help you eliminate the guesswork around medication management app development and dodge the common challenges associated with such projects.
Orangesoft has over 13 years of experience in health tech development and a track record of over 300 projects. Contact us, and we’ll guide you through the entire development process, hand-in-hand.
