We won’t be the first to point it out: traditional healthcare services are in a rough spot right now. Buffeted by the increasing costs of care, staff shortages, and access disparities, the healthcare industry is struggling to deliver on its promise of patient welfare. Although unable to completely fix all the systemic issues, healthcare apps have the tangible potential to bridge critical gaps in the industry.
There’s a lot to healthcare mobile app development if you want your product to be compliant, fully accessible, and highly valuable. We’ve been in health tech since 2011 and decided to put all that experience together in an all-in blueprint.
Healthcare app market overview
Almost 73% of U.S. adults sour on the healthcare system, as the latter fails to meet their needs in at least one way. This dissatisfaction is the big ‘why’ behind the burgeoning healthcare app market.
- The global healthcare mobile application market size was valued at over $114 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 45.2% from 2025 to 2030.
- In the United States, 43% of the population used health apps in 2024.
- By the end of 2025, the global in-app purchase revenue of health and fitness apps is slated to surpass $4 billion, more than 100% growth over the past five years.
- In 2024, health tech companies raked in $25.2 billion in venture capital globally.
The adoption of healthcare applications is expected to pick up more steam due to the focus on preventive care and self-management that, combined, help address the growing rates of chronic diseases.
Trending types of healthcare apps in 2026
Your roadmap to healthcare app development largely depends on the type of healthcare app you’re building. Below, we’ve put together a quick look at the healthcare apps patients and healthcare professionals use the most today.
Telemedicine applications
Designed to address the scarcity of healthcare professionals and accessibility barriers, telemedicine apps offer remote consultations, diagnoses, and follow-up care.
Regardless of the healthcare area, all telemedicine apps include video and/or audio consultations with HIPAA-secure messaging, appointment management, e-prescriptions, and payment integration.
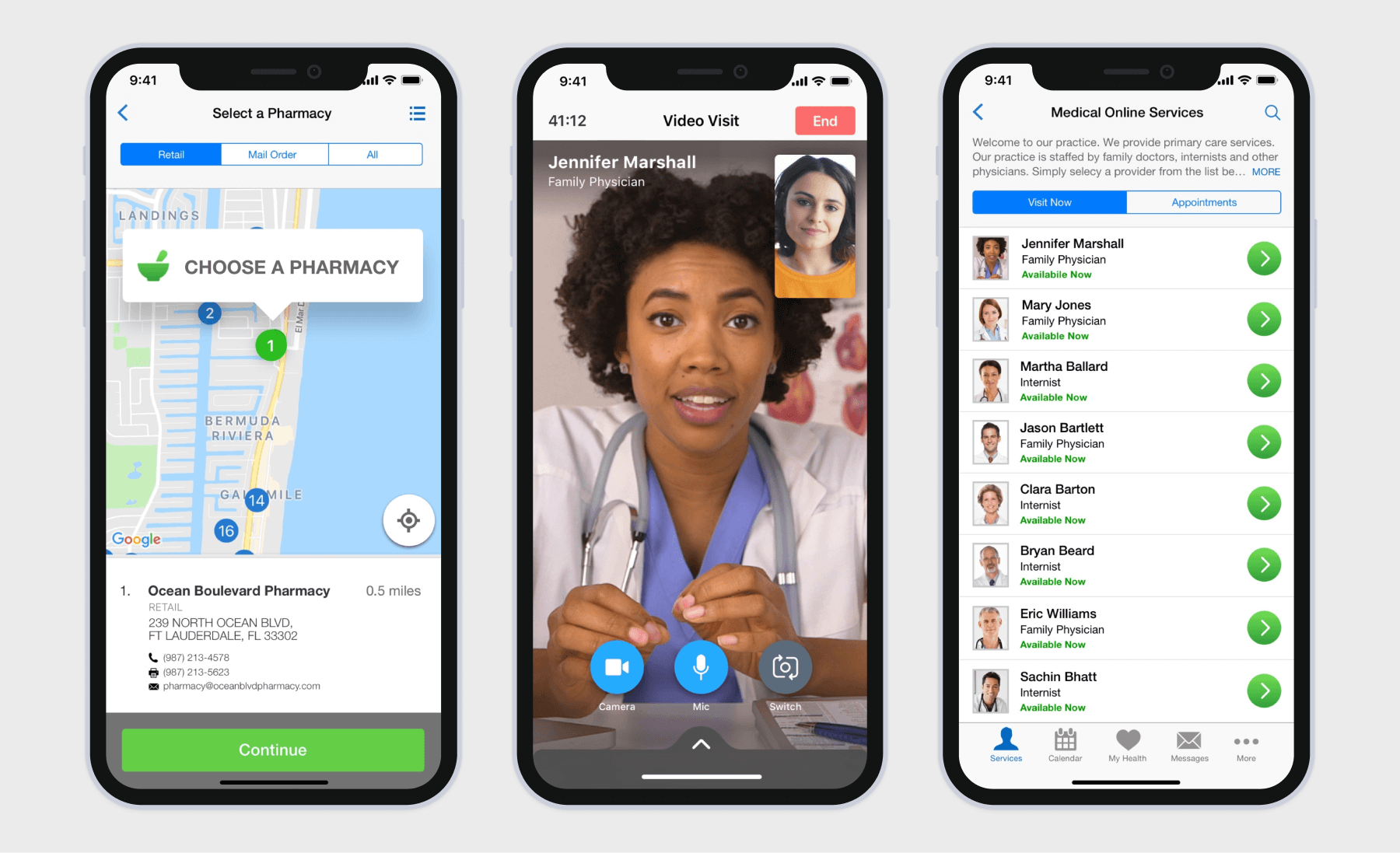
Most telemedicine apps also bank heavily on artificial intelligence capabilities, such as AI-enabled clinical transcription, AI-powered symptom triage, and AI-driven diagnostics.
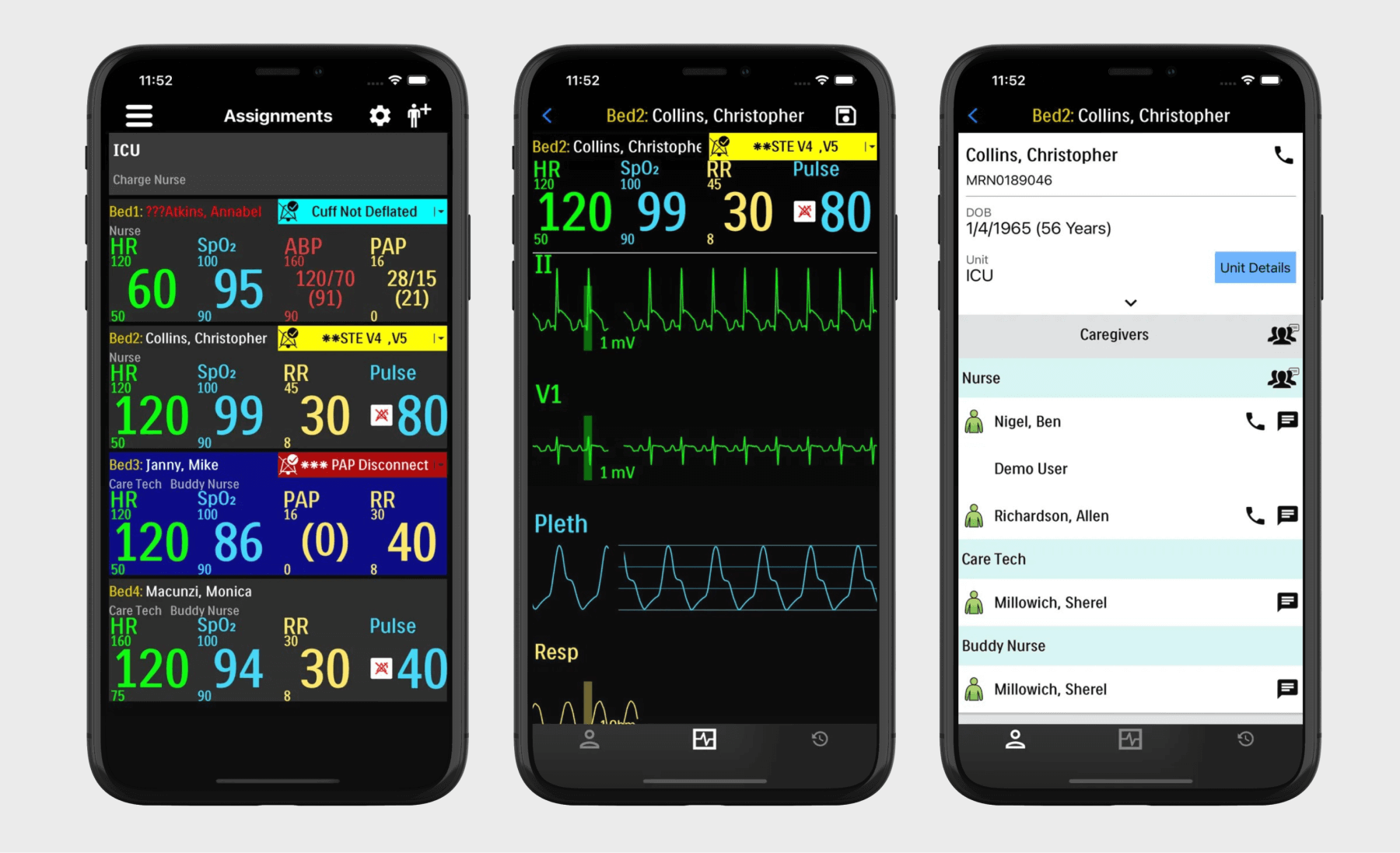
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) applications
RPM systems — which usually consist of monitoring devices, patient mobile apps, and provider web portals — allow care teams to keep tabs on patients from afar, within and beyond clinical settings.
Patient-focused RPM mobile apps usually incorporate health data tracking, telehealth capabilities, wearable data integration and analytics, and notifications and alerts for abnormal readings. Also, RPM applications typically are connected to pharmacies, labs, and community resources.
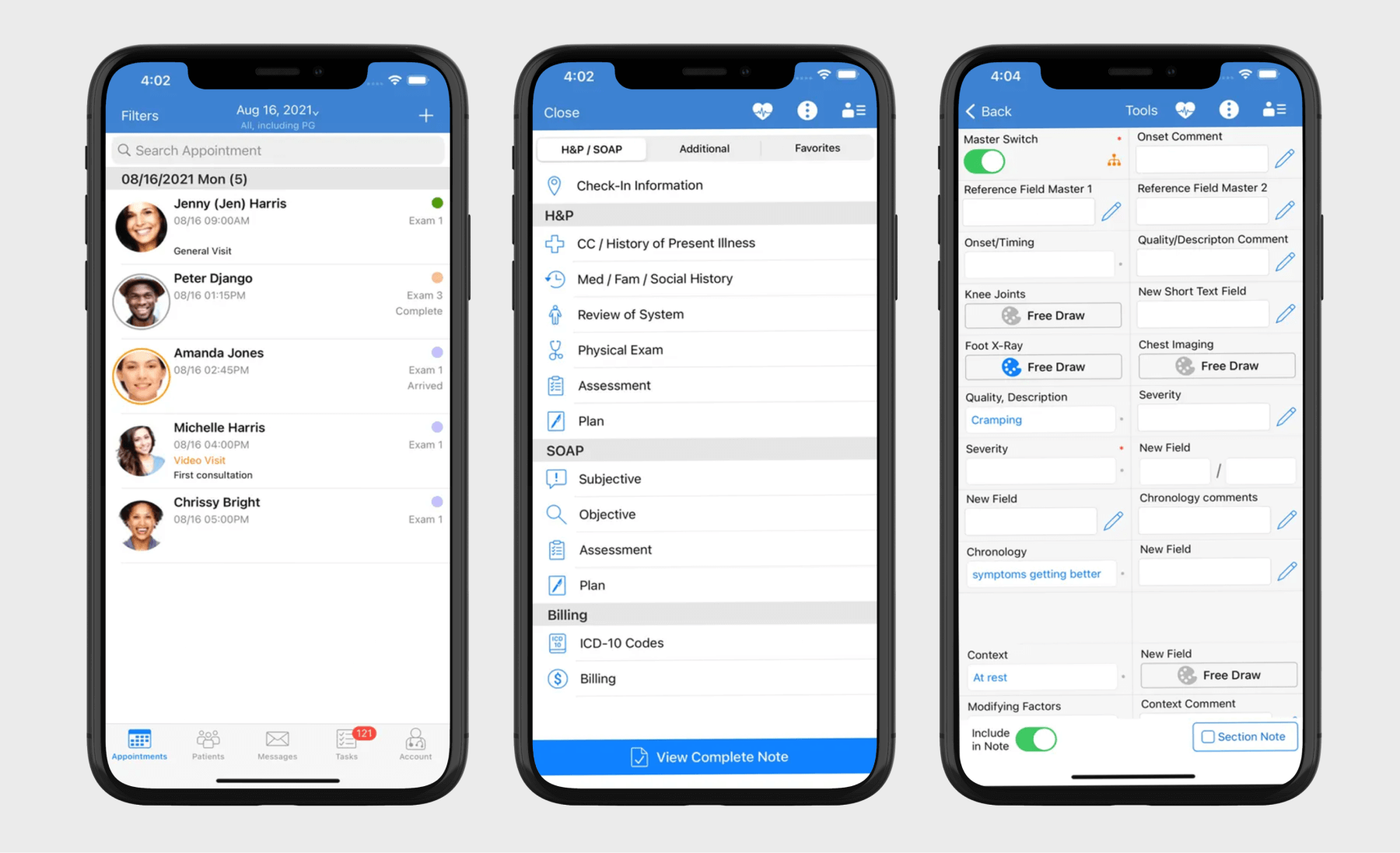
EHR/EMR applications
EHR/EMR mobile apps offer on-the-go access to patient health records and allow for point-of-care charting. Such applications can feature capabilities such as patient records and data management, clinical decision support (CDS), medication and prescription management, medical billing, appointment scheduling, telemedicine integration, and secure messaging and notifications.
Mental health applications
Mental health applications serve as a source of support, resources, and interventions for individuals experiencing mental health challenges or those looking to improve their overall well-being.
Such applications come in different forms and shapes, including meditation apps, telebehavioral health apps, therapy applications, CBT tools, AI-based virtual therapists, and more.
Core functionalities differ by app, with mainstays such as self-monitoring tools, communication with therapists and counselors, as well as meditations and mindfulness exercises.
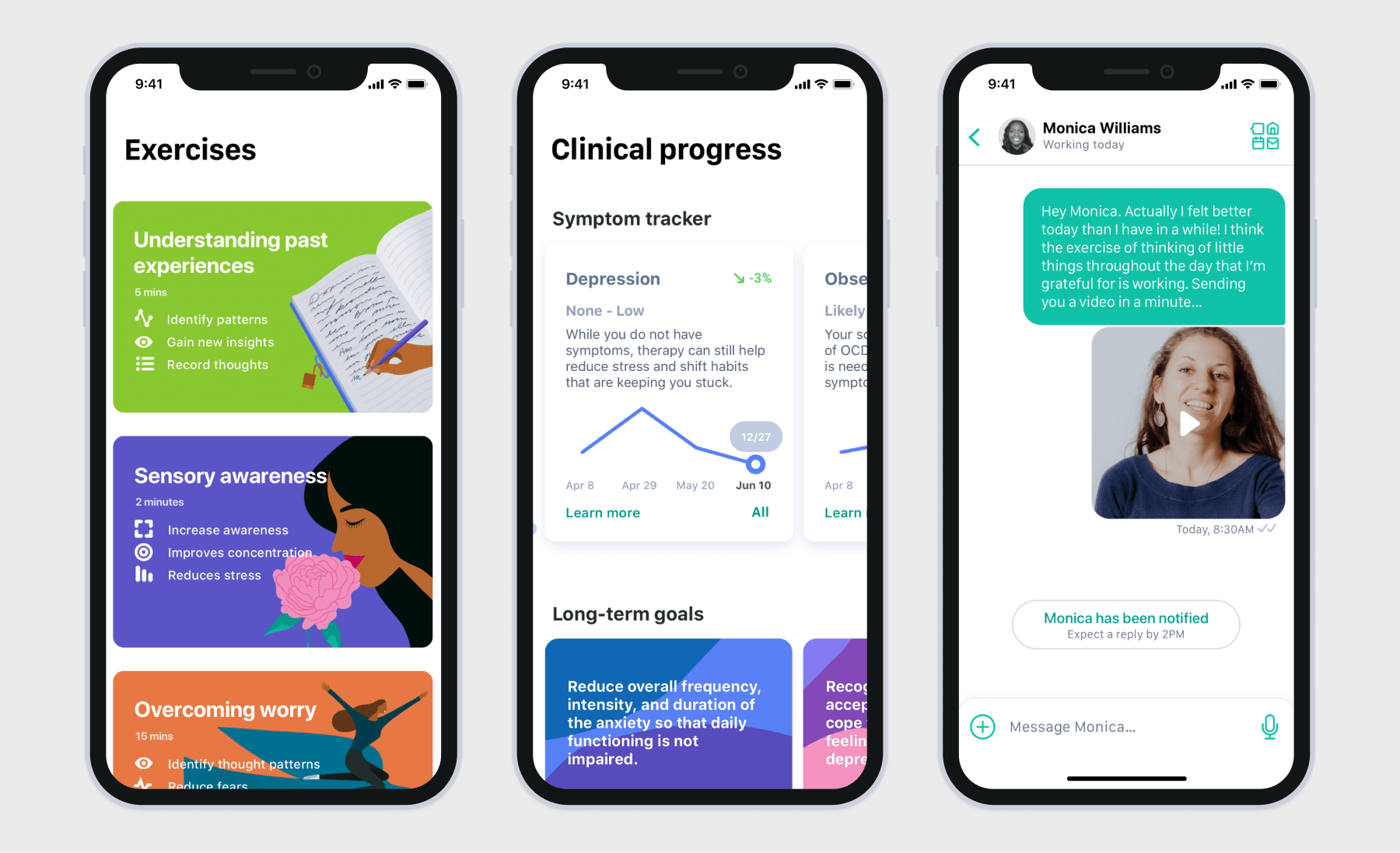
Also, mental health applications, like the majority of other healthcare apps, grew to favor AI-powered features such as adaptive therapy and smart chatbots. Wearable integration is another nice-to-have for this app category, as it gives more comprehensive insights into physiological data.
Medical imaging and diagnostic apps
This app cohort empowers radiologists to capture, analyze, and share DICOM images on the go. Supplemented with AI algorithms, such apps can also automatically analyze medical images and detect abnormalities.
The exact set of features varies by app and modality, but usually, medical imaging apps come equipped with DICOM viewing, image annotation and measurement capabilities, AI-enhanced analysis, and 3D image reconstruction. Integrations with such internal systems as PACS, RIS, and EHR make sure that imaging data is readily available to healthcare professionals.
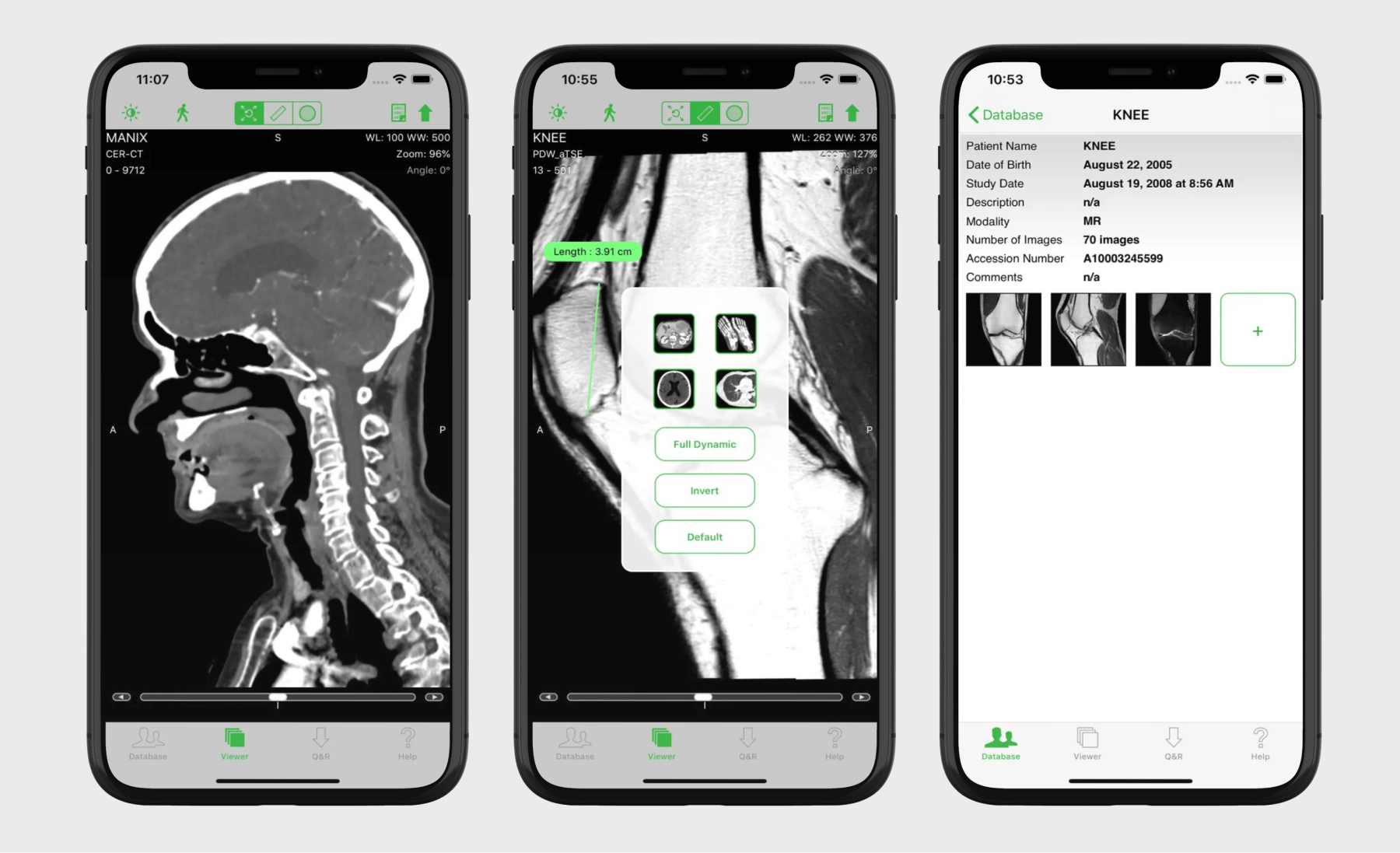
Apps for clinical decision support
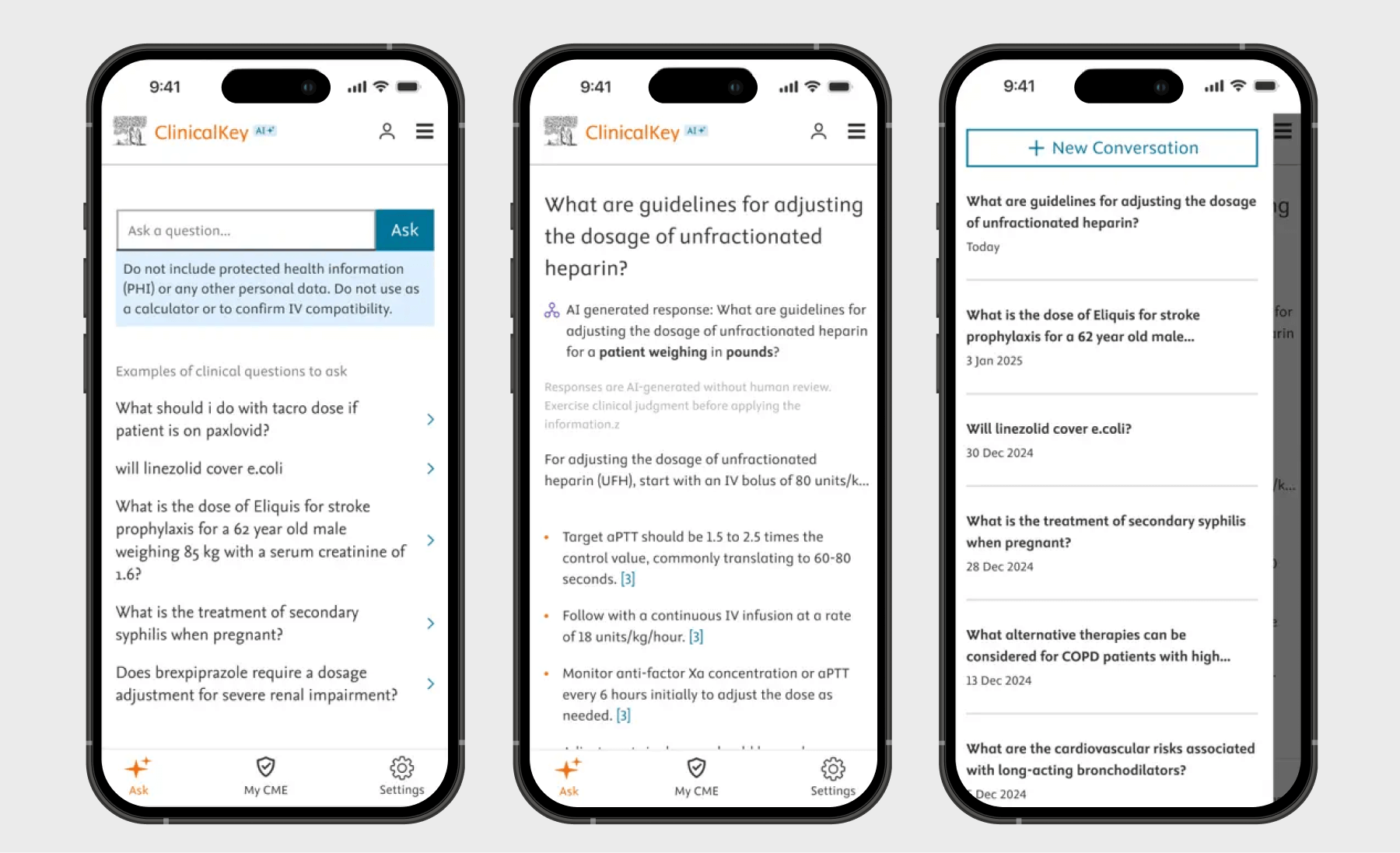
Developed to assist clinicians with point-of-care decisions, clinical decision support apps provide real-time, evidence-based information and guidance for healthcare providers.
Core features of such apps include clinical guidelines and protocols, drug interaction checkers, symptom checkers and differential diagnosis generators, clinical calculators, and integrations with medical information databases. Also, clinical decision support apps can be powered by AI insights and generative AI interfaces to offer real-time decision support and can be integrated with EHR and PACS to easily access patient data.
Fitness and wellness apps
While fitness apps are designed to help users get in shape, wellness applications improve users’ mental well-being.
Features are as different as these apps themselves and may include pre-designed workout routines and personalized workout plans, activity tracking, nutrition and diet features, and progress tracking and analytics — paired with wellness and mental health features for a more holistic well-being approach.
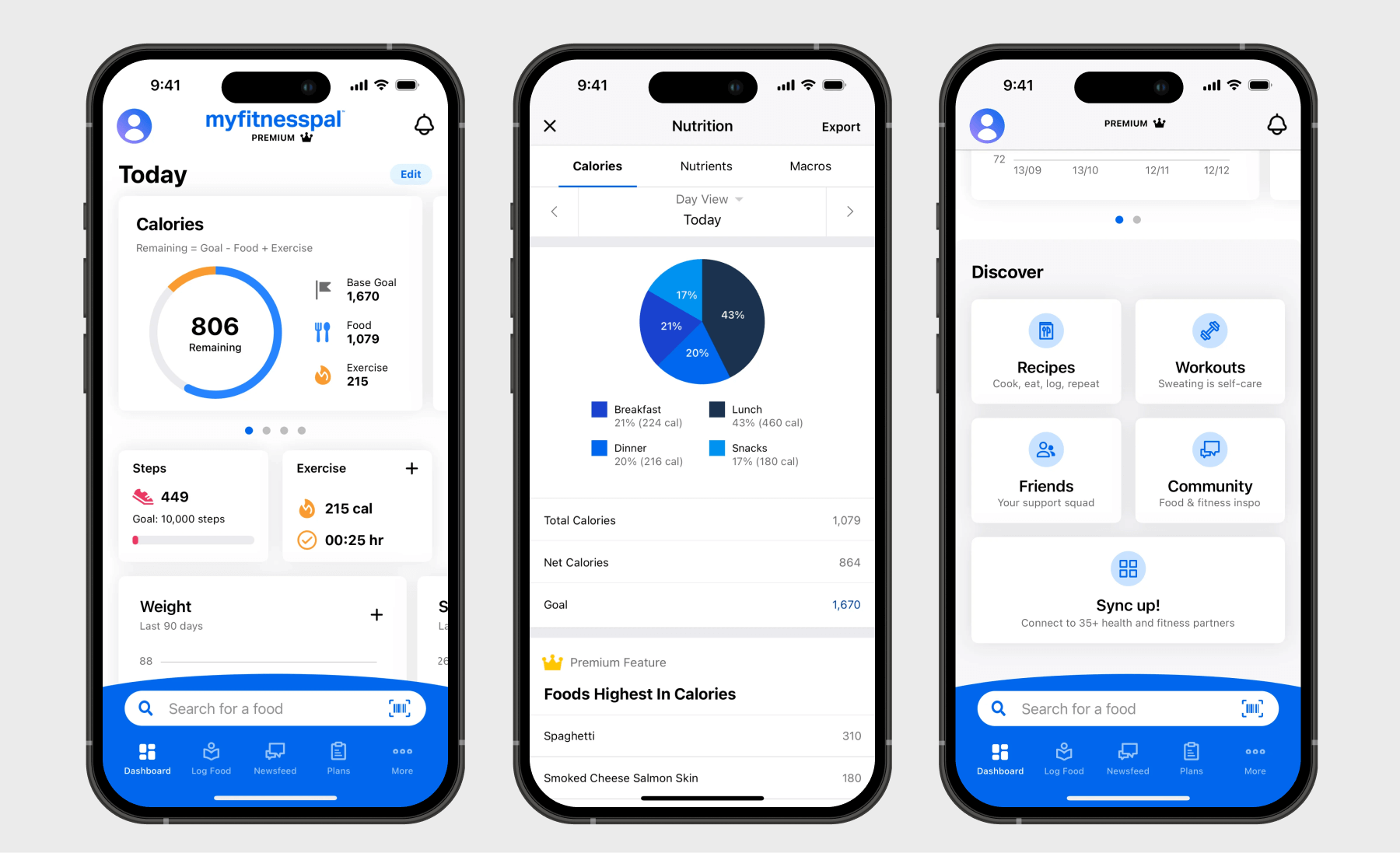
To deliver fitness or wellness advice tailored to the user’s preferences, behavior, and habits, such apps rely on AI-based personalization. They also hang their hats on gamified elements, such as badges, leaderboards, and challenges, to boost user motivation and engagement.
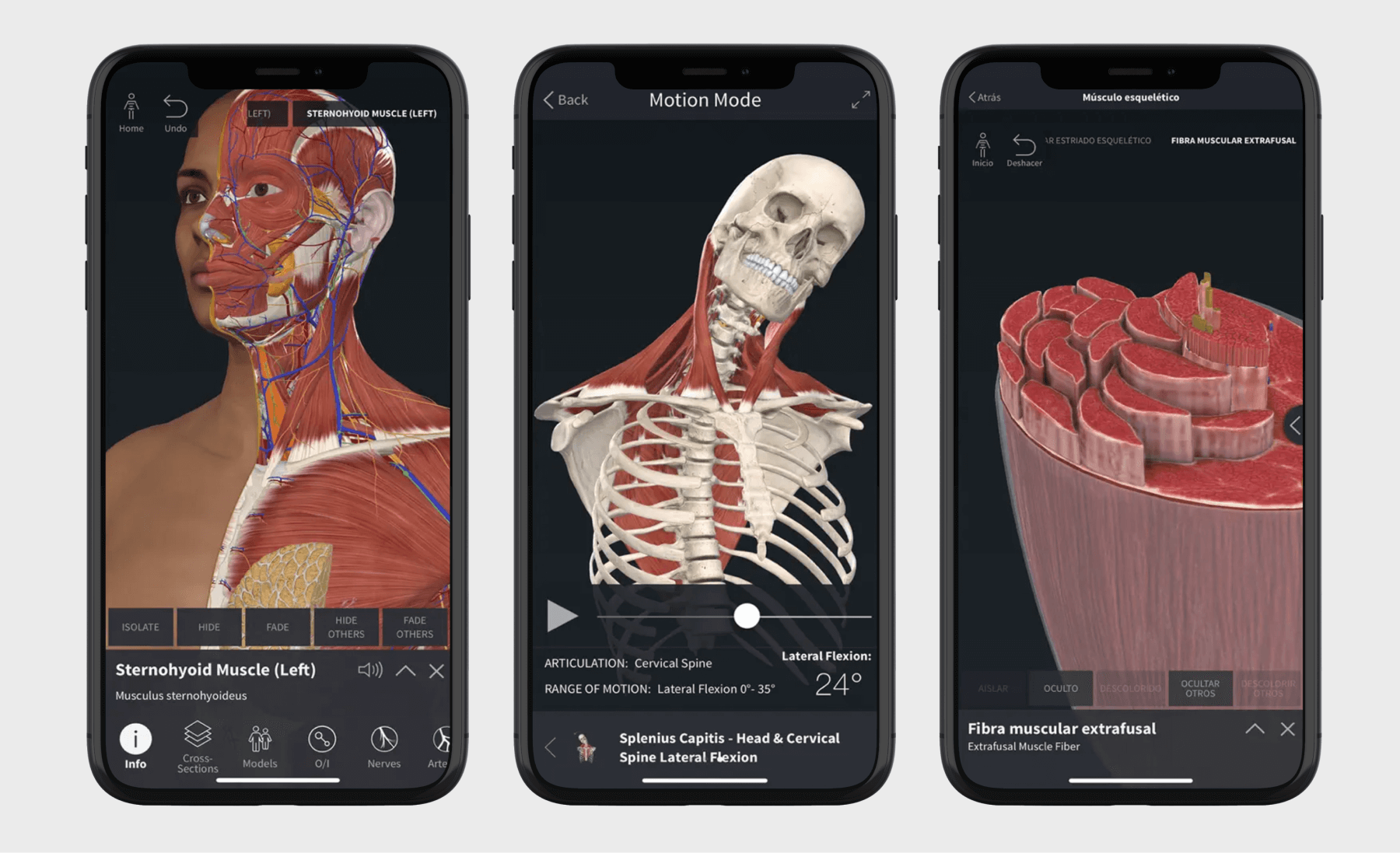
Health education and training apps
If we’re talking about solutions geared toward healthcare professionals, healthcare education and training apps are designed to enhance professional development for healthcare providers, medical assistants, and medical students. Such applications may be kitted out with features like personalized learning workflows, interactive content, communication features, and more.
Also, health education and training mobile apps can draw on advanced technologies such as augmented and virtual reality to create immersive and interactive learning experiences.
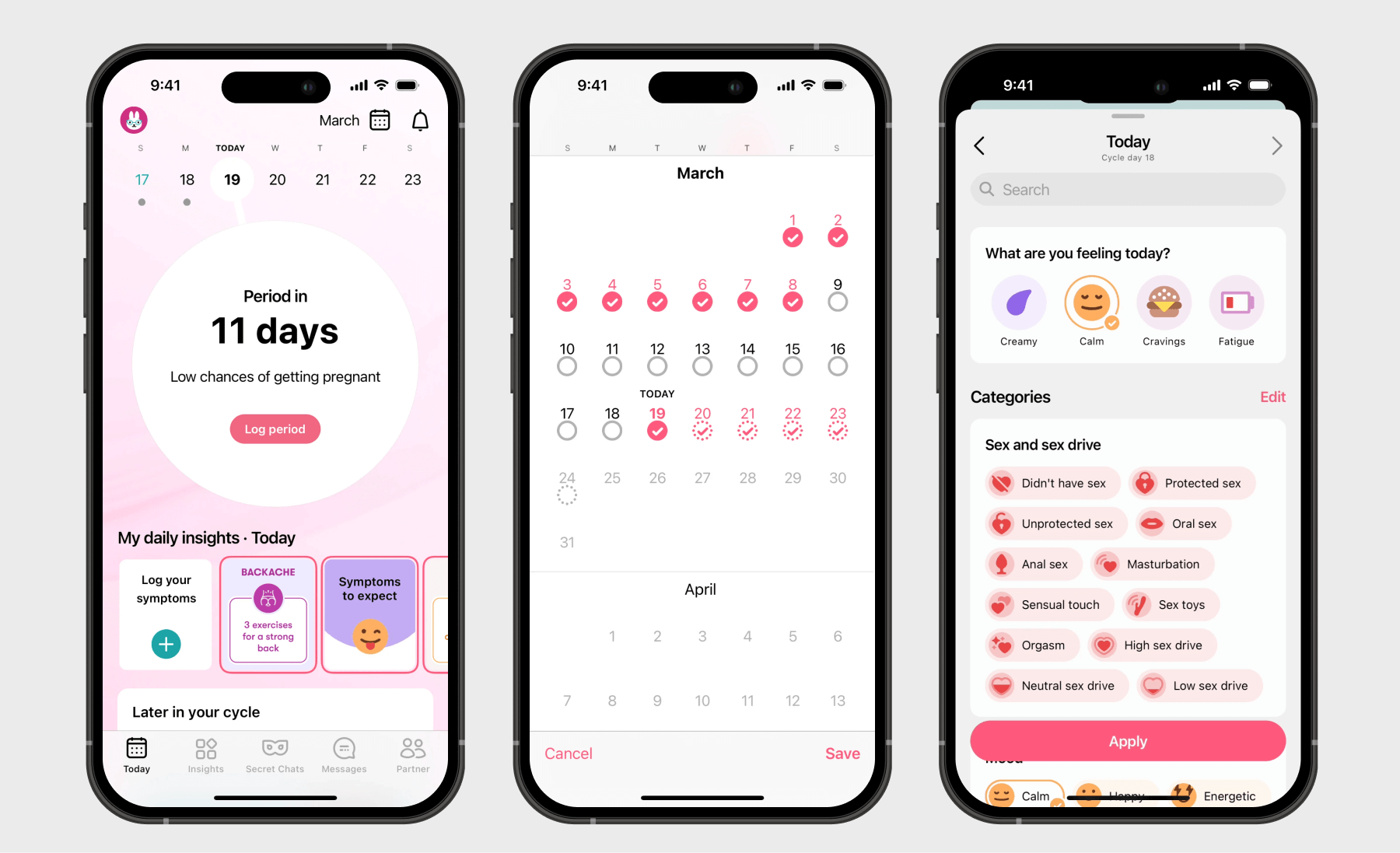
Women's health apps
Femtech apps are one of the promising areas of health mobile app development. Women’s health apps are mainly focused on tracking, managing, and improving various aspects of women's health.
Depending on the type, femtech apps may center on menstrual cycle and ovulation tracking, symptom tracking and analysis, and pregnancy and postpartum support. Women’s health features also aim to educate female users on health-related topics through a variety of educational content, including community forums, expert-reviewed information, and evidence-based educational content focused on reproductive and sexual health.
Medication management applications
On a mission to battle medication non-adherence, medication management mobile apps remind users to take medications at a specific time, provide information about prescriptions, and allow users to get refills on medications remotely.
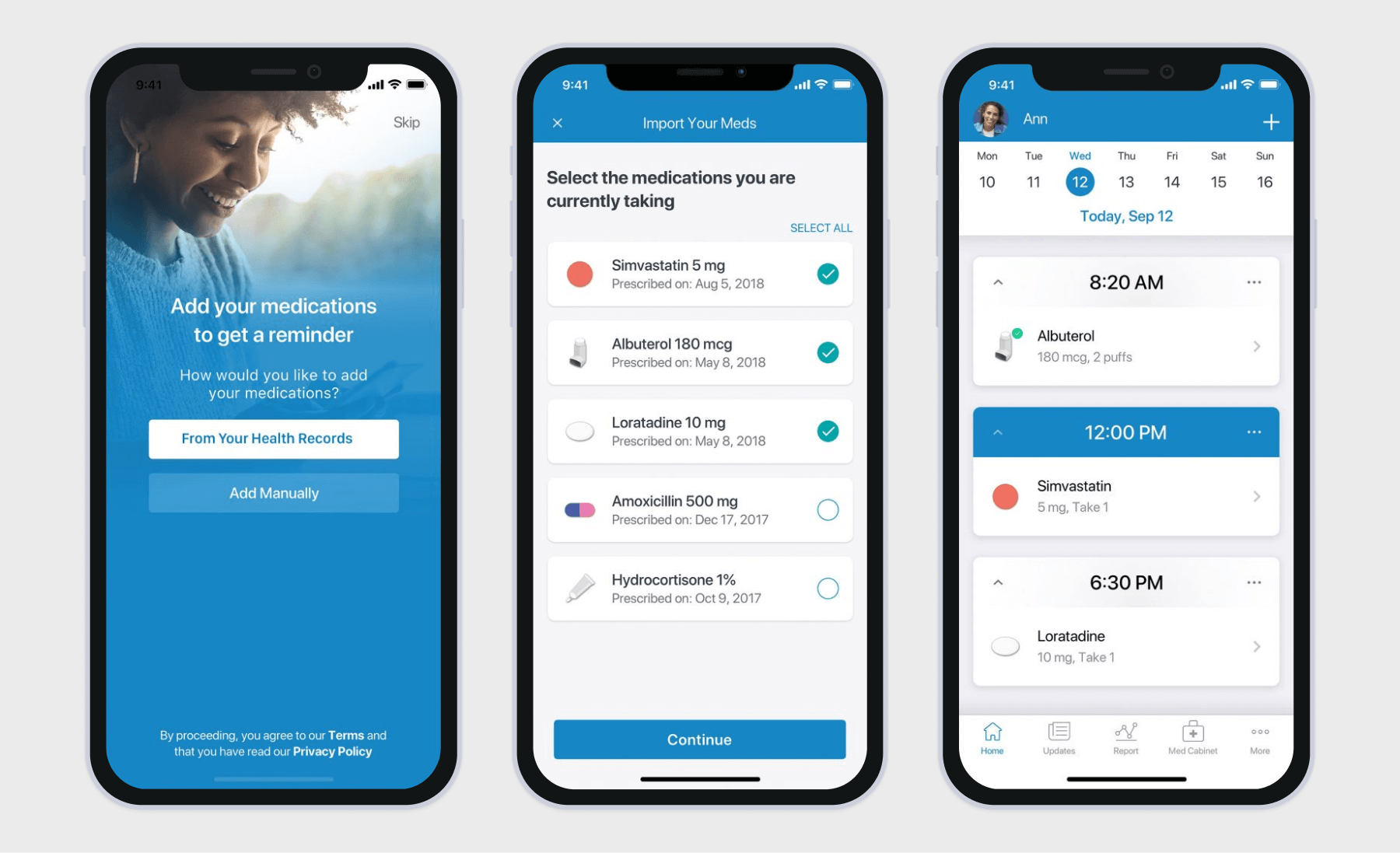
Medication management apps typically include medication tracking and scheduling, drug interaction checkers, and symptom and health trackers. Other common features are drug information and dosage instructions along with pharmacy and EMR/EHR integration.
Benefits of healthcare apps for medical professionals
Understaffed, stretched thin, and maxed out, healthcare professionals always look for innovative ways to optimize their workflow and improve patient outcomes. That’s where healthcare mobile apps pitch in.
Automating the tedious
Moonlighting as admin assistants, clinicians spend around 28 hours per week on administrative duties, such as maintaining patient records, scheduling follow-ups, and replying to clinical questions from the billing department. Healthcare apps can automate time-consuming operational tasks, allowing healthcare professionals to spend more time on patient-focused tasks.
Specifically, healthcare mobile apps can take over:
- Clinical note-taking — ambient scribes from mobile apps let physicians truly listen while they record a patient visit, structure the transcribed text into a standardized medical note, and prompt the clinical to fill in the gaps.
- Scheduling follow-ups — an app can be designed to automatically trigger follow-up appointments based on predefined protocols or clinician instructions and also provide direct access to the appointment scheduling functionality for patients.
- Payment processing — medical applications can connect with EHRs and billing systems to auto-create invoices with patient information, service charges, and more.
AI-enabled mobile applications can also aid in checking eligibility, verifying insurance benefits, and performing prior authorization.
Reducing the cost of care, both directly and indirectly
In the U.S., chronic disease and mental health conditions account for 90% of healthcare spending. If this remains the status quo, the healthcare industry will be looking at $8.1 trillion of chronic disease and mental health management costs by 2028.
Healthcare applications can help address this costly “epidemic” by promoting proactive healthcare for those with emerging conditions and by providing more effective management of chronic diseases and mental health issues for existing patients.
Specifically, medical apps can drive direct and indirect cost savings through:
- Better medication adherence — dedicated medication management functionality helps track taken and missed doses and sends this data to health professionals and caregivers.
- More efficient care coordination — mobile apps can serve as a centralized hub for all patient information, including discharge summaries, follow-up recommendations, and other data, allowing for continuity of care.
- Fewer hospitalizations and readmissions — with medication reminders, educational materials, and patient-doctor communication, healthcare apps can promote better compliance with diet and lifestyle changes among patients.
- Preventative care — by consolidating data from wearables, manual entries, and EHRs, healthcare apps can deliver tailored healthcare recommendations and identify early warning signs of potential health issues.
Powering new care delivery models
By 2032, the U.S. home healthcare services market is projected to grow to $176.30 billion — from $100.95 billion in 2024. Remote monitoring platforms and telehealth applications spearhead the shift to virtual care, allowing doctors and care teams to keep tabs from afar, reducing the strain on healthcare staff, and meeting consumers where they are.
Whether it’s chronic condition management, mobility assistance, or primary care, these technologies make healthcare more convenient, increase the number of patients, and allow traditional providers to embrace hybrid healthcare offerings.
Benefits of healthcare apps for patients
Emphasis on patient-centered care, shared decision-making, and near-term appointments — is what patients demand now, but traditional healthcare fails to come through. Conversely, healthcare apps offer the tools and functionalities to meet these expectations.
Simplifying and enabling accessibility of healthcare services
In the US, 1 in 4 adults skip or postpone getting the health care they need because of the cost. Some patients end up in ER departments — a costly wallop on the healthcare system and patients alike — because their primary care physician is unavailable or they need urgent attention.
Mobile health applications, especially those focused on telehealth and appointment scheduling, improve access to healthcare for a lot of patient demographics. More importantly, virtual visits can save patients $141 per visit and reduce wait times, a key driver of telehealth adoption cited by 46% of telehealth users.
Putting patients in the driver’s seat
Over 50% of U.S. consumers prefer to use a mobile app to schedule appointments, manage prescriptions, and access medical records. These statistics highlight patients’ need for self-service capabilities and their desire for greater control over their healthcare journey.
Healthcare app solutions advocate the beyond-the-pill approach, allowing patients to access personal health information, control their medication regimens, monitor their vital signs, manage other aspects of their healthcare, and communicate with providers at their convenience, all from the palm of their hands.
Improving the quality of care and patient outcomes
Serving the twin goals of engaging patients in their care and keeping them in the loop, patient-facing healthcare applications enhance medication adherence, increase physical activity, and improve chronic disease management.
Combined, these capabilities encourage healthy habits and give patients the confidence to take control of their health. Ultimately, this leads to better care outcomes — far better than those had the patient been left alone post-discharge.
Seven steps to develop a healthcare application and set it up for market success
In healthcare mobile app development, the trick is to strike a delicate balance between the value and security of the application. That’s why at Orangesoft, we rely on a calibrated quality management system based on ISO 13485 to make sure you get a high-quality app and can demonstrate your commitment to regulatory compliance.

Conduct market research
The initial stage of mobile app development can differ depending on the goal and target users of the application. For healthcare organizations, the development project should start with specifying their business requirements, assessing the tech infrastructure, and considering the needed integrations with HIEs, EHRs, LISs, and other systems. For product companies, the process is a bit different: they dive straight into the market and competitor research.
What’s common for both types of companies is target audience analysis, which allows the team to gain a definite image of end users’ needs, behaviors, and pain points. Based on the market and user research, the team distills the must-have mobile app features, puts together wireframes to decide on the app design, and develops a high-level software architecture that lays the foundation for a scalable product.
Tip: To design a truly accessible digital health experience, make sure to engage different user groups within your target audience in your design research, including people with accessibility needs.
Study the regulatory landscape
If your mobile app directly impacts healthcare outcomes, deals with personal health information, or is used to connect to or control medical devices, it’s likely subject to healthcare regulations such as HIPAA, FDA, GDPR, CE Marking, and others.
Depending on the exact regulatory requirements your app must comply with, you should identify the optimal data security measures to implement from the beginning of the development process. These measures can include:
- Data encryption at rest and in transit
- Access controls and authentication
- Data minimization and anonymization (especially important for AI-enabled mobile applications)
- Audit trails, and more.
Along with data security measures, your mobile app development team prepares a risk management plan, quality management system documentation, and software development lifecycle documentation to maximize and demonstrate the security of your mobile application.
Project planning
Next, your healthcare app developers scope the project, creating an outline for all the work, tasks, resources, timelines, deliverables, and success metrics for the project. At this stage, your medical app developers also select a suitable development approach and match your project with the right technology stack based on scalability, performance, and other requirements.
Healthcare mobile app developers finalize your app’s architecture and design an API strategy to prepare for integrations with other systems.
Select a monetization strategy
The first step towards a successful monetization strategy is realizing how the mobile application fits within the broader healthcare ecosystem. In simple words, health tech companies should decide whether their mobile app aims at supplementing their core products, establishing a market barrier, or raking in the dough directly.
Whatever monetization approach you opt for, we recommend you try the following:
- Adopt the “land and expand” strategy, which is a phased approach to monetization where you offer customers a low-risk trial with clear and simple pricing (freemium, limited-time unlocks, usage-based pricing).
- Do not limit your product to a single revenue stream, combine a few to target multiple segments and stakeholders.
- Consider data monetization or developing offshoot data products that can create additional value for healthcare organizations. However, approach this revenue opportunity with extreme caution and ethical responsibility.
Design the user experience and interface
During the discovery stage, your UX/UI team prepares a few wireframes for you to decide on the interface structure. Sometimes, wireframes can be put in front of sample users to get feedback. Based on the selected wireframe, the design team then crafts an interactive prototype — either focused on a single feature or the entire product — that you and your sample users can click and navigate.
Prototypes make a great research tool to validate design hypotheses related to user behavior and interface usability. Once your team tests the prototype with real users, they prepare the final layouts and hand them over to the development team.
Develop and test an MVP
Mobile medical app development benefits from an iterative, start-small approach whereby your development team gradually builds an MVP for your application and fail-proofs their efforts with real user feedback. It’s when third-party and internal integrations are set up, too.
Together with the development, the quality assurance team tests each functionality, making sure you end up with a high-quality, compliant product. Joined by the development team, the QA team wraps up the software development documentation to help you prepare for regulatory approvals.
Launch the application and refine it
At the end of the MVP development process, the mobile health app development team releases the app into the target environment and monitors its performance in the wild. As an alternative to a full launch, you can pilot-launch your medical application to a small group of users and gather their feedback to polish the solution.
When the app is live, your development team keeps an eye on it to catch any bugs and resolve any issues. Your application’s journey doesn’t end there: once it gains enough traction, the development team adjusts its architecture and code to cater to a larger number of users. Following the user and stakeholder feedback collected post-release, your mobile app development team prioritizes new features for upcoming product versions.
Top seven features your mobile health application needs
Although there isn’t a universal blueprint for must-have features to include in all medical mobile applications, some features have become fixtures in the majority of such solutions. Without them, your mobile healthcare application will have a hard time vying for the top spot.
User authentication and profile management
Medical mobile applications are more prone to PHI breaches than any other solution because smartphones might be stolen or lost. Unless the sensitive data is protected by robust authentication mechanisms, it can become easily accessible to unauthorized individuals.
To prevent this scenario, your healthcare mobile application should incorporate:
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and biometric login (Face ID, fingerprint). However, make sure your authentication mechanism includes alternative methods to accommodate various user needs, such as limited finger dexterity, cognitive disabilities, or motor impairments.
- Role-based access controls to make sure only authorized users can view patient data in doctor-focused mobile apps.
- Session management to automatically log out inactive users after a specified period, plus allow for remote logging out.
When it comes to profile management, medical applications typically bundle:
- Profiles with separate roles for different user groups, such as patients, doctors, and caregivers.
- Manual data entry capabilities for patients to enter and edit their personal health records.
- Consent controls for different types of data and uses.
Telemedicine capabilities for doctor-patient interaction apps
Virtual care applications, remote patient monitoring systems, practice management apps, and many other health tech solutions leverage telemedicine features to set up a direct communication channel between the two sides of care.
Telemedicine capabilities can manifest as:
- Secure video and/or audio conferencing with or without direct access to patient records.
- HIPAA- and/or GDPR-compliant chats and messaging for asynchronous communication and file sharing.
- Electronic prescriptions enable doctors to send prescription orders directly to pharmacies electronically, while patients can request electronic refills from the app.
Appointment scheduling and reminders
Effective appointment scheduling can become a game-changer for clinic success as it reduces back-and-forth calls, minimizes no-shows, and reduces idle time.
To enable this functionality, your healthcare mobile app requires:
- Accurate booking system that directs patients to best-fit provider and modality options based on the reason for visit, slot availability, and location.
- Real-time appointment confirmations.
- Contactless payment options to let patients pay online for select services.
- The ability to automatically book recurring appointments.
- Automated email and text reminders with the ability to set the lead time.
Health tracking and wearable integration
For chronic disease management and fitness applications, continuous tracking of longitudinal health data is an invaluable source of insights that lays the foundation for personalized recommendations and proactive interventions.
Your healthcare mobile application needs the following enablers to leverage this feature:
- Integration with wearables (e.g., smartwatches and fitness trackers) and medical devices (e.g., glucose monitors, blood pressure monitors, and more).
- Low-latency, real-time health data monitoring with built-in data validation, error handling, and data security.
- AI-based wearable data analysis and its integration with clinical decision support systems and clinical workflows, if applicable.
Medication and treatment management
To achieve optimal therapeutic outcomes, patients need to take a systematic approach toward prescribed medication and treatment regimens. The following medication and treatment management features will make sure the prescribed medicines are taken and the treatment plan is followed:
- Customizable medication reminders and alerts to accommodate even the most complex medication regimens.
- Medication tracking and logging, with the option for users to share their data with providers.
- Treatment plan summaries with detailed instructions and provider notes.
- Educational resources – drug interaction checkers, reliable information about health conditions, and more.
- Gamification – rewards, challenges, and progress tracking to improve adherence rates.
Electronic Health Records (EHR) integration
The longer doctors wait to document a patient's visit, the more likely they are to forget subtle but important details. Mobile EHR integration allows healthcare professionals to cut inpatient data management time and tap crucial patient information in real-time.
Compared with other features, EHR integration isn’t easy to pull off. Not only will you have to integrate with EHR individually, but you’ll also have to obtain specific IT and security requirements from each healthcare provider.
The Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) standard can simplify this process as it includes specifications for application programming interfaces (APIs) that allow applications to access particular data elements within an EHR instead of a full-scale integration.
Emergency assistance and support
In healthcare apps, emergency assistance and geolocation are one of those life-saving features that can move the needle in critical situations. Regardless of the app type, make sure you incorporate:
- Easily accessible and visible SOS buttons for emergencies that either send notifications to designated emergency contacts or automatically call local emergency services.
- Automated location sharing via GPS, Wi-Fi, or cell tower triangulation.
- In-app emergency protocols direct users to basic, condition-specific emergency protocols or instructions.
Next-gen features to future-proof your healthcare application
With greater change at the healthcare system’s door requiring tech innovations to battle pressing issues, the following technologies are already or will be at the forefront of the industry’s transformation.
AI-powered virtual health assistants and chatbots
In 2024, investors injected $10.5 billion into healthcare AI, bullish about its potential and enthusiastic about emerging innovations. One area in the limelight is conversational healthcare interfaces already used for healthcare guidance, appointment scheduling, triage, mental health support, and other healthcare tasks.
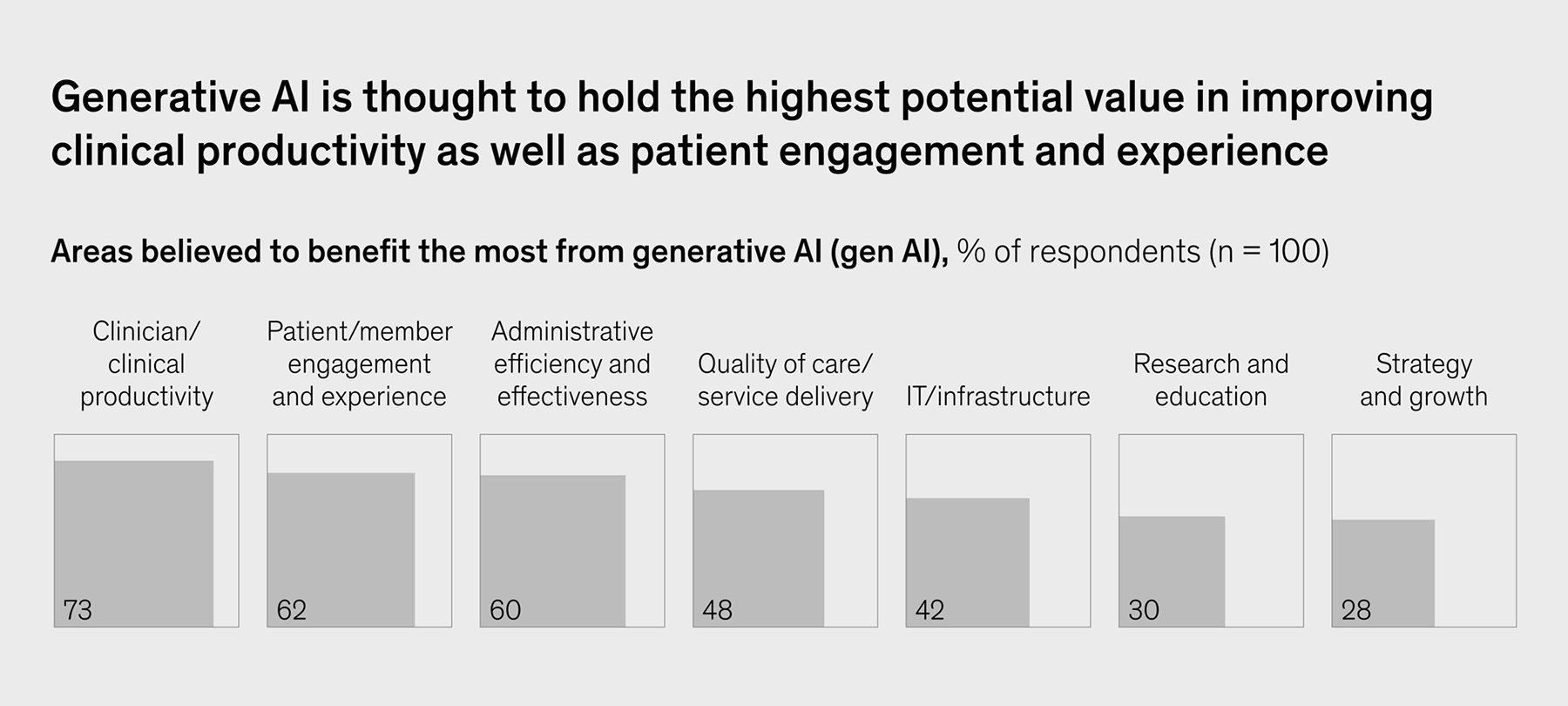
Currently, 1 in 5 consumers is ready to use Gen AI as a doctor’s sidekick. Responding to the consumers’ shared desire, over 70% of healthcare organizations are planning to or have already implemented gen AI capabilities for a whole plethora of tasks, including patient-facing, admin-focused, and clinical ones.
In the healthcare sector, the pace and magnitude of generative AI adoption hinge on the accessibility of healthcare data and tech infrastructure — both are challenges yet to be overcome.
Predictive and preventive healthcare with AI/ML
Weary of the flawed and costly healthcare system, both patients and healthcare providers place their bets on prevention. Today, over 1,000+ FDA-approved AI/ML-enabled medical devices help doctors predict at-risk individuals, intervene proactively, and detect onset diseases across radiology, neurology, urology, cardiovascular health, and other healthcare modalities.
Following suit is longevity-focused solutions, a trend that aims not only to prevent illness but to extend lifespan and improve healthspan. In 2024, U.S.-based longevity solutions that include biotech innovations to personal health management tools attracted $1 billion in funding.
Considering Millennials and Gen Z’s zing for proactive health management as well as the growing prevalence of biomonitoring and wearables, the trend for longevity is slated to accelerate.
Advanced biometric sensors for remote monitoring
Doctors are still cautious about relying solely on wearable data for clinical decision-making. Data variability, false positives, noise in the data, and other concerns cast a shadow over the reliability of wearables for continuous data collection.
Over the last few years, 2D materials-based wearable sensors and RPM biosensors have emerged to flip the script. More sensitive, flexible, and incredibly thin 2D materials can provide more accurate, detailed, and diverse bio-signals, opening up new possibilities for remote patient monitoring.
Besides data erraticism, RPM teams grapple to make sense of all the wearable data sensors collect and share. Wearable AI — the one where AI is baked into wearables — can transform heaps of wearable data into ready-to-use insights directly at the source, making wearable data more impactful for RPM programs.
AR and VR for therapy and training
In healthcare, immersive technologies are proving their mettle as engaging therapeutic tools used for mental health, pain management, rehabilitation, and even surgical training. In 2024, the global AR and VR market in healthcare was estimated at $3.7 billion. By 2033, it’s expected to reach $19.6 billion, driven by technological advancements.
Extended reality artificially intelligent ally, EMDR therapy kits, VR self-confidence therapy, and XR-powered digital therapeutics are some of the innovations currently fueled by augmented and virtual realities. Provided the industry addresses the issues of high costs, clinical validation, and tech limitations, the transformative impact of AR and VR on patient care and medical training will come through in the next few years.
Digital twin technology for personalized healthcare
The bright future of personalized medicine depends on the comprehensive understanding of patient health, and the digital twin technology has much to offer in this department. Mirroring individual health profiles, digital twins allow providers to dynamically simulate potential treatment strategies based on multi-modal data such as clinical, genetic, molecular, environmental, and social factors. With the simulation results in tow, doctors can develop tailored treatment plans tailored to the individual patient's needs.
Although the technology is still in its infancy, leading healthcare research organizations like the Mayo Clinic have digital twins already in the works. By 2027, about $73.5 billion is likely to be spent on this technology, including product, data, and system twins.
Genomics and DNA-based personalized healthcare
Another harbinger of personalized intervention, genomics, and its current clinical applications draw upon an individual's genetic profile to tailor health care. So far, this approach has manifested in pharmacogenomics, cancer genomics, and genetic risk assessment. However, the field is rapidly developing to include nutrigenomics, reproductive genomics, longevity, and other modalities.
By 2034, the global genomics market size is predicted to surpass $175 billion, from $37.94 billion in 2024, driven by AL/ML-based computation tools, government funding, and reduced costs of genome sequencing.
Best practices for healthcare mobile application development
With healthcare mobile app development comes a critical responsibility: you have to leave no stone unturned when it comes to patient security, regulatory compliance, and, ultimately, patient well-being. The following best practices will help you build applications that are both effective and trustworthy.
Compliance with regulations
As we’ve mentioned earlier, those applications that directly contribute to care outcomes usually fall under healthcare regulations. Let’s review the most common acts and guidelines that may apply to your medical solutions:
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) — applies to healthcare mobile applications that collect, store, and share personal health information with covered entities or their business associates.
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations — regulate medical devices, including software as a medical device and mobile applications used to control the device.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) — protects the personal data and privacy of individuals within the EU.
- Medical Device Regulation (MDR) — governs the production and distribution of medical devices in the European Union.
Each of these regulations has specific requirements for healthcare mobile applications and the security controls they have. The first thing you should do is determine what types of data your app will deal with and whether it falls under the purview of any specific regulations. In the U.S., you should also keep in mind that some state data privacy laws may override federal ones — so you need to assess regulations at both levels.
Whatever the case, if your mobile app is subject to regulations, it’s easier and cheaper to bake privacy and security into the app early on instead of the bolt-on approach later. We also recommend hiring a compliance consultant to figure out what applies specifically to your application and how to meet compliance requirements.
Interoperability and integration
The healthcare IT ecosystem is a complex patchwork of different systems and applications that store data in different formats, with data transfers still done via HL7 and flat files. To break down the healthcare data silos, FHIR was introduced as an integration standard go-to for EHRs and payers.
Here’s what it means for your healthcare application:
- If your app is designed to team up with legacy hospital systems that primarily use HL7 v2, you need to opt for an integration with HL7 v2.
- However, if you’re developing a healthcare app that exchanges data with EHRs, payers, and other systems adopting interoperability standards, you must make your application FHIR-compliant.
- When a system your app is integrating with uses a legacy HL7 system internally and converts data to FHIR via a gateway, your application needs to integrate with FHIR only.
User-centered design and accessibility
Designing for accessibility, you ensure everyone can access healthcare services regardless of their needs or tech limitations. In medical mobile app development, accessible design is one outcome of an effective inclusive design process that:
- Is not guided by the team’s guesswork but is based on real user accessibility needs gathered during early user testing.
- Seeks feedback from various user groups, including those with various disabilities, ages, and cultural backgrounds.
- Adheres to the principles and guidelines outlined in WCAG and ADA.
- Is compatible with assistive technologies and offers alternative input methods such as smart voice and gesture controls.
- Prioritizes real-world testing over simulation software at the final development stages.
Security and data protection
Besides best industry data security practices, your security and data protection strategy is also shaped by the specific regulatory requirements. That’s why your development team should outline the security strategy, keeping in mind the following:
- Applicable regulations (they can create a matrix that maps regulatory requirements to specific app features and functionalities);
- Data classification and the specific security safeguards for each data classification;
- Compliance documentation that documents all the compliance efforts, including policies, procedures, risk assessments, and testing results;
- Potential risks and security vulnerabilities;
- Best industry data security practices, including data encryption, access controls, and others.
- Security safe nets that need to be integrated throughout the entire software development lifecycle.
Scalability and performance
Scalability is the backbone of any data-rich healthcare application, ensuring it can grow and handle increasing data volumes without potentially jeopardizing patient safety. Specific scalability requirements vary by the project. For example, if it’s an internal healthcare system with a defined number of potential system users, a private server will suffice. However, if you expect your application to handle sudden traffic spikes and support heavy data loads, you’ll need a cloud-based infrastructure with automated scaling.
As for software architecture styles, there are two common approaches: microservice architecture and monolithic architecture. The microservices one is considered more scalable compared to the monolithic approach, as the former allows you to scale individual components independently based on demand. Multi-module healthcare systems where each module has its own scalability needs (e.g., hospital management systems, billing systems, etc.) are a good mesh for a microservices architecture.
The monolithic architecture has all components and elements tightly coupled within a single codebase, meaning it’s more difficult to scale.
When selecting a database, always consider the type and amount of patient data your system has to process. Traditional relational databases are more suitable for structured data with clear relationships, while large troves of unstructured or semi-structured data are better off with NoSQL databases.
How much does it cost to create a healthcare app?
It’s hard to calculate a tentative budget for healthcare app development services without knowing the solution's specs. There are a lot of factors that can impact the costs of healthcare app development projects, from the number of platforms to project complexity to the necessary integrations.
Building on previous projects, our team has prepared approximate estimates for MVP development based on your app category:
| Healthcare app category | MVP development cost |
|---|---|
| Telemedicine application | $75,000 – $150,000 |
| Remote patient monitoring (RPM) app | $50,000 – $200,000 |
| Mental health application | $25,000 - $100,000 |
| Medical imaging and diagnostic app | $70,000 – $500,000 |
| Fitness and wellness application | $30,000 – $120,000 |
| Clinical decision support system (CDSS) | $100,000 – $500,000 |
| EHR / EMR application | $150,000 – $500,000 |
| Medication management application | $25,000 – $100,000 |
| Women's health app | $30,000 – $150,000 |
Note: These estimates cover core development costs only. Additional expenses for market research, UI/UX design, testing, compliance consulting, and advanced technologies (AI/ML, AR/VR) would need to be budgeted separately.
How to choose a healthcare app development company
If you decide to outsource healthcare mobile app development, you need to hand-pick a reliable tech partner to implement your solution. Here are the sure signs that you've found the right fit:
- Strong healthcare development expertise with a portfolio of successfully delivered projects to validate it.
- Commitment to data security and compliance, paired with adherence to common healthcare regulations such as HIPAA, FDA, MDR, and others, as well as development processes based on ISO.
- Full-cycle mobile app development expertise supplemented by knowledge of complementary technologies, including IoT, AI, AR/VR, and others, if your solution requires the implementation of advanced capabilities.
- An autonomous development team that’s small enough to care and big enough to scale your development.
- Strong accessibility design expertise, including knowledge of ADA and WCAG guidelines.
Develop your healthcare mobile application with Orangesoft
Since 2011, Orangesoft has operated as a healthcare app development company, helping health tech startups and healthcare providers deliver better patient care. With over 300 projects in our portfolio, we’ve outlined a proven delivery approach based on ISO 27001 and ISO 13485 that allows us to deliver secure, compliant, and accessible healthcare applications in line with healthcare regulations.
Here are some of the healthcare and wellness projects we’ve successfully delivered to our clients:
- FDA-compliant stroke management platform — equipped with telemedicine features, this application supports a post-stroke patient monitoring program in a renowned US hospital network.
- Complimentary Android and iOS mobile apps for a virtual hospital platform — incorporating AI medical imaging, e-prescription, IoMT integration, and telemedicine features, our healthcare applications enable remote care delivery at a patient’s convenience.
- Heart rate monitoring with hardware-level accuracy — at the app’s core is a custom algorithm for precise heart rate monitoring that uses facial or finger pulse analysis based on a camera-captured video.
If you’re looking for a reliable, end-to-end tech development partner with strong, hands-on experience in healthcare mobile app development, Orangesoft’s team is a click away.
